
前言
前些日子看到群里有老师说:行空板如果做文字键盘输入比较复杂。在之前我们的信息输入大多数用语音识别来完成的,我就想能不能像手机输入法里的手写字输入法那样:我在屏幕手写字体,输入法会自动识别到我们的字迹呢!为此我们在上一篇【行空板教程】写字板中实现了如何将线条留着我们的屏幕上,那么现在本次教程就让我们开始手写输入法的编写。好了废话不多说,Let's go!
项目思路
我先来说一下我们手写输入法的整体项目思路吧!
如果没有应用的读者,点击创建应用
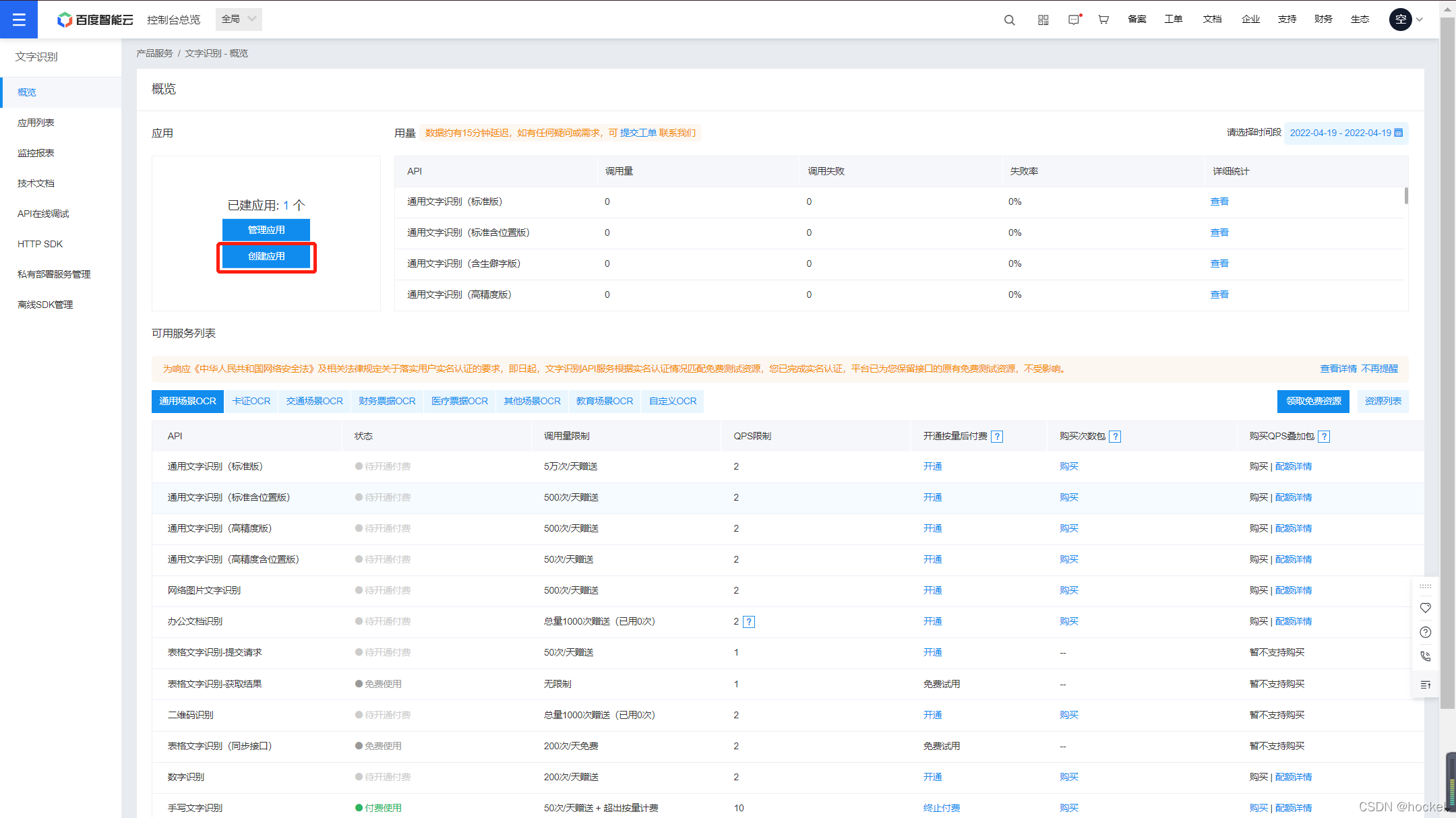
输入一些相关信息即可完成应用的创建。

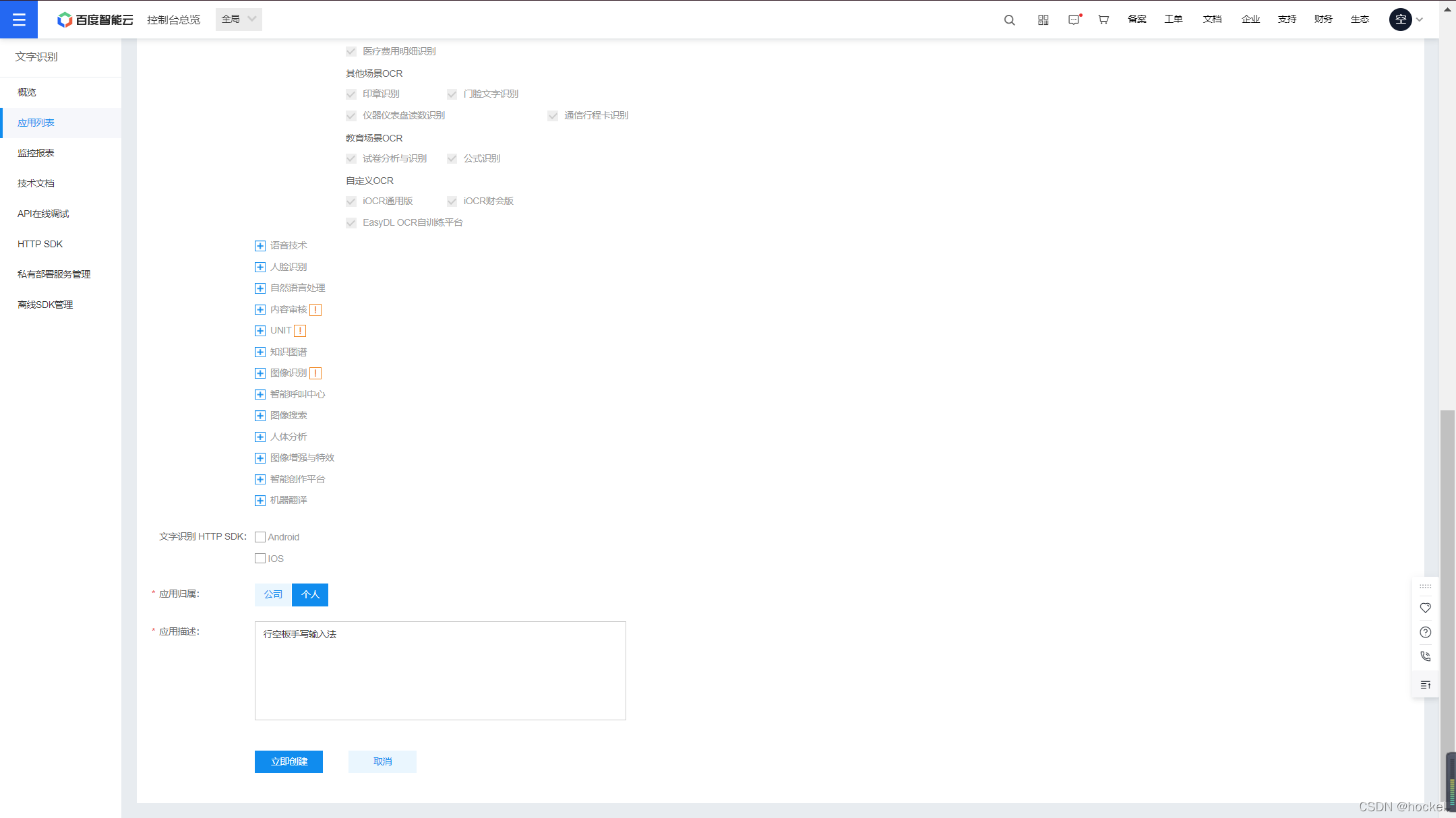
点击查看应用详情
里面的API key和 Secret Key后面我们会有用到。先记录下来。
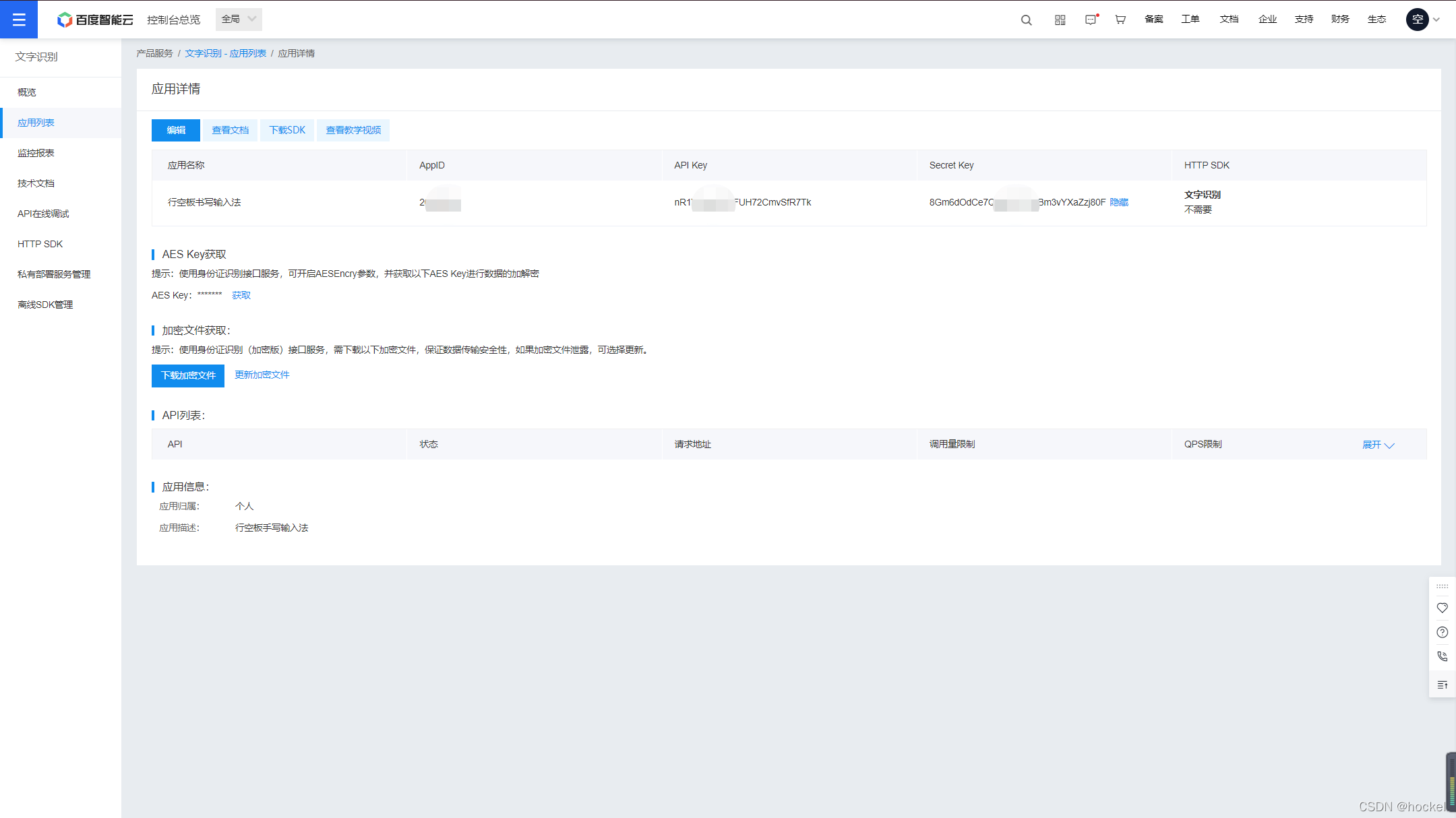
「注:文字识别接口的调用每天是有限制的,如果超了,可以使用钞能力!付费使用哈」
2、安装百度aip接口
之前语音识别的文章已经详细讲了这里不再赘述。打开终端输入pip insatll baidu-aip
3、安装Scrot截图工具
我们要把屏幕的显示的文字进行截图,需要安装Scrot截图工具,(之前用了PIL进行图片保存,报错!这里感谢DF的李工给予的技术支持)
打开终端输入apt-get install scrot

Scrot的具体操作可以看访问这个地址(http://manpages.ubuntu.com/manpages/jammy/en/man1/scrot.1.html)
scrot [-bcfhikmopsuvz] [-a X,Y,W,H] [-C NAME] [-D DISPLAY] [-d SEC] [-e CMD]
[-F FILE] [-l STYLE] [-n OPTS] [-q NUM] [-S CMD] [-t NUM | GEOM] [FILE]
我们这里只需要用到[-a X,Y,W,H]
程序设计
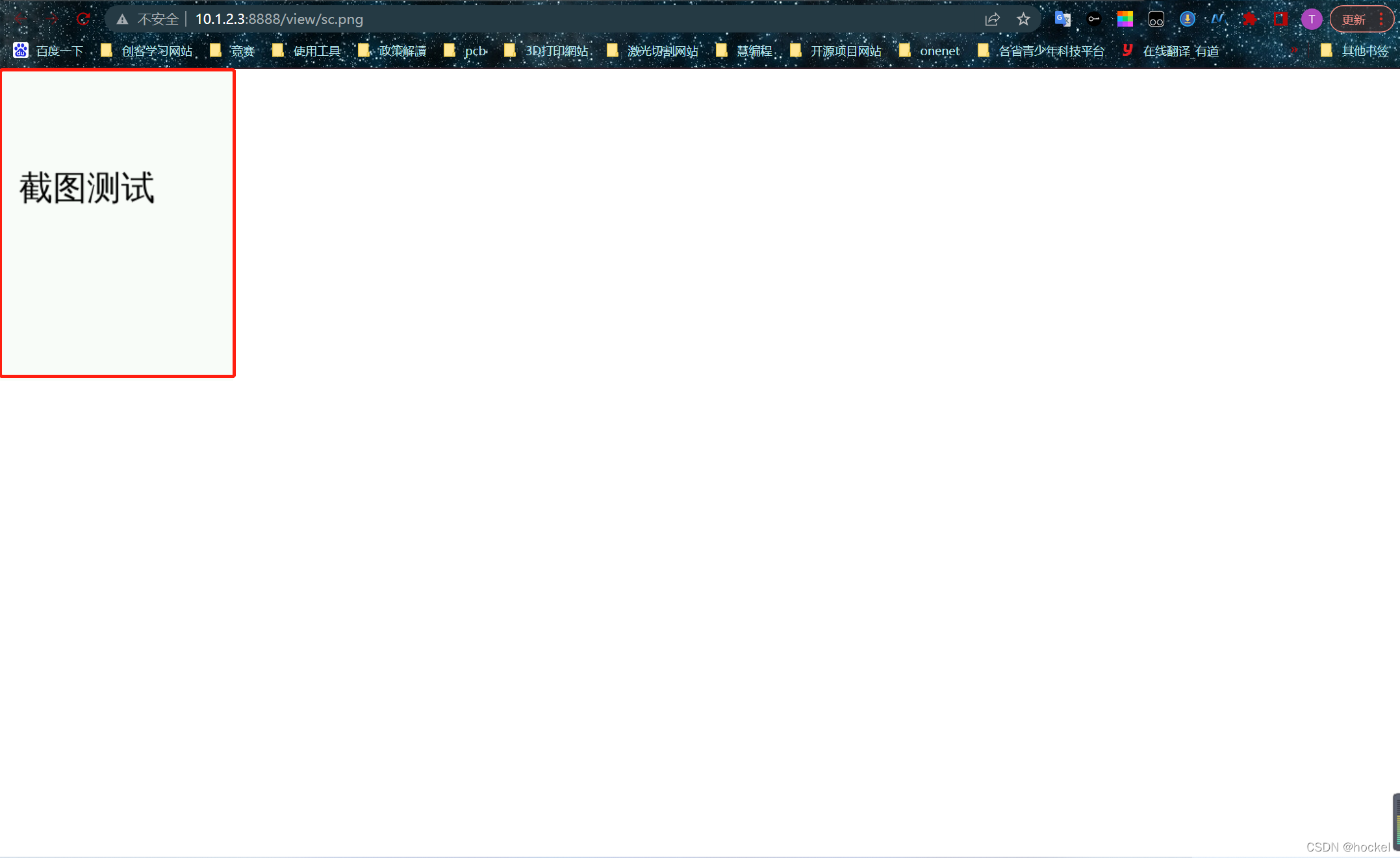
1、截图保存到本地
from unihiker import GUI
import os
import time
gui=GUI() #实例化GUI类
info_text2 = gui.draw_text(x=20, y=100,font_size=25 ,text='截图测试')
os.system("scrot -a 0,0,240,320 sc.png") # 在坐标(0.0)进行截图高320宽240输出的图片名称为sc.png
whileTrue:
time.sleep(1)
效果:
2、将截图进行文字识别
from unihiker import GUI
import requests
import base64
import os
import time
gui=GUI() #实例化GUI类
info_text2 = gui.draw_text(x=20, y=100,font_size=25 ,text='截图测试')
API_Key = ""# 输入自己的api_key
Secret_Key = ""#输入自己的secret_key
# client_id 为官网获取的AK, client_secret 为官网获取的SK
host = 'https://aip.baidubce.com/oauth/2.0/token?grant_type=client_credentials&client_id='+API_Key+'&client_secret='+Secret_Key
response = requests.get(host)
if response:
access_token = response.json()['access_token']
print(access_token)
os.system("scrot -a 0,0,240,320 sc.png") # 在坐标(0.0)进行截图高320宽240输出的图片名称为sc.png
request_url = "https://aip.baidubce.com/rest/2.0/ocr/v1/handwriting"
# 二进制方式打开图片文件
f = open('sc.png', 'rb')
img = base64.b64encode(f.read())
params = {"image":img}
request_url = request_url + "?access_token=" + access_token
headers = {'content-type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'}
response = requests.post(request_url, data=params, headers=headers)
response_result = response.json()['words_result']
print(response.json())
print(response_result)
if response_result :
result= response_result[0]
if result["words"]:
print(result["words"])
whileTrue:
time.sleep(1)
效果:
GUI is cleared because of reinit
24.f284c0a9fade4bd5cb2d058298395602.2592000.1652947434.282335-*******4
{'words_result': [{'location': {'top': 102, 'left': 16, 'width': 147, 'height': 38}, 'words': '截图测试'}], 'words_result_num': 1, 'log_id': 1516326710653341845}
[{'location': {'top': 102, 'left': 16, 'width': 147, 'height': 38}, 'words': '截图测试'}]
截图测试
3、手写输入法
from unihiker import GUI #导入包
import requests
import base64
import time
import os
gui=GUI() #实例化GUI类
pos_xy = []
ORC_msg = []
text_msg =""
gui.on_a_click(lambda: show_char()) # A键进行识别
gui.on_b_click(lambda: del_char()) # B键进行清空操作
API_Key = ""# 输入自己的api_key
Secret_Key = ""#输入自己的secret_key
# client_id 为官网获取的AK, client_secret 为官网获取的SK
host = 'https://aip.baidubce.com/oauth/2.0/token?grant_type=client_credentials&client_id='+API_Key+'&client_secret='+Secret_Key
response = requests.get(host)
if response:
access_token = response.json()['access_token']
# print(access_token)
def character_Recognize():#手写文字识别
request_url = "https://aip.baidubce.com/rest/2.0/ocr/v1/handwriting"
# 二进制方式打开图片文件
f = open('sc.png', 'rb')
img = base64.b64encode(f.read())
params = {"image":img}
request_url = request_url + "?access_token=" + access_token
headers = {'content-type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'}
response = requests.post(request_url, data=params, headers=headers)
response_result = response.json()['words_result']
print(response_result)
if response_result :
result= response_result[0]
if result["words"]:
print(result["words"])
return result["words"]
def show_char():# 显示文字
global text_msg
os.system("scrot -a 0,60,240,260 sc.png") #这里是从(0,60)这个坐标进行截图,为了防止把生成的文本显示在上面。
msg = character_Recognize()
if msg:
gui.clear()
ORC_msg.append(msg)
text_msg="".join(ORC_msg) # 将列表转为字符串
print(text_msg)
gui.draw_text(x=0, y=20,w=200, text=text_msg)
else:
gui.clear()
gui.draw_text(x=0, y=20,w=200, text=text_msg)
def del_char():#清空数据
ORC_msg.clear()
text_msg=""
gui.clear()
def mouse_move(x, y):# 画线
global temp_time
temp_time = time.time()
'''
首先判断pos_xy列表中是不是至少有两个点了
然后将pos_xy中第一个点赋值给point_start
利用中间变量pos_tmp遍历整个pos_xy列表
point_end = pos_tmp
画point_start到point_end之间的线
point_start = point_end
这样,不断地将相邻两个点之间画线,就能留下鼠标移动轨迹了
'''
pos_xy.append([x,y])
if len(pos_xy) > 1:
point_start = pos_xy[0]
for pos_tmp in pos_xy:
point_end = pos_tmp
line_text = gui.draw_line(x0=point_start[0],y0=point_start[1],x1=point_end[0],y1=point_end[1],width=2, color=(122,222,125))
point_start = point_end
def on_release(event):
pos_xy.clear()
gui.master.bind("<ButtonRelease>", on_release)# 抬笔检测
gui.on_mouse_move(mouse_move) #鼠标检测
whileTrue:
#增加等待,防止程序退出和卡住
time.sleep(0.5)
「效果」

 沪公网安备31011502402448
沪公网安备31011502402448