使用 Python 的简单雷达
在本教程中,我想向您展示如何轻松快速地创建雷达界面。在阅读完这些说明后,您应该能够自行扩展它们并将其用于您的 DIY 项目。
硬件清单
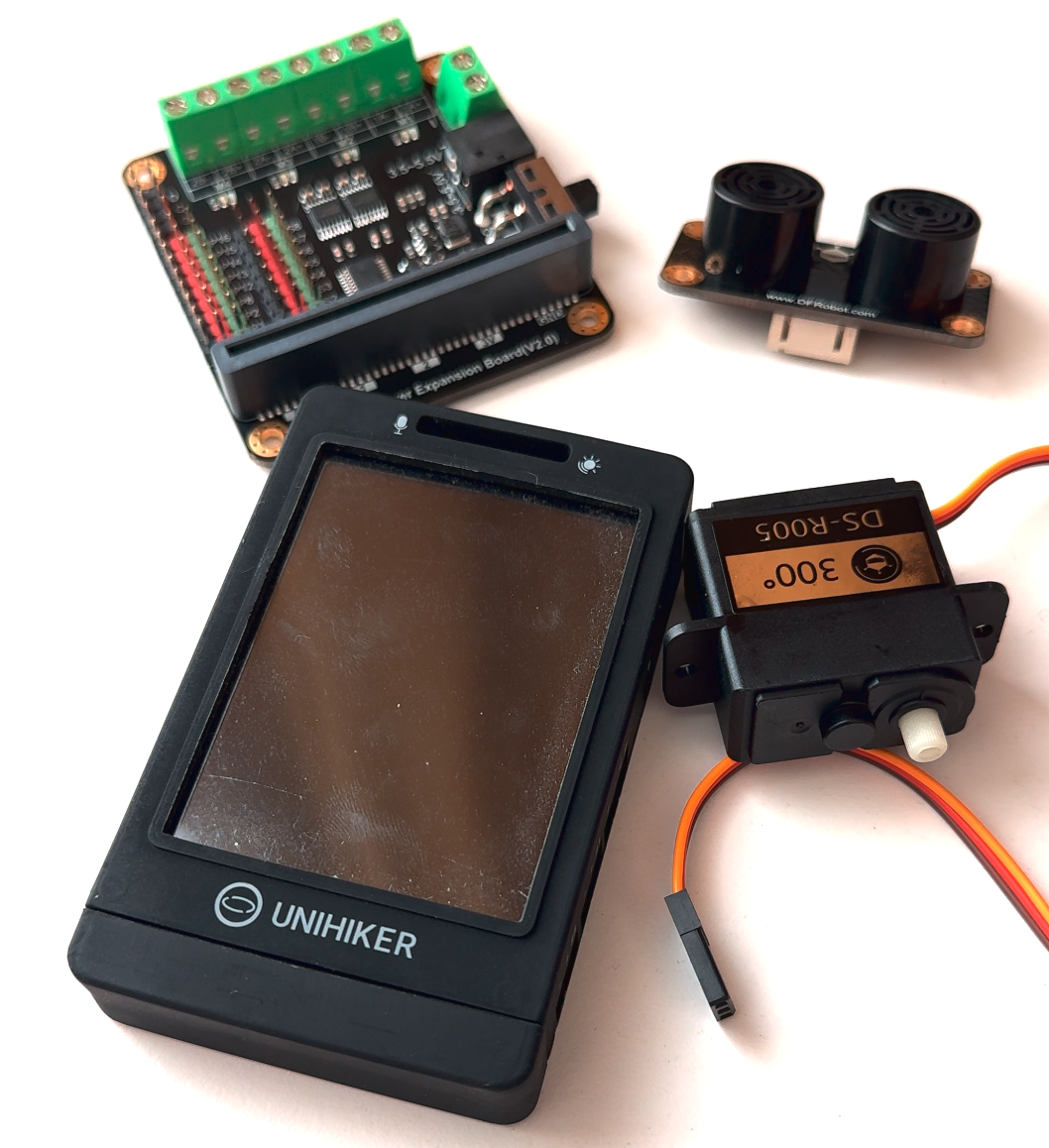


步骤1 连接硬件
连接硬件非常简单!将行空板插入micro:Driver扩展板(Gravity标准接口)。接下来,通过 I2C 将超声波传感器与行空板连接。然后将伺服电机连接到 micro:Driver 扩展板(例如连接到引脚 S8)。最后,您必须将超声波传感器连接到伺服电机上。我用了一些纸板和尼龙搭扣。它看起来不太好,但它很快而且持久。
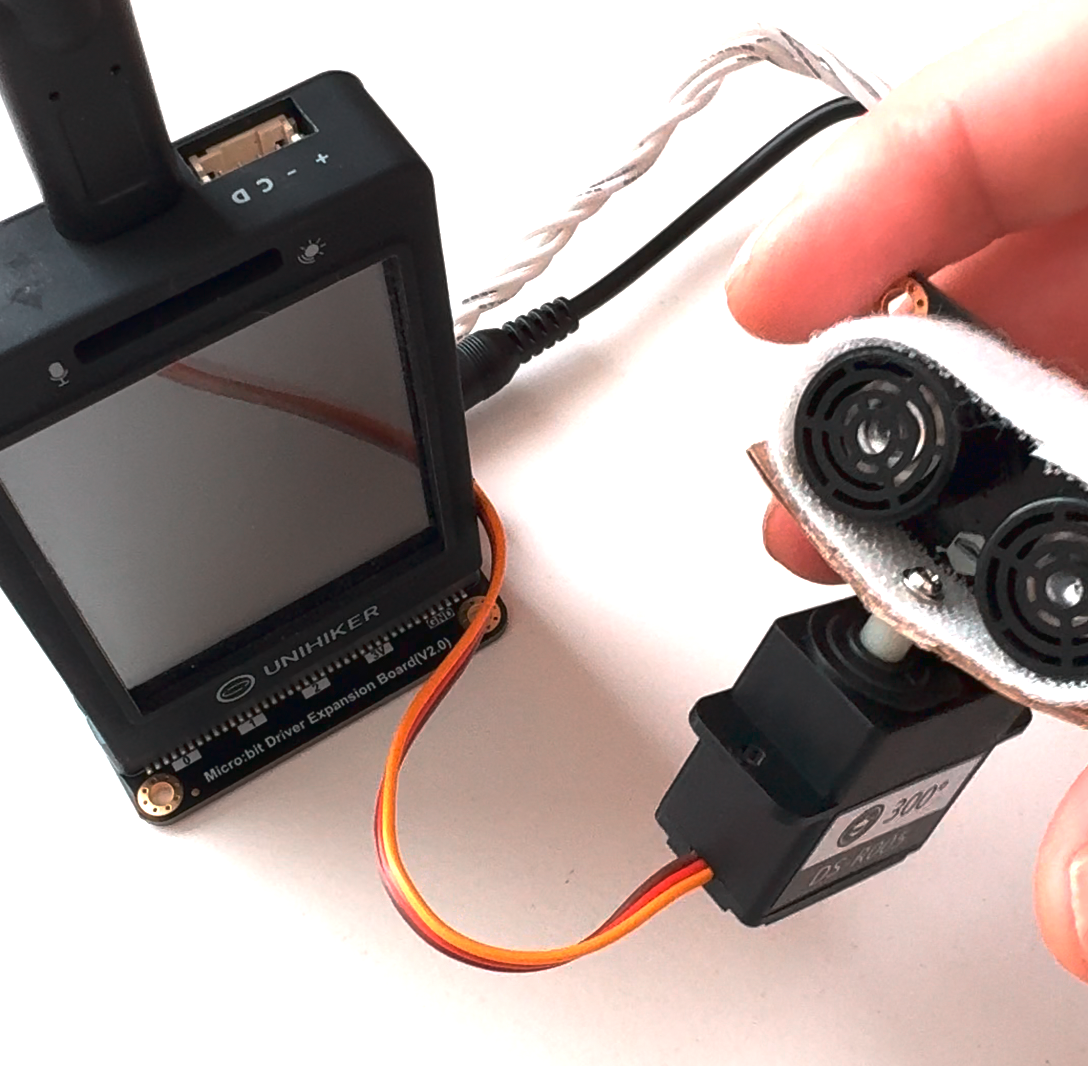


连接所有硬件部件
步骤2 编写Python代码
现在我们从 Python 代码开始。为了保证更好的可维护性和可重用性,我们创建了两个Python脚本。建议将 UI 创建为 Python 模块(例如作为类)。在您的开发项目中,您应该创建一个“lib”文件夹并在其中创建一个“radar.py”文件(例如 YOUR-PROJECT/lib/radar.py)。
代码
from tkinter import Tk, Canvas, BOTH
from math import cos, sin, radians
class Radar:
"""
Radar class to represent a Radar UI via a Tk interface
"""
_DISTANCE: str = "cm"
_FONT: str = "Helvetica"
_COLORS: dict = {
'radar': 'white',
'background': 'black',
'point': 'yellow',
'line': 'lawn green',
'line_text': 'cyan'
}
_ARC_STEPS: int = 3
_SONAR_OBJECTS: dict = {}
def __init__(self, screen_width: int, screen_height: int) -> None:
"""
Radar UI interface constructor
:param screen_width: width of the screen
:param screen_height: height of the screen
"""
self._screen_width = int(screen_width)
self._screen_height = int(screen_height)
self._center_x = self._screen_width // 2
self._center_y = self._screen_height - 50
self._line_width = None
self._angle_start = None
self._angle_end = None
self._max_radius = None
self._arc_distance = None
self.screen = Tk()
self.screen.geometry(f'{self._screen_width}x{self._screen_height}+0+0')
self.screen.resizable(width=False, height=False)
self.canvas = Canvas(self.screen, bg=self._COLORS['background'])
self.canvas.pack(expand=True, fill=BOTH)
def configure(self, line_width: int, max_radius: int, arc_distance: int, start_angle: int, end_angle: int) -> None:
"""
Configure the radar
:param line_width: line width of the graphics
:param max_radius: arc max radius
:param arc_distance: arc distance in pixel
:param start_angle: start angle in degrees for arcs
:param end_angle: end angle in degrees for arcs
:return: None
"""
self._line_width = int(line_width)
self._angle_start = int(start_angle)
self._angle_end = int(end_angle)
self._max_radius = int(max_radius)
self._arc_distance = int(arc_distance)
def _draw_line(self, angle: int, color: str) -> None:
"""
Draw line with given angle and color on interface
:param angle: angle in degrees
:return: None
"""
in_radian = radians(int(angle))
x1 = self._center_x
y1 = self._center_y
x2 = x1 + self._max_radius * cos(in_radian)
y2 = y1 - self._max_radius * sin(in_radian)
self.canvas.create_line(x1, y1, x2, y2, width=self._line_width, fill=str(color))
def _draw_text(self, x: int, y: int, text: str, color: str, font_size: int = 20) -> None:
"""
Draw given text with values on interface
:param x: x position as integer
:param y: y position as integer
:param text: string with current line angle
:param color: color of the text as string
:param font_size: optional font size (default: 20)
:return: None
"""
x_pos = int(x)
y_pos = int(y)
font = (self._FONT, int(font_size))
self.canvas.create_text(x_pos, y_pos, text=str(text), font=font, fill=color)
def _draw_background(self, show_measurement: bool = True) -> None:
"""
Draw radar background graphic on interface
:param show_measurement: whether to show the measurement or not
:return: None
"""
color = self._COLORS['radar']
angle_total = self._angle_start + self._angle_end
x1 = self._center_x - self._max_radius
y1 = self._center_y - self._max_radius
x2 = self._center_x + self._max_radius
y2 = self._center_y + self._max_radius
for _ in range(self._ARC_STEPS):
self.canvas.create_arc(x1, y1, x2, y2,
start=self._angle_start,
extent=self._angle_end,
width=self._line_width,
outline=color)
x1 += self._arc_distance
y1 += self._arc_distance
x2 -= self._arc_distance
y2 -= self._arc_distance
for value in range(0, 360, 45):
if self._angle_start <= value <= angle_total:
self._draw_line(angle=value, color=color)
radius = self._max_radius
if bool(show_measurement):
for _ in range(self._ARC_STEPS):
text_start_x = self._center_x + radius * cos(radians(self._angle_start))
text_start_y = self._center_y - radius * sin(radians(self._angle_start))
text_end_x = self._center_x + radius * cos(radians(angle_total))
text_end_y = self._center_y - radius * sin(radians(angle_total))
if self._angle_start == 0:
text_start_x -= 25
text_start_y += 10
if angle_total == 180:
text_end_x += 25
text_end_y += 10
if self._angle_start <= 90:
text_start_x += 25
if angle_total >= 90:
text_end_x -= 25
self._draw_text(x=text_start_x,
y=text_start_y,
text=f'{radius}{self._DISTANCE}',
color=color,
font_size=10)
self._draw_text(x=text_end_x,
y=text_end_y,
text=f'{radius}{self._DISTANCE}',
color=color,
font_size=10)
radius -= self._arc_distance
def _draw_point(self, distance: int, angle: int) -> None:
"""
Draw point on radar with given distance and angle on interface
:param distance: distance in centimeters
:param angle: angle in degrees
:return: None
"""
color = self._COLORS['point']
in_radian = radians(int(angle))
x = self._center_x + int(distance) * cos(in_radian)
y = self._center_y - int(distance) * sin(in_radian)
self.canvas.create_oval(x - 5, y - 5, x + 5, y + 5, fill=color)
def update(self, distance: int, angle: int) -> None:
"""
Update the radar with given distance and angle
:param distance: distance in centimeters
:param angle: angle in radian
:return: None
"""
current_distance = int(distance)
current_angle = int(angle)
self._SONAR_OBJECTS[angle] = current_distance
end = self._angle_start + self._angle_end
self.canvas.delete("all")
self._draw_background(show_measurement=False)
self._draw_text(x=self._center_x,
y=self._center_y + 15,
text=f'{current_angle}°',
color=self._COLORS['line_text'])
for key, value in self._SONAR_OBJECTS.items():
if 1 <= value <= self._max_radius and self._angle_start <= key <= end:
self._draw_point(distance=value, angle=key)
if self._angle_start <= current_angle <= end:
self._draw_line(angle=current_angle, color=self._COLORS['line'])
直接在项目文件夹中创建另一个文件“main.py”(例如 YOUR-PROJECT/main.py)。这里所有其他库实际上只是导入,控制伺服电机并读取超声波传感器。
代码
from time import sleep
from pinpong.board import Board
from pinpong.libs.dfrobot_urm09 import URM09
from pinpong.libs.microbit_motor import DFServo
from lib.radar import Radar
SCREEN_WIDTH: int = 240
SCREEN_HEIGHT: int = 320
ARC_LINE_WIDTH: int = 1
ARC_MAX_RADIUS: int = 150
ARC_DISTANCE: int = 50
ARC_START: int = 45
ARC_EXTENT: int = 90
SERVO_PIN: int = 8
DELAY_SECONDS: float = .25
def generate_numbers(minimum: int, maximum: int, step: int):
"""
Generates numbers between minimum and maximum by step
:param minimum: minimum value
:param maximum: maximum value
:param step: step value
"""
g_minimum = int(minimum)
g_maximum = int(maximum)
g_step = int(step)
number = g_minimum
direction = 1
while True:
yield number
number += g_step * direction
if number > g_maximum:
direction = -1
number = g_maximum
elif number < g_minimum:
direction = 1
number = g_minimum
if __name__ == '__main__':
Board("UNIHIKER").begin()
print('Init servo motor')
servo = DFServo(SERVO_PIN)
servo.angle(45)
sleep(.5)
print('Init ultrasonic sensor')
sensor = URM09()
sensor.set_mode_range(sensor._MEASURE_MODE_AUTOMATIC, sensor._MEASURE_RANG_150)
print('Init angle generator')
generator = generate_numbers(minimum=45, maximum=135, step=1)
print('Init radar UI')
display = Radar(screen_width=SCREEN_WIDTH, screen_height=SCREEN_HEIGHT)
display.configure(line_width=ARC_LINE_WIDTH,
max_radius=ARC_MAX_RADIUS,
arc_distance=ARC_DISTANCE,
start_angle=ARC_START,
end_angle=ARC_EXTENT)
while True:
servo_angle = next(generator)
servo.angle(servo_angle)
sensor_distance = sensor.distance_cm()
display.update(distance=sensor_distance, angle=servo_angle)
display.screen.update()
sleep(DELAY_SECONDS)
步骤3 上传并测试
现在将所有必要的文件夹和文件加载到行空板上。为此,必须启动行空板并通过 USB 或 WLAN 进行访问。我为此使用了“SCP”,并将所有文件从本地计算机递归复制到 UNIHIKER:“$scp -r ~/Projects/unihiker/Radar root@10.1.2.3:/root/Projects/”。重要的!该命令只是一个示例。你必须自己适应它。上传成功后,您可以测试一切。以下是终端的示例:“$ cd Projects/Radar && python3 -B main.py”。但您也可以使用行空板 UI 来启动一切!
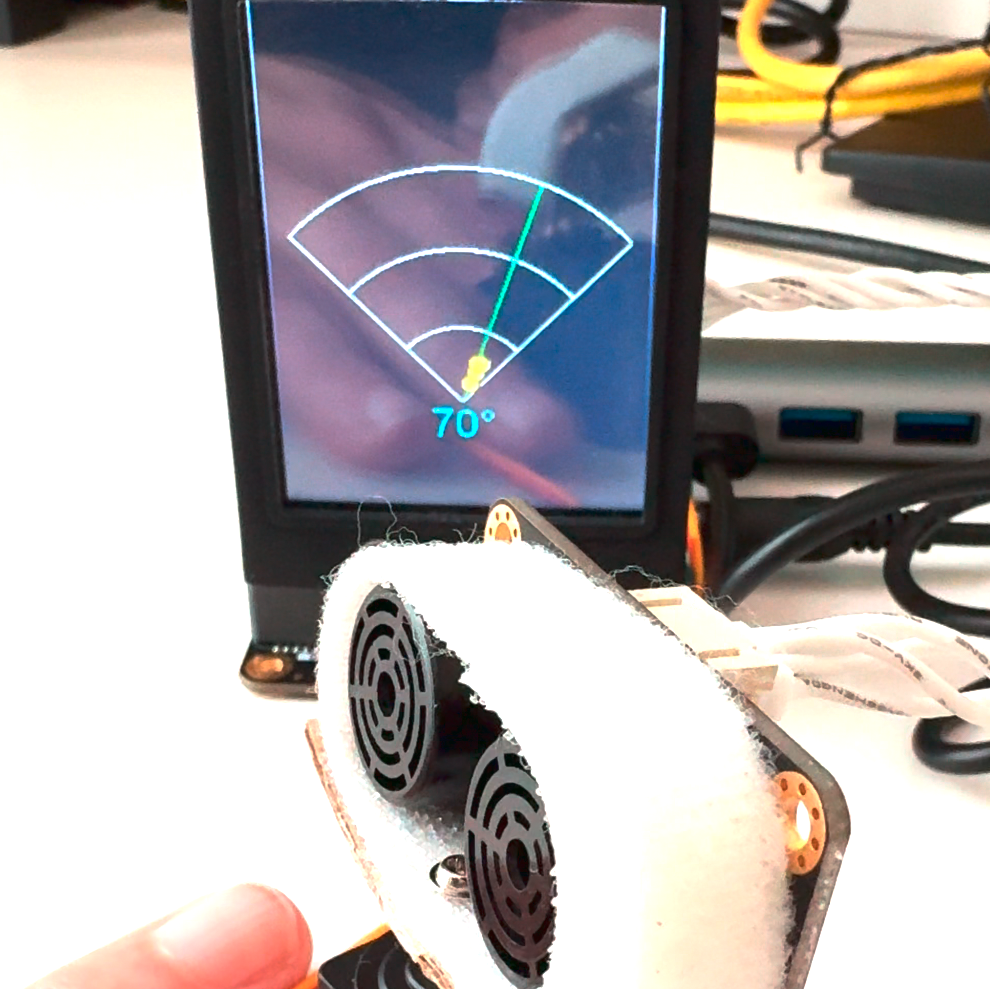
雷达试运行
注解
- 您可以调整/修改用户界面(例如颜色、弧线或线宽)!仔细查看“radar.py”和“main.py”文件。每个文件中都有一些常量可以帮助您解决此问题。另外,我尝试对所有重要的内容进行评论或为其编写文档字符串。
- 行空板上已预装相应的 pinpong 包/模块(用于伺服器和传感器)。
- 您不必使用相同的伺服电机或超声波传感器。DFRobot还提供其他设备(根据您的需求)。但要修改代码!
 沪公网安备31011502402448
沪公网安备31011502402448