|
9007| 6
|
Smart Distributed Waste Management System |
|
本帖最后由 xiayc 于 2016-11-27 10:36 编辑 这是一个利用了Edison,为市政管理人员设计的一套智能分布式废物管理系统。 第一部分: 对于垃圾桶来说,我们需要用到的传感器有 超声波测距模块(本教程使用的是HC-SR04)、温湿度传感器(本教程使用的是DHT11)、火焰传感器、IR Distance Interupter、alcohol sensor、button、jhd1313-lcd。因为Edison的Arduino扩展板引脚有限,我们额外使用了一块Arduino UNO板,然后Edison和Arduino通过USB串口通信。 1:设计功能与在Edison和Arduino上传感器的连接(by xiezhq) a.第一个功能是提醒路人捡起没有扔进垃圾桶的垃圾,这一部分的功能通过人体红外传感,超声波传感,蜂鸣器,LCD显示屏与Arduino本地运算实现。  b. 第二个功能在于探测垃圾桶是否装满,通过简单的两个红外距离传感器实现,然后将信号通过Edison传到服务器端,由服务端将指令传到前段提醒工作人员并在LCD显示屏上显示以提醒路人。  c.通过报警按钮与火焰传感器,收集更多的异常状况,发出警报蜂鸣与传到服务端与前端。   2:下载对应的源码。 Arduino:https://github.com/maverick117/h ... c/detect/detect.ino Edison:https://github.com/maverick117/h ... ee/master/Edison-py Arduino的源码请下载后用Arduino IDE打开烧录进你的Arduino UNO。 !!重要!!将Arduino与Edison用USB连接起来,此时Edison系统中会多出一个串口设备(详细步骤见:http://xyc.ezsta.com/?p=95),请将这个串口名替换掉Edison源码下total.py中第36行的/dev/ttyACM0 (记得保留左右的单引号)  Edison的代码用的是python2,而且Edison-py目录下的文件夹都只是用来调试特定传感器是否能用的,所以不是必须要的。通过ssh连接到你的Edison后,将源码放到Edison中,进入源码所在目录后直接python total.py就能开始运行垃圾桶与传感器有关的程序啦 云服务部分: 1. HTTP Server与HTTP Client(by liujzh)  为了实现对废物回收终端的云端监视和协同控制,我们需要写一个简单的HTTP Server和HTTP Client实现服务器和客户端之间的通信。为了简化流程,我们用json文件进行信息交换,使得客户端到服务端对于终端驻留程序和服务端主控程序(在我们的实例中为前端)透明传送。为了进行快速开发,我们选择使用Python作为编程语言。 HTTP Server [mw_shl_code=python,true]#!/usr/bin/python2 from BaseHTTPServer import BaseHTTPRequestHandler,HTTPServer from os import curdir, sep import cgi import json import time import os import sys PORT_NUMBER = 8080 #This class will handles any incoming request from #the browser class myHandler(BaseHTTPRequestHandler): #Handler for the GET requests def do_GET(self): if self.path=="/": self.path="/index.html" elif self.path == "/rec": try: f = open(os.path.join(sys.path[0], 'data.json')) except IOError: self.send_error(500,'Internal Server Error. Database could not be opened.') self.send_response(200) self.send_header('Content-type','text/html') self.end_headers() self.wfile.write(f.read()) f.close() return try: #Check the file extension required and #set the right mime type self.path = self.path[1:] sendReply = False if self.path.endswith(".html"): mimetype='text/html' sendReply = True if self.path.endswith(".json"): mimetype='application/json' sendReply = True if self.path.endswith(".jpg"): mimetype='image/jpg' sendReply = True if self.path.endswith(".png"): mimetype='image/png' sendReply = True if self.path.endswith(".gif"): mimetype='image/gif' sendReply = True if self.path.endswith(".js"): mimetype='application/javascript' sendReply = True if self.path.endswith(".css"): mimetype='text/css' sendReply = True if sendReply == True: #Open the static file requested and send it f = open(os.path.join(sys.path[0], self.path)) self.send_response(200) self.send_header('Content-type',mimetype) self.end_headers() self.wfile.write(f.read()) f.close() return except IOError: self.send_error(404,'File Not Found: %s' % self.path) def do_POST(self): if self.path!="/send": self.send_response(403) return self.data_string = self.rfile.read(int(self.headers['Content-Length'])) #print self.data_string self.send_response(200) data = json.loads(self.data_string) data['Client_IP'] = self.client_address try: with open(os.path.join(sys.path[0],'data.json')) as data_file: database = json.load(data_file) except: database = {} database[data["id"]] = data with open(os.path.join(sys.path[0],'data.json'),mode='w') as data_file: json.dump(database,data_file) self.analyze(database) return def analyze(self,database): for d in database: pass try: #Create a web server and define the handler to manage the #incoming request server = HTTPServer(('', PORT_NUMBER), myHandler) print 'Started httpserver on port' , PORT_NUMBER #Wait forever for incoming http requests server.serve_forever() except KeyboardInterrupt: print '\nSIGINT received, shutting down the web server' server.socket.close() [/mw_shl_code] HTTP Client [mw_shl_code=python,true]#!/usr/bin/python3 import requests import json import time import os import sys # POST data print('HTTP Client started') try: with open(os.path.join(sys.path[0],'conf.json')) as conf_file: conf = json.load(conf_file) except IOError: print('Could not open config file. Program terminated.') exit(0) print('Current Configuration') print(conf) ip = conf['server_addr'] port = conf['server_port'] while True: try: with open(os.path.join(sys.path[0],'stat.json')) as data_file: data = json.load(data_file) print(data) print('POST in progress:') r_p = requests.post('http://'+ip.strip()+':'+port.strip()+'/send',json=data) print('GET in progress:') r_g = requests.get('http://'+ip.strip()+':'+port.strip()+'/rec') print(r_g.json()) with open(os.path.join(sys.path[0],'data.json'),mode='w') as data_file: json.dump(r_g.json(),data_file) time.sleep(5) except requests.exceptions.ConnectionError: print("Connection Error.") time.sleep(30) except KeyboardInterrupt: print('\nSIGINT received. Program terminated.') exit(0) [/mw_shl_code] 为了对Client进行很方便的配置修改,我们将服务器IP地址和端口设置放置在同目录下的config.json文件中,保证数据不会被hard-code在代码中。config.json的格式如下: [mw_shl_code=text,true]{ "server_addr":"XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX", "server_port":"8080" } [/mw_shl_code] 其中XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX填写服务器端的IP地址,而8080是服务端的默认端口号,可以进行修改。 我们传输的数据在stat.json里, [mw_shl_code=text,true]{ "id":"0x01", "package_type":0, "volume":0, "state_code":0, "rate":0, "emergency_type":0 } [/mw_shl_code] 这个只要是正确的json格式都能够通过客户端透明传送给服务端。 4.客户端雏形 由于时间紧张最终没有完成移动端的开发而用前段网页借以替代,网页源代码见https://github.com/maverick117/h ... e/master/httpserver,下面简单用两张图展示表达效果与预期效果 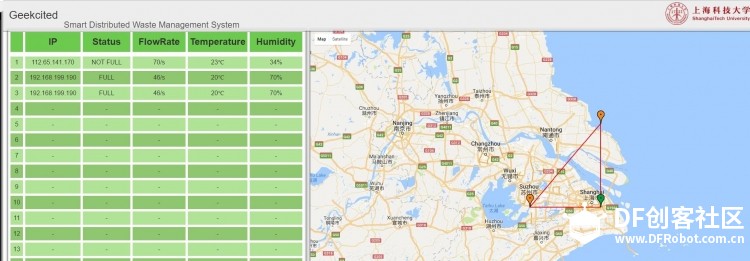 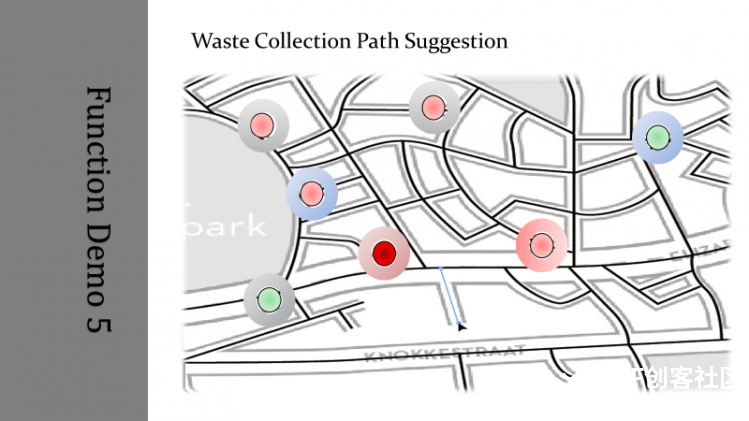 最后的成品图: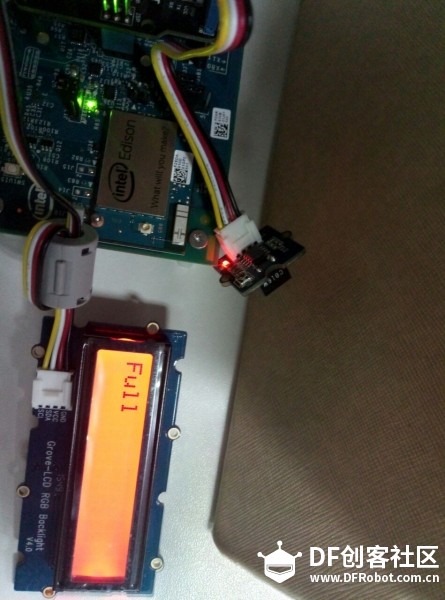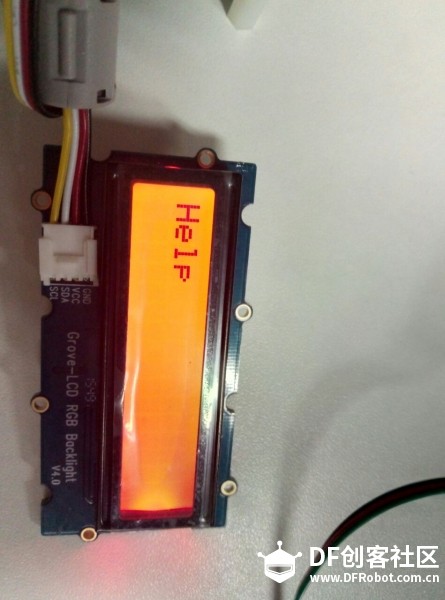  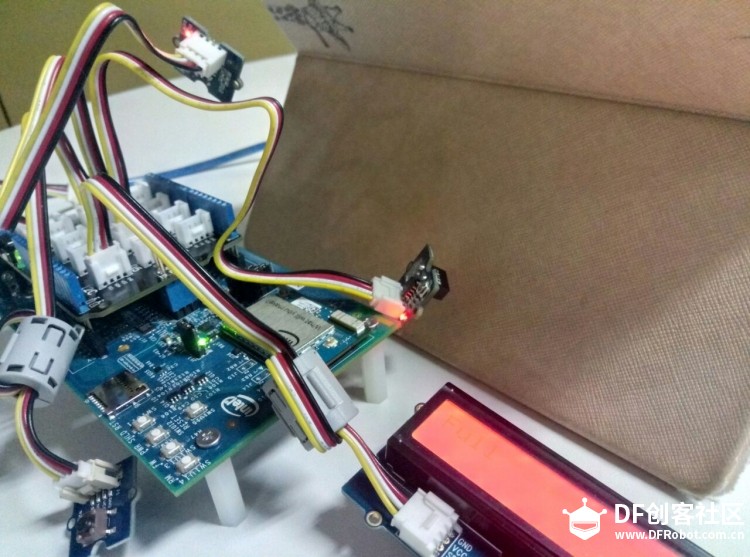    |
 沪公网安备31011502402448
沪公网安备31011502402448© 2013-2026 Comsenz Inc. Powered by Discuz! X3.4 Licensed