|
1790| 2
|
[项目] 【Arduino 动手做】ESP32 + BaseCam 蓝牙云台控制 |
|
BaseCam 无刷云台控制器 (BGC) 系列产品广泛用于电影摄影行业的相机云台控制和稳定系统,此处提供了 YouTube 介绍性视频: • BaseCam Electronics 简介 除了让 3 个 DM5005 万向节电机对 BaseCam Extended Long 控制器板上的板载 IMU 做出反应外,我还希望能够读取和处理来自 3 个独立单轴纵杆的信号,以通过 BaseCam 控制器板控制这些相同万向节电机的滚动、俯仰和偏航。为此,我使用 ESP32 微控制器从纵杆读取输入,并将这些值中继到 BaseCam 控制器,一种情况下是直接有线,另一种情况下是通过 2 个 ESP32 板使用低功耗蓝牙 (BLE) 无线传输。 BaseCam 系列万向节控制器具有接收不同信号类型的功能,包括 PWM 和模数 (ADC) 读数。但是,我希望通过 ESP32-S3 开发板来控制信号在 BaseCam 控制器读入之前的处理方式。该项目的布线和设置允许进行这种类型的控制,无论是直接有线还是使用 BLE 无线。我希望它对您的下一个 BaseCam 项目有用! 用品 1.3 x 单轴纵杆模块 2.2 x ESP32-S3 DevKitC 开发板 3.1 x Basecam BGC Extended Long 控制器 4.1 x 面包板 5.1 x 22AWG 实心线 6.1 x 各种多色热缩管 7.1 x 各种跳线 8.2 x Micro-USB 转 USB-A 电缆 9.1 x 1.25mm 预压接连接器套件(用于 BaseCam Extended Long 板的 CANbus 连接器) 10.1 x 烙铁 11.1 x 焊料卷 12.1 x 电池组 13.1 x 各种预压接 ZH 1.5mm 连接器(用于 CAN 驱动板) 14.1 x 4S 锂聚合物 (LiPo) 电池 15.1 x XT-60 电池连接器 16.1 个 2 针 JST-XH 连接器,用于将 LiPo 电池连接到 BaseCam 电池针脚 17.1 x 各种 M2 黄铜支座和螺钉套装(用于演示组装) 18.1 台 FDM 3D 打印机 19.1 x 1 千克卷轴 1.75 毫米厚的黑色 PLA+ 线材 20.1 x 各种夹式线连接器(可选,可用于原型设计) 21.1 x 扎带套装(可选,用于电线管理) 对于仅使用 1 个 ESP32-S3 开发板读取数据的情况,3 个单轴摇杆将 3 个摇杆中的每一个的 VCC 和 GND 分别连接到 ESP32 板上的 3V3 和 GND。摇杆模块充当弹簧加载的电位器,因此我们将使用具有模数转换 (ADC) 功能的 ESP32 引脚(GPIO4、GPIO5、GPIO6)。我们将使用 ESP32 上的硬件 Serial1 引脚(GPIO17、GPIO18)连接到 BaseCam 控制器板上的 UART1_RX、UART1_TX 引脚。请注意,ESP32 上的 RX 引脚连接到 BaseCam 板上的 TX 引脚,反之亦然。如果您想从 BaseCam 板为 ESP32 供电,请将两块板上的 5V 引脚连接在一起,然后将两块板上的 GND 引脚连接在一起。将 BaseCam 板连接到您的计算机以提供 5V 电源,并在 BaseCam Simple GUI 软件和控制器板之间进行通信。 引脚连接摘要: ESP32 GPIO6 - 摇杆 #1 SIG 引脚(白色) ESP32 GPIO7 - 摇杆 #2 SIG 引脚(绿色) ESP32 GPIO15 - 摇杆 #3 SIG 引脚(紫色) ESP32 RX (GPIO18) - BaseCam UART1_TX 引脚(蓝色) ESP32 TX (GPIO17) - BaseCam UART1_RX 引脚(绿色) ESP32 5V 引脚 - BaseCam 5V 引脚(红色) ESP32 3V3 引脚 - 连接到所有 3 个摇杆 VCC 引脚(黄色) ESP32 GND 引脚 - 连接到所有 3 个纵杆 GND 引脚,以及 BaseCam GND 引脚(黑色) 电池正极(红色)端子 - 并联连接到所有 3 个万向节电机驱动器的 VCC 引脚,以及 BaseCam 板上的 +BAT 引脚。 电池负极(黑色)端子 - 并联连接到所有 3 个万向节电机驱动器的 GND 引脚,以及 BaseCam 板上的电池 GND 引脚(正极 BAT+ 引脚下方)。 BaseCam CAN_H 针 - 与 CANH 针并联,全部在所有 3 个云台电机驱动器上(黄线) BaseCam CAN_L 针 - 与 CANL 针并联,全部在所有 3 个云台电机驱动器上(蓝线) 对于使用 2 个 ESP32 将摇杆信息中继到 BaseCam 控制器的情况下,第一个客户端/主 ESP32 读取 3 个摇杆,并将这些读数持续发送到第二个外设/从属 ESP32,后者又使用 BaseCam API 将它们中继到 BaseCam 控制器。在布线方面,这只是意味着从外设 ESP32 上移除 3 个摇杆连接,而是将它们连接到客户端 ESP32。所有其他接线与 Direct Wiring 情况相同。此外,主客户端 ESP32-S3 开发板可以由任何 5V 电源供电,例如电池组、笔记本电脑 USB 端口或通过 micro-USB 转 USB-A 电缆的壁挂式 5VDC 电源。 该项目成功演示了如何将命令从 ESP32-S3 开发板发送到 BaseCam 云台控制器板,以便通过 CANbus 连接控制云台电机。您也可以通过低功耗蓝牙将信号从一个 ESP32 发送到另一个 ESP32,为您的 BaseCam 控制器添加无线功能! 以下是进一步推进此项目的一些想法: 构建具有三个或更多轴的自定义完整万向节组件,并将此处提到的电子设备合并到该组件中。这可用于远程控制的摄像机监控、电影摄影、机器人遥测等。 添加基于 ESP32 的电容式触摸屏模块,带有屏幕按钮和文本字段,用于创建、更改、保存和修改发送到 BaseCam 控制板的设置和命令。 设计并 3D 打印一个外壳,以容纳客户端 ESP32 模块和用户界面设备(纵杆等),以创建便携式电池供电的万向节控制器。 使用 KiCAD 设计和使用基于 ESP32 的定制 PCB。 试验各种输入设备,如电位计旋钮、触觉开关和其他输入传感器和开关,以扩展用户与 BaseCam 板的交互方式。 使用一对带有 EMT 导管的耦合器创建一个可伸缩的 EMT 导管监控杆,并在杆顶部附近安装一个摄像头万向节,并沿杆安装控制电子设备。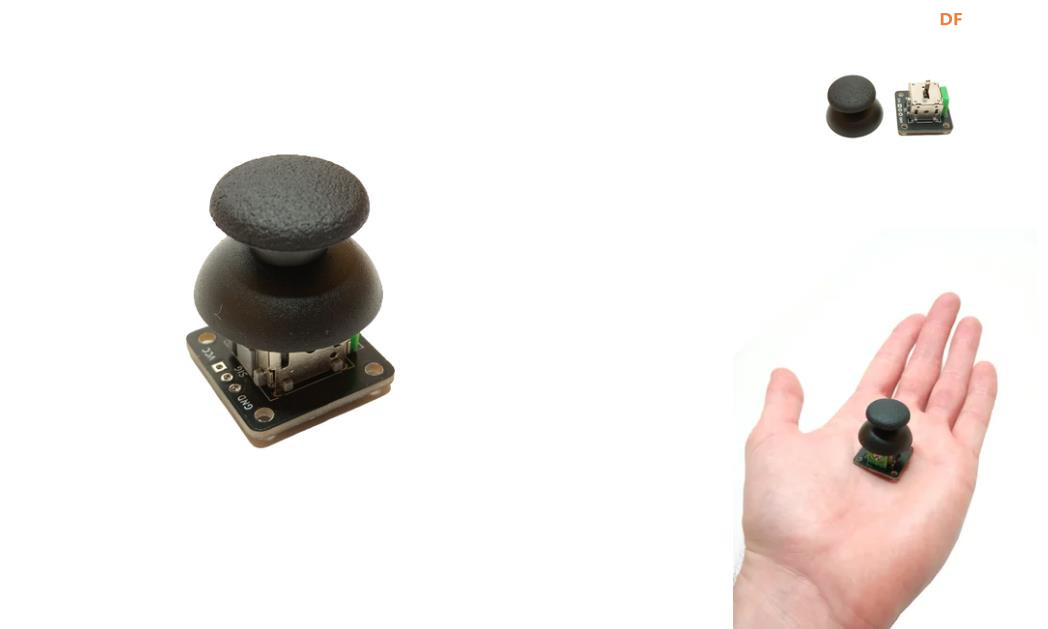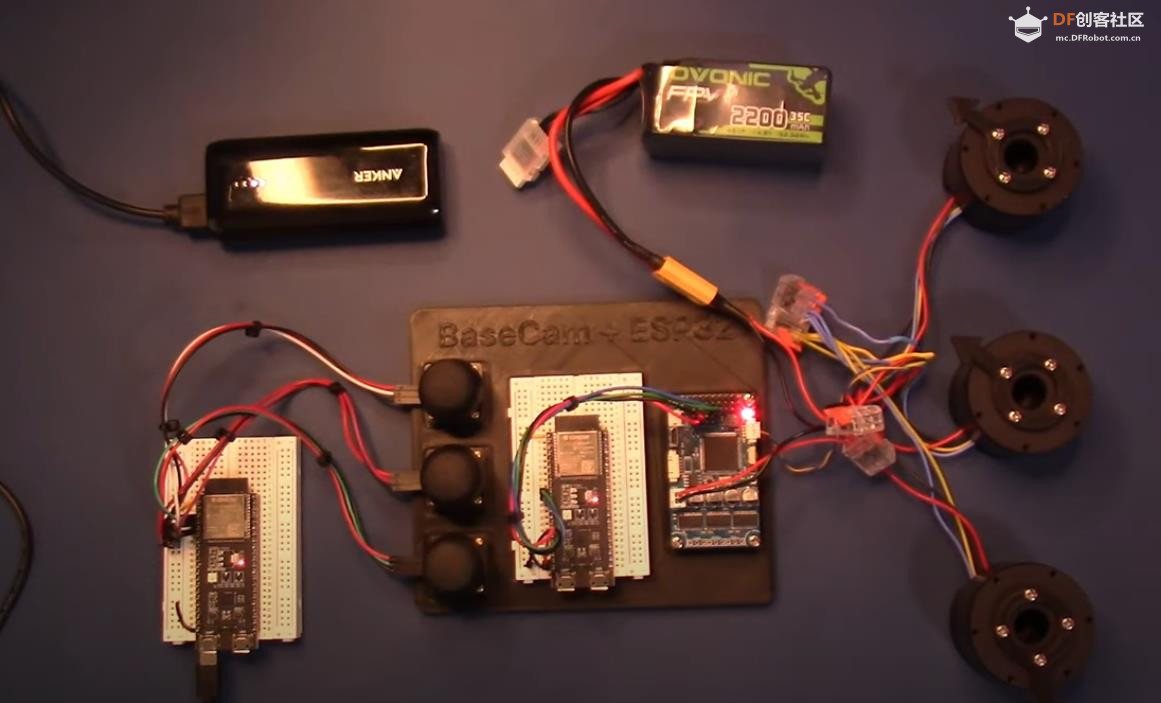  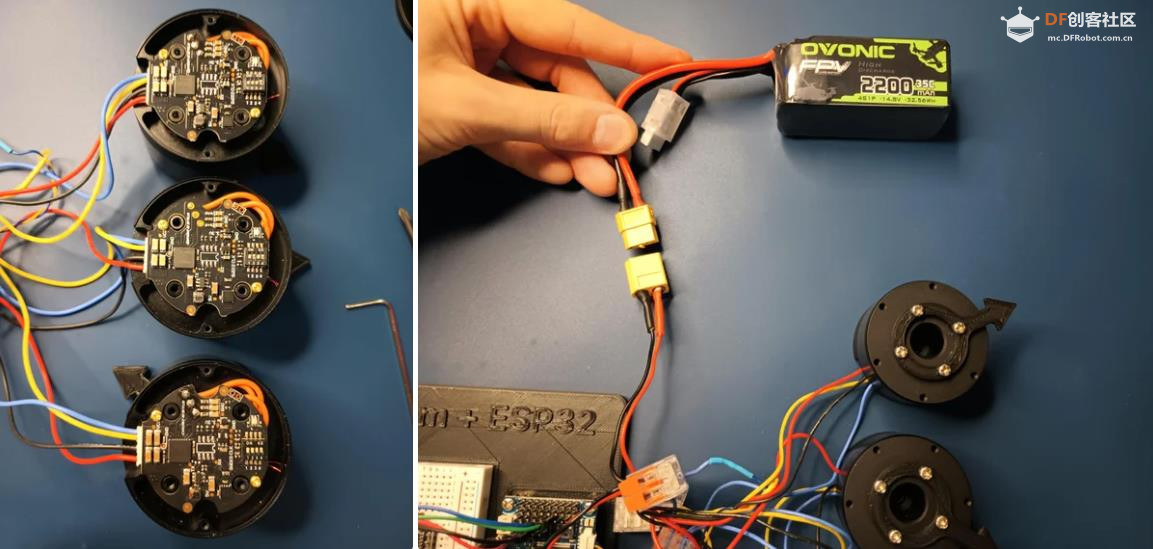 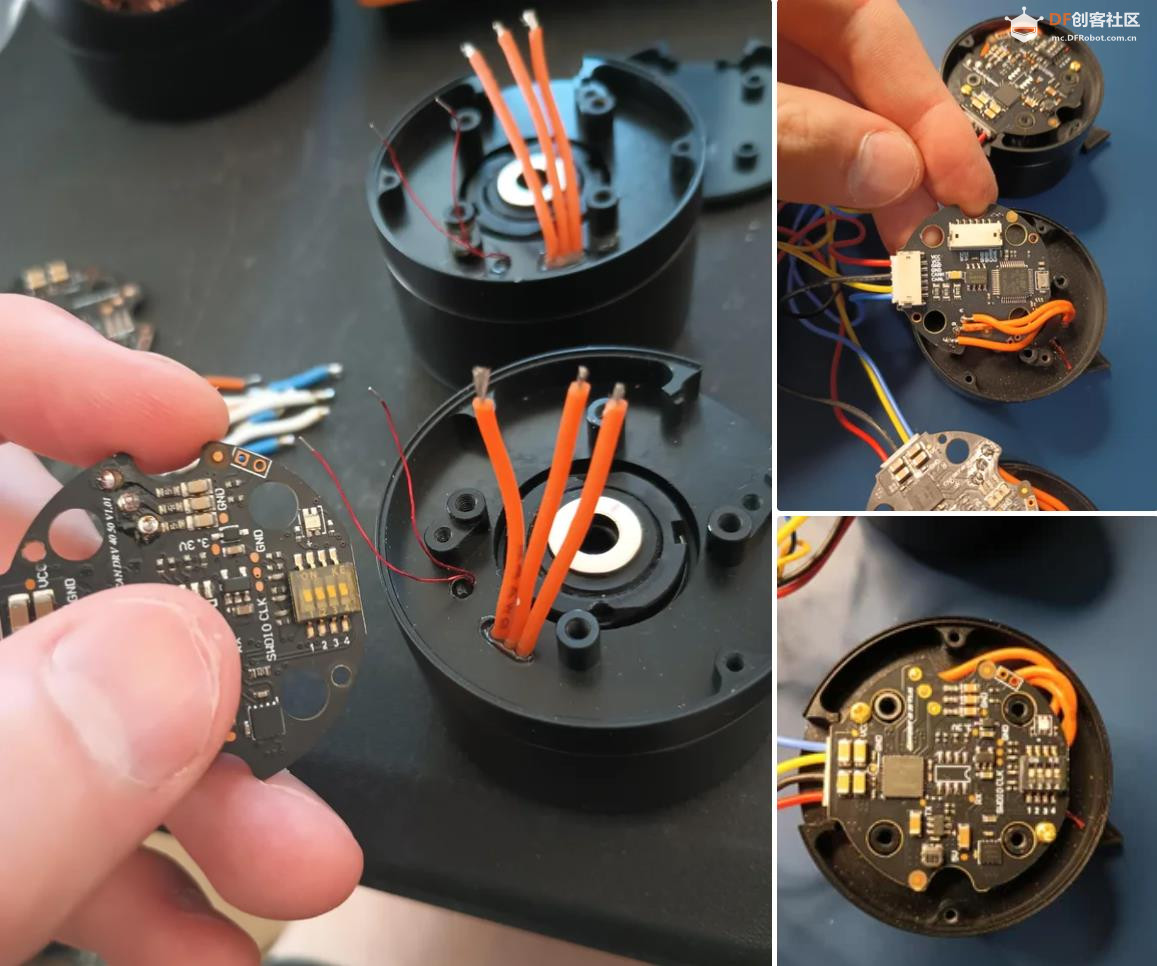  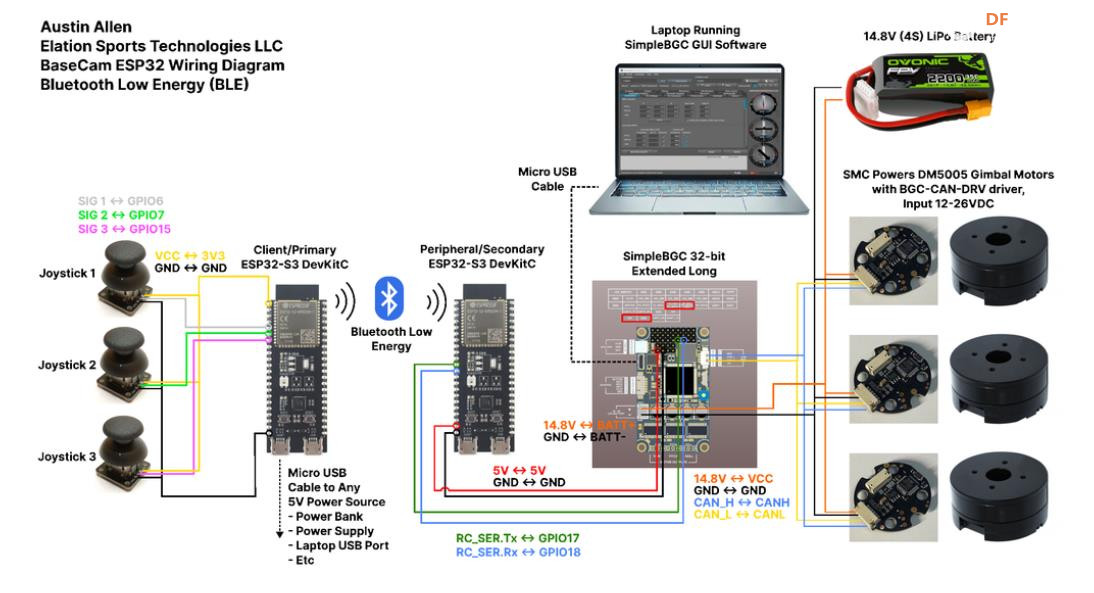 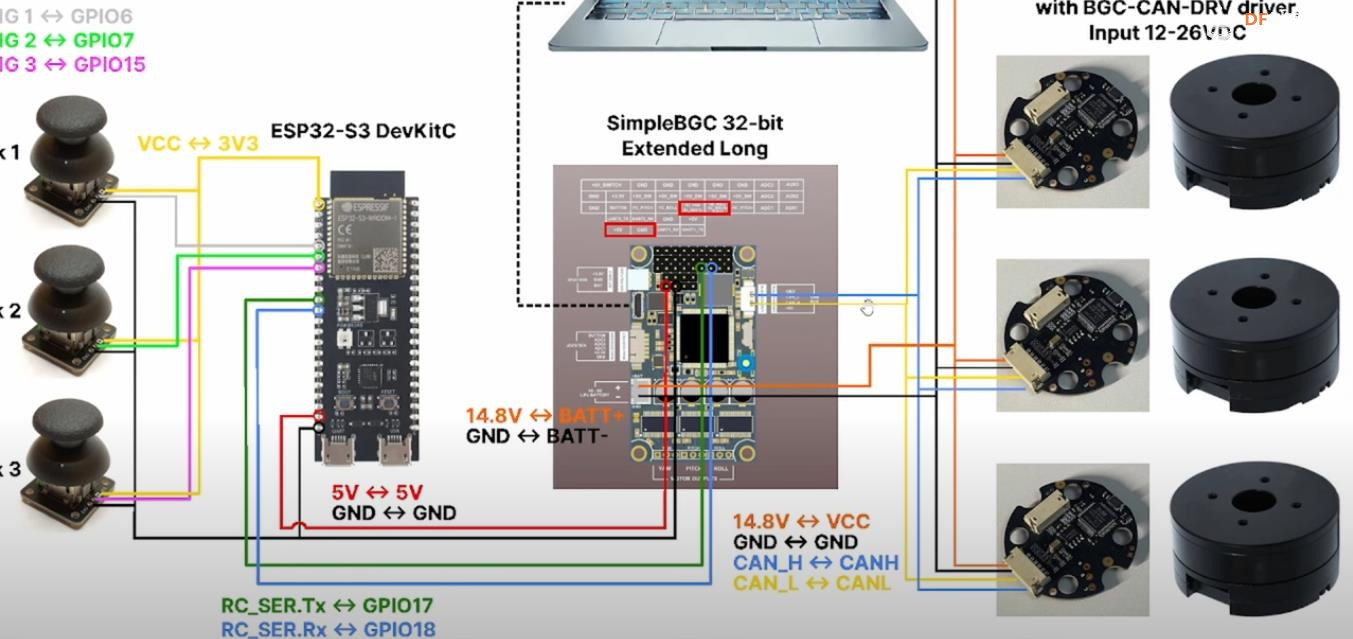 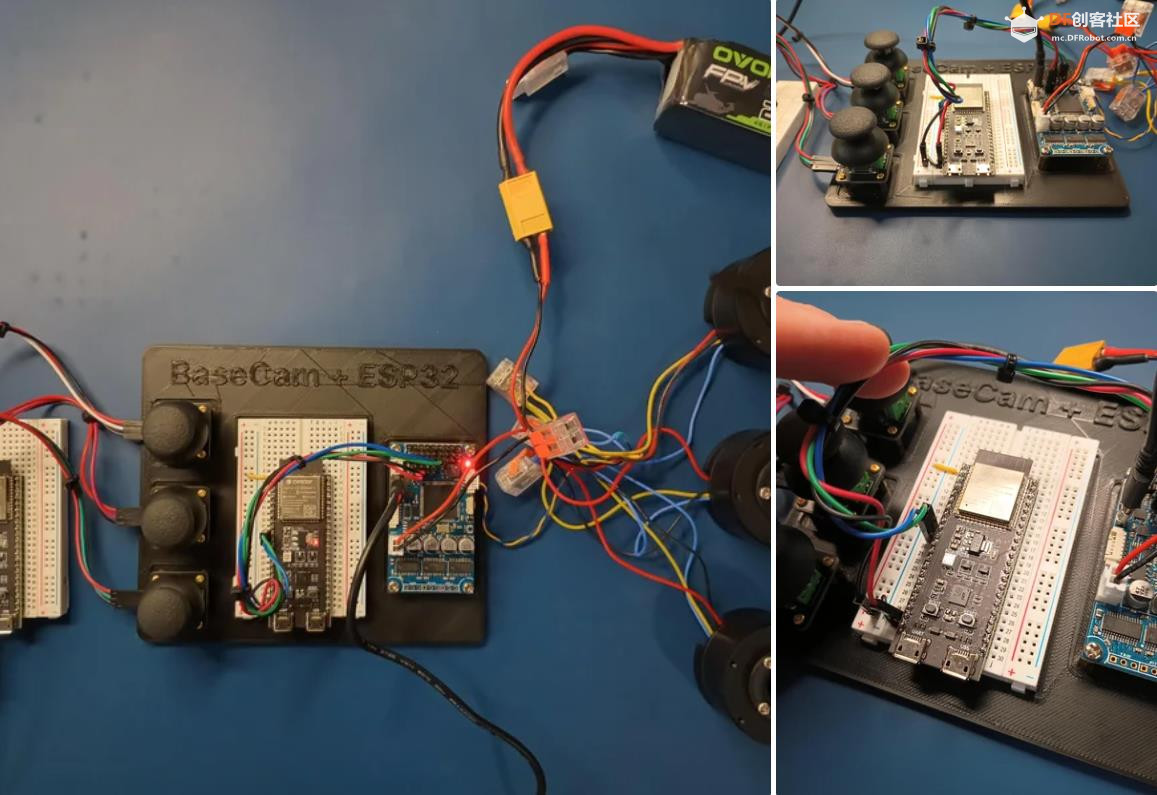 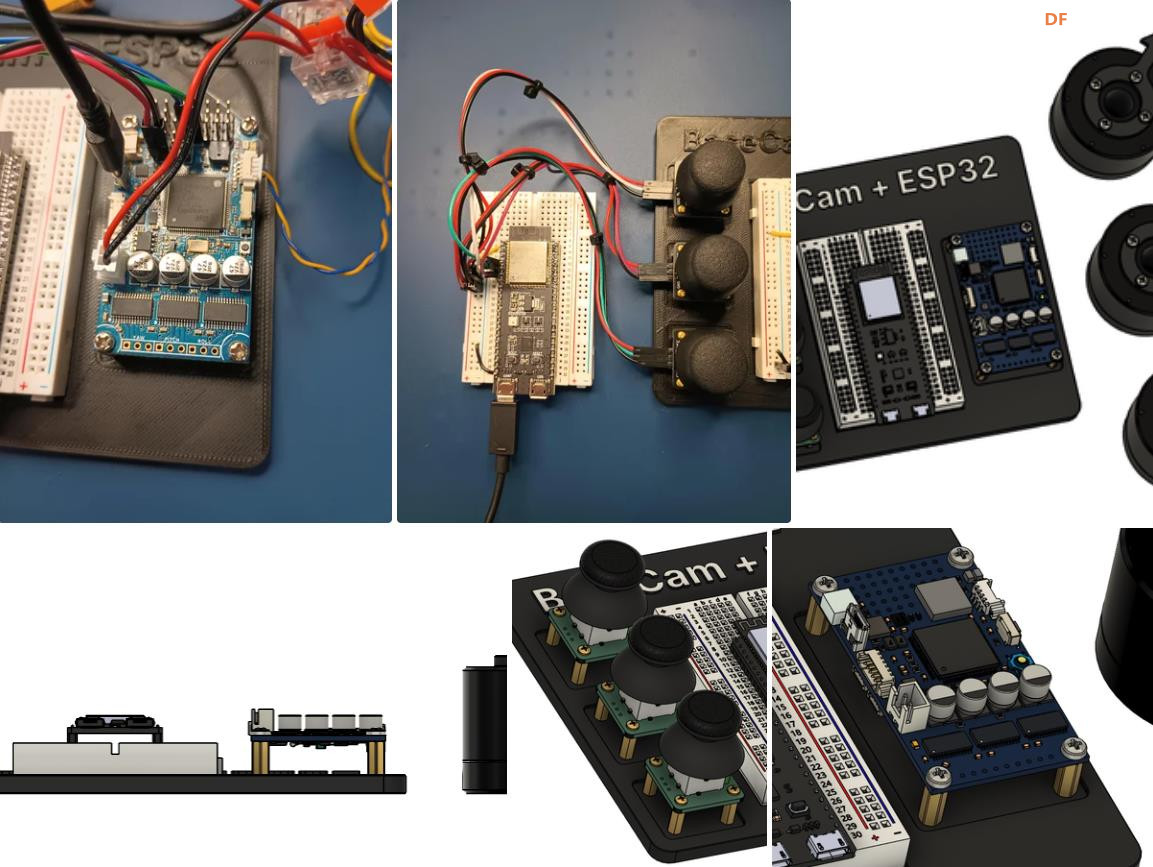 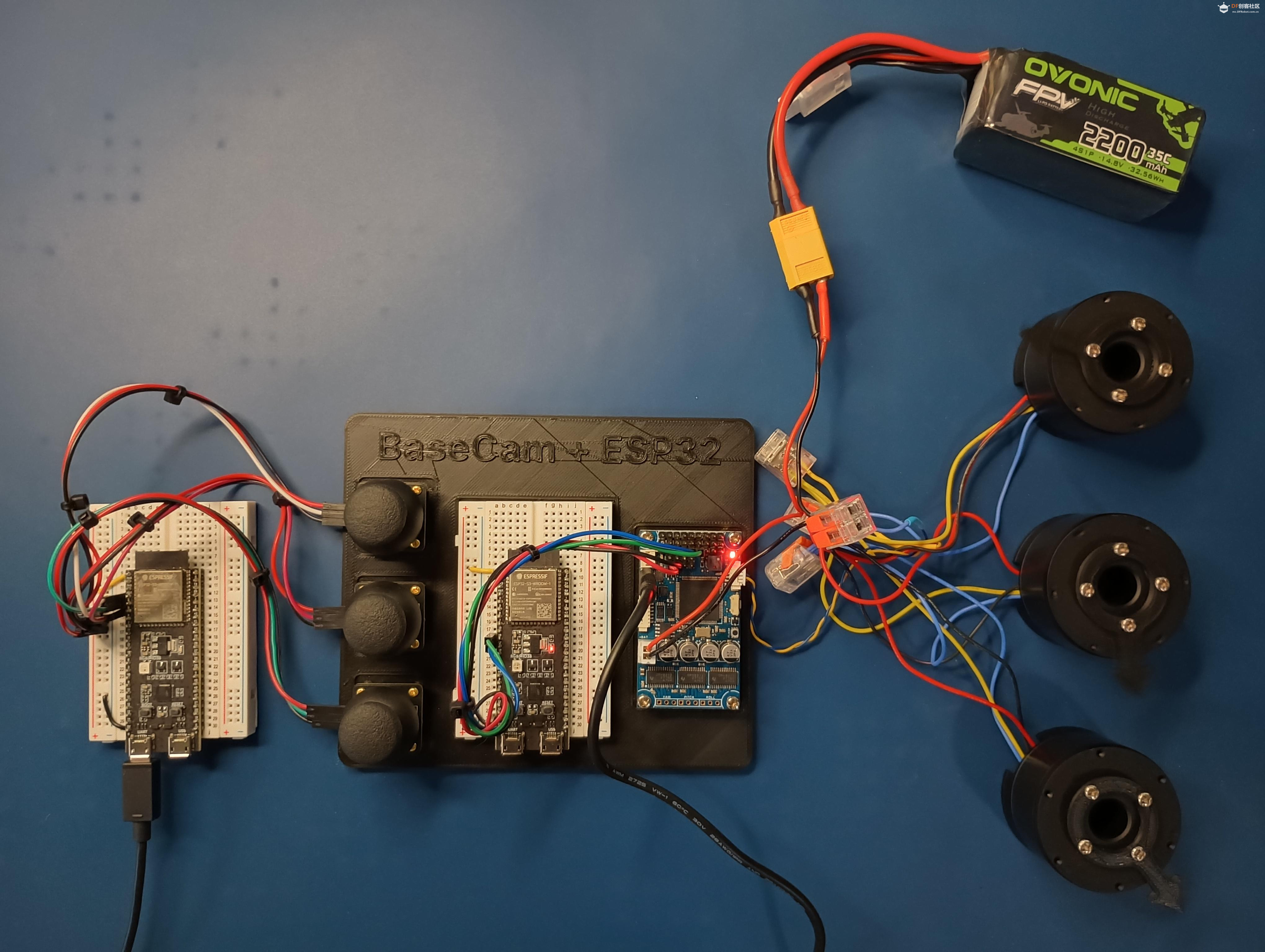 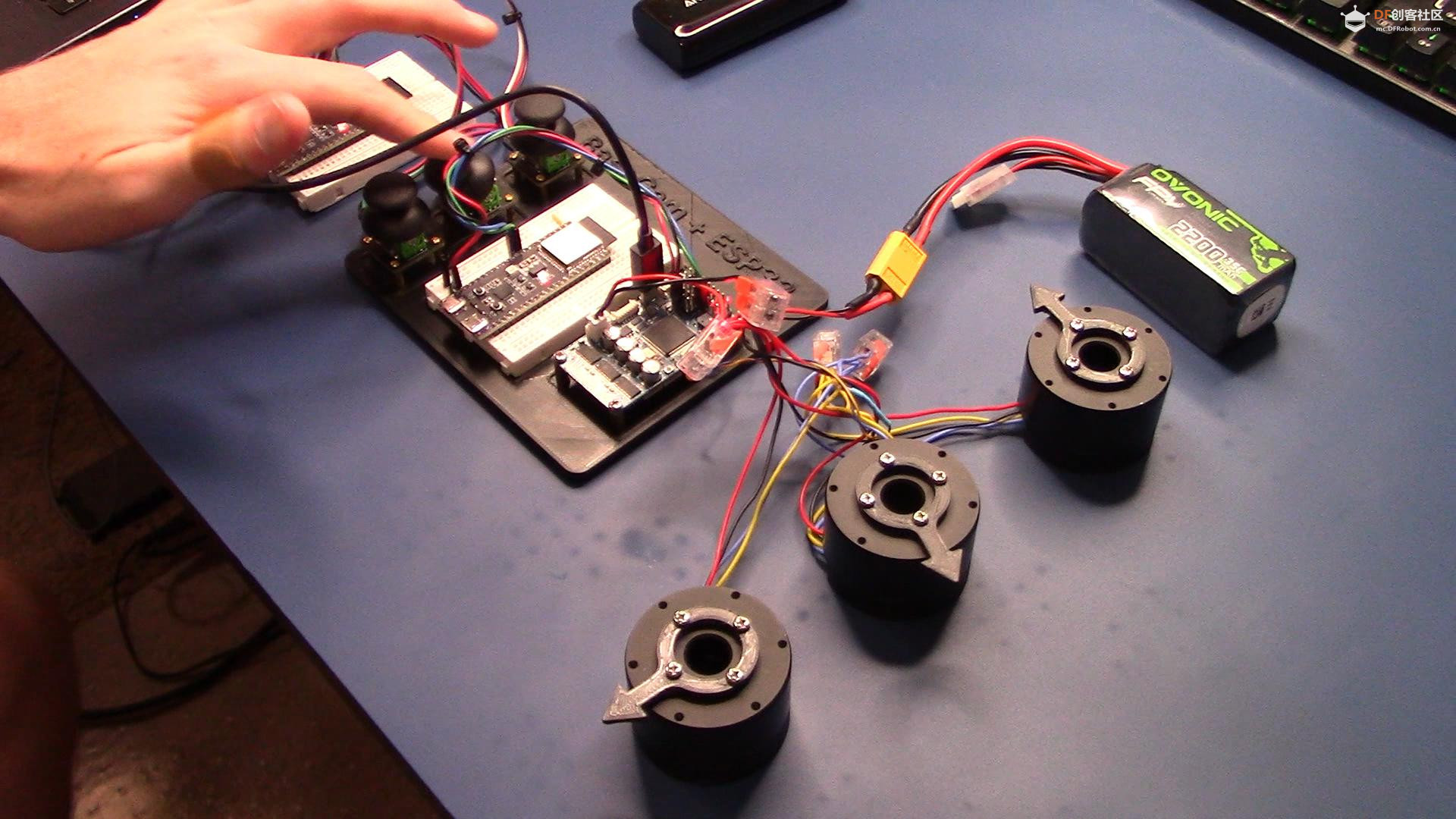 |
项目代码 |
|
【Arduino 动手做】ESP32 + BaseCam 蓝牙云台控制 项目链接:https://www.instructables.com/ES ... oth-Gimbal-Control/ 项目作者:洛杉矶 Penguingineer 项目视频:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7FAC-9hZs3E 项目代码:https://github.com/TheESTest/BaseCam-ESP32-Controller 3D打印文件: https://content.instructables.co ... F5FGMA9LZCPTYUF.stl https://content.instructables.co ... FS9VR2OLZCPTYTN.stl API 库:https://github.com/basecamelectronics/sbgc32-se-rial-ap CAN 接线和通信协议文档:https://content.instructables.co ... F9KOFQOLZCPTR48.pdf 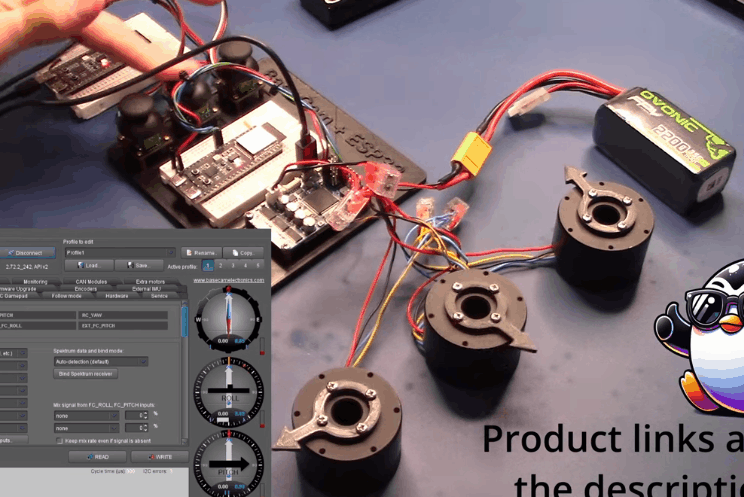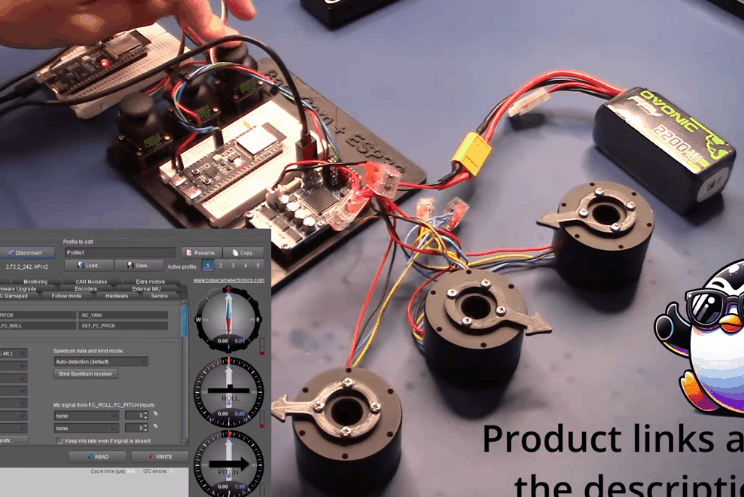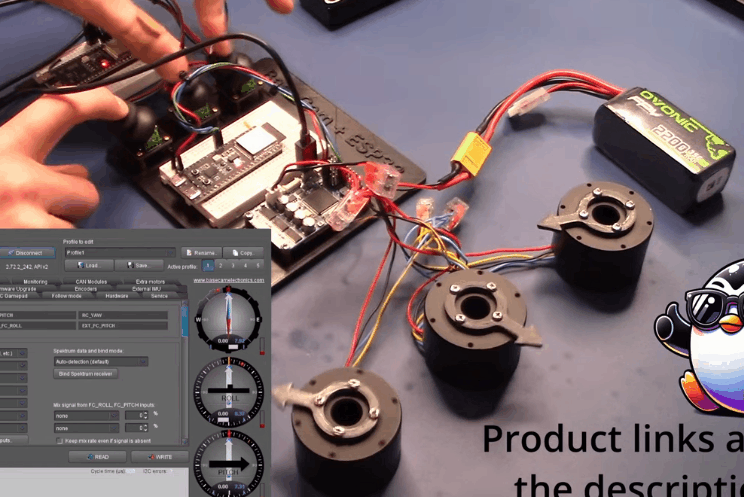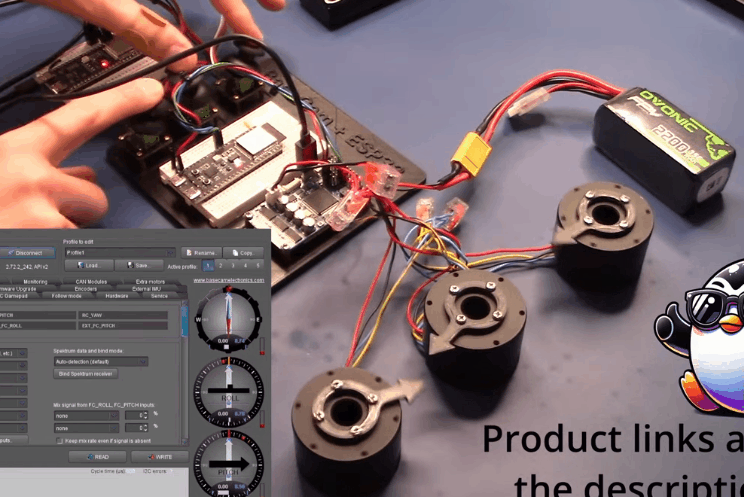 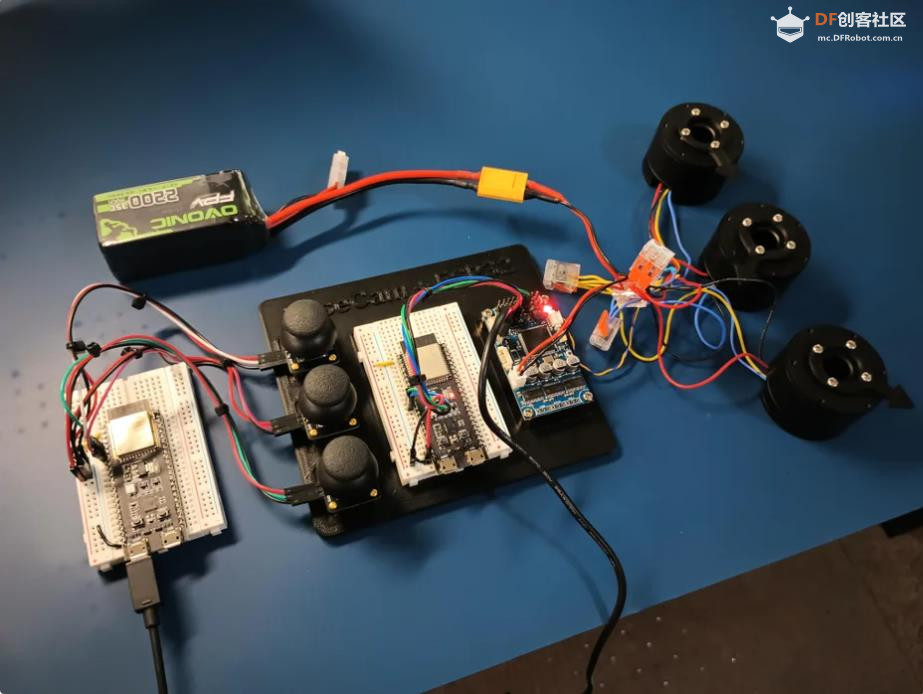 |
 沪公网安备31011502402448
沪公网安备31011502402448© 2013-2026 Comsenz Inc. Powered by Discuz! X3.4 Licensed