所需材料
- Firebeetle2 ESP32-S3
- OV2640摄像头
- L298N模块
- TT马达 X 2
- 计算机(用于编程)
- Arduino IDE
准备工作
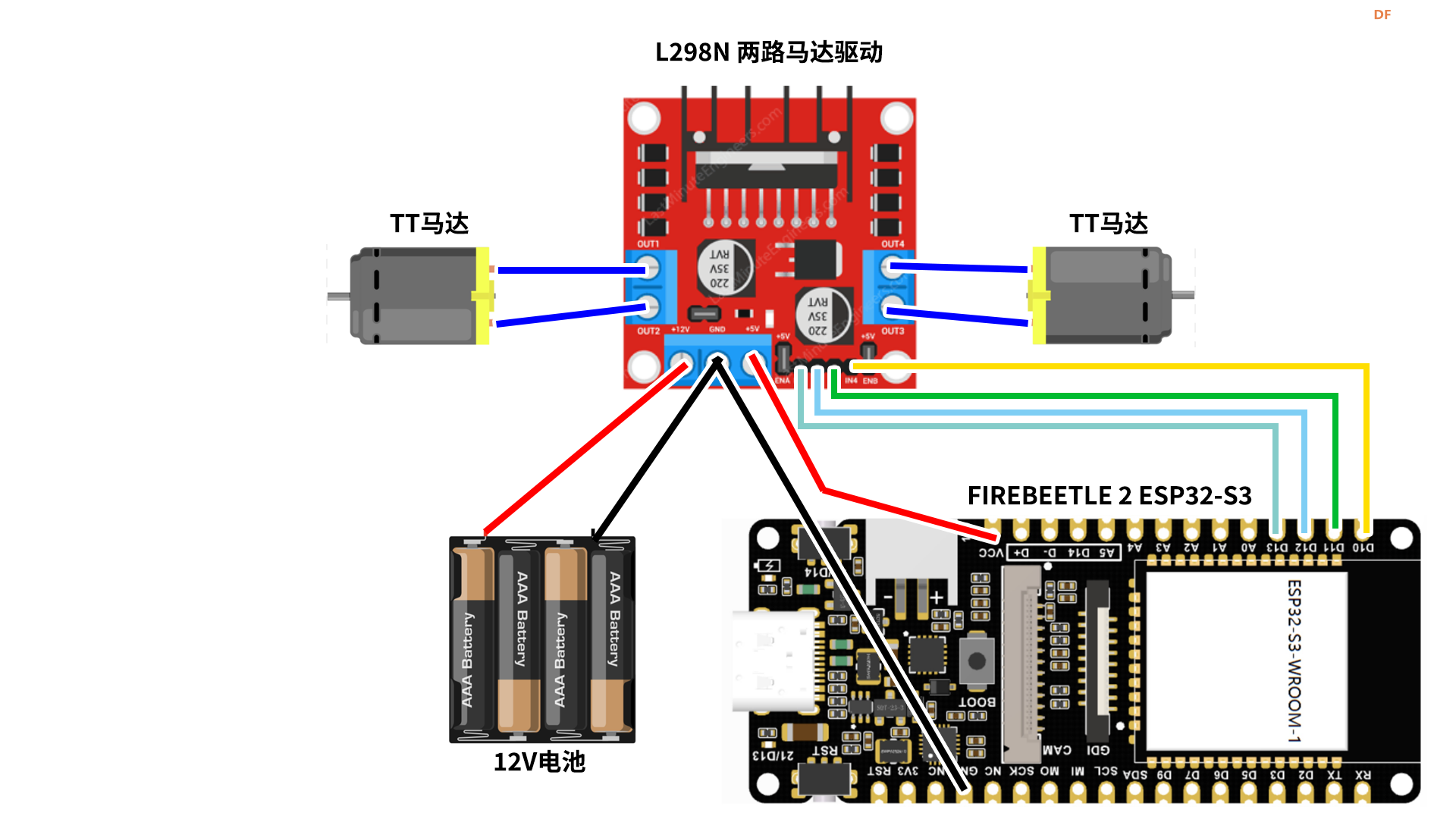
硬件连接
OV2640直接安装在Firebeetle 2 ESP32-S3 上即可
L298N OUT
马达没有正负极,需调整OUT1跟2的马达线确认转动方向)
- OUT1:左轮马达线1
- OUT2:左轮马达线2
- OUT3:右轮马达线1
- OUT4:右轮马达线2
L298 IN
- IN1:Firebeetle 2 ESP32-s3的D13
- IN2:Firebeetle 2 ESP32-s3的D12
- IN3:Firebeetle 2 ESP32-s3的D11
- IN4:Firebeetle 2 ESP32-s3的D10
L298N 电源
- GND:Firebeetle 2 ESP32-S3的GND + - 外接12V电源的负极
- +12V:外接12V电源的正极
- +5V:Firebeetle 2 ESP32-S3的VCC
完整代码
#include <WiFi.h> // 包含用于连接WiFi的库
#include <ESPAsyncWebServer.h> // 包含用于创建异步Web服务器的库
#include "esp_camera.h" // 包含ESP32摄像头库
#include "DFRobot_AXP313A.h" // 包含DFRobot_AXP313A电源管理模块库
DFRobot_AXP313A axp; // 创建DFRobot_AXP313A对象,用于管理电源
const char* ssid = "eva"; // 定义WiFi网络的名称
const char* password = "12345678"; // 定义WiFi网络的密码
const int motorDirection1 = 21; // 定义用于控制电机方向的引脚
const int motorDirection2 = 12;
const int motorDirection3 = 13;
const int motorDirection4 = 14;
// 定义摄像头引脚
const int XCLK_GPIO_NUM = 45;
const int PWDN_GPIO_NUM = -1; // 不使用该引脚
const int RESET_GPIO_NUM = -1; // 不使用该引脚
const int SIOD_GPIO_NUM = 1;
const int SIOC_GPIO_NUM = 2;
const int Y9_GPIO_NUM = 48;
const int Y8_GPIO_NUM = 46;
const int Y7_GPIO_NUM = 8;
const int Y6_GPIO_NUM = 7;
const int Y5_GPIO_NUM = 4;
const int Y4_GPIO_NUM = 41;
const int Y3_GPIO_NUM = 40;
const int Y2_GPIO_NUM = 39;
const int VSYNC_GPIO_NUM = 6;
const int HREF_GPIO_NUM = 42;
const int PCLK_GPIO_NUM = 5;
AsyncWebServer server(80); // 创建一个异步Web服务器对象,监听端口80
bool motorRunning = false; // 布尔变量,用于跟踪电机是否正在运行
void configInitCamera() {
camera_config_t config;
// 摄像头配置参数
config.ledc_channel = LEDC_CHANNEL_0; // LEDC通道0用于控制LED闪光灯
config.ledc_timer = LEDC_TIMER_0; // 使用LEDC计时器0
config.pin_d0 = Y2_GPIO_NUM; // 配置摄像头数据引脚
config.pin_d1 = Y3_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_d2 = Y4_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_d3 = Y5_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_d4 = Y6_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_d5 = Y7_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_d6 = Y8_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_d7 = Y9_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_xclk = XCLK_GPIO_NUM; // 配置时钟引脚
config.pin_pclk = PCLK_GPIO_NUM; // 配置像素时钟引脚
config.pin_vsync = VSYNC_GPIO_NUM; // 配置帧同步引脚
config.pin_href = HREF_GPIO_NUM; // 配置行同步引脚
config.pin_sscb_sda = SIOD_GPIO_NUM; // 配置SCCB数据引脚
config.pin_sscb_scl = SIOC_GPIO_NUM; // 配置SCCB时钟引脚
config.pin_pwdn = PWDN_GPIO_NUM; // 配置电源引脚
config.pin_reset = RESET_GPIO_NUM; // 配置重置引脚
config.xclk_freq_hz = 20000000; // 配置时钟频率为20 MHz
config.pixel_format = PIXFORMAT_JPEG; // 配置像素格式为JPEG
if (psramFound()) {
config.frame_size = FRAMESIZE_VGA; // 如果存在PSRAM,则使用VGA分辨率
config.jpeg_quality = 30; // JPEG图像质量
config.fb_count = 2; // 分配两个图像缓冲区
config.grab_mode = CAMERA_GRAB_LATEST; // 采集模式为最新帧
} else {
config.frame_size = FRAMESIZE_QVGA; // 如果没有PSRAM,则使用QVGA分辨率
config.jpeg_quality = 60; // JPEG图像质量
config.fb_count = 1; // 分配一个图像缓冲区
}
esp_err_t err = esp_camera_init(&config); // 初始化摄像头
if (err != ESP_OK) {
Serial.printf("Camera initialization failed, error code 0x%x", err); // 如果初始化失败,打印错误消息
delay(1000); // 等待1秒
ESP.restart(); // 重启ESP32
}
}
///定义了一个HTML模板,用于创建一个包含摄像头图像和控制按钮的Web页面///
const char* htmlTemplate = R"(
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<style>
.button-container {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
.button {
width: 250px;
height: 250px;
border-radius: 50%;
font-size: 80px;
margin: 5px;
}
.button-blank{
background-color: white;
width: 250px;
height: 250px;
border-radius: 50%;
font-size: 40px;
margin: 5px;
}
.image-container {
text-align: center;
}
#cameraImage {
width: 640px;
height: auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Camera Car Control</h1>
<div class="image-container">
<img id="cameraImage">
</div>
<div class="button-container">
<button class="button" onmousedown='startMotor("forward")' ontouchstart='startMotor("forward")' onmouseup='stopMotor()' ontouchend='stopMotor()'>↑</button>
</div>
<div class="button-container">
<button class="button" onmousedown='startMotor("left")' ontouchstart='startMotor("left")' onmouseup='stopMotor()' ontouchend='stopMotor()'>←</button>
<button class="button-blank"></button>
<button class="button" onmousedown='startMotor("right")' ontouchstart='startMotor("right")' onmouseup='stopMotor()' ontouchend='stopMotor()'>→</button>
</div>
<div class="button-container">
<button class="button" onmousedown='startMotor("backward")' ontouchstart='startMotor("backward")' onmouseup='stopMotor()' ontouchend='stopMotor()'>↓</button>
</div>
<script>
function updateCameraImage() {
var imageElement = document.getElementById("cameraImage");
imageElement.src = "/image?" + new Date().getTime();
setTimeout(updateCameraImage, 200);
}
function startMotor(direction) {
motorRunning = true;
fetch('/startMotor?direction=' + direction);
}
function stopMotor() {
motorRunning = false;
fetch('/stopMotor');
}
updateCameraImage();
</script>
</body>
</html>
)";
void handleImage(AsyncWebServerRequest* request) {
camera_fb_t* fb = esp_camera_fb_get(); // 获取摄像头图像帧缓冲
if (fb) {
AsyncWebServerResponse* response = request->beginResponse_P(200, "image/jpeg", fb->buf, fb->len); // 创建图像响应对象
request->send(response); // 发送图像响应
esp_camera_fb_return(fb); // 释放图像帧缓冲
}
}
void handleRoot(AsyncWebServerRequest* request) {
char dynamicContent[512];
snprintf(dynamicContent, sizeof(dynamicContent), R"(
<p><button onmousedown='startMotor("forward")' ontouchstart='startMotor("forward")' onmouseup='stopMotor()' ontouchend='stopMotor()'>Forward</button></p>
<p><button onmousedown='startMotor("backward")' ontouchstart='startMotor("backward")' onmouseup='stopMotor()' ontouchend='stopMotor()'>Backward</button></p>
<p><button onmousedown='startMotor("left")' ontouchstart='startMotor("left")' onmouseup='stopMotor()' ontouchend='stopMotor()'>Left</button></p>
<p><button onmousedown='startMotor("right")' ontouchstart='startMotor("right")' onmouseup='stopMotor()' ontouchend='stopMotor()'>Right</button></p>
)"); // 创建动态HTML内容,包含按钮控制小车运动
char html[8192];
snprintf(html, sizeof(html), htmlTemplate, dynamicContent); // 使用HTML模板插入动态内容
request->send(200, "text/html", html); // 发送HTML响应
}
void handleMotorRequest(AsyncWebServerRequest* request) {
String direction = request->arg("direction"); // 从请求中获取控制方向参数
if (direction == "forward") {
// 控制前进逻辑
digitalWrite(motorDirection1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(motorDirection2, LOW);
digitalWrite(motorDirection3, HIGH);
digitalWrite(motorDirection4, LOW);
} else if (direction == "backward") {
// 控制后退逻辑
digitalWrite(motorDirection1, LOW);
digitalWrite(motorDirection2, HIGH);
digitalWrite(motorDirection3, LOW);
digitalWrite(motorDirection4, HIGH);
} else if (direction == "right") {
// 控制左转逻辑
digitalWrite(motorDirection3, HIGH);
digitalWrite(motorDirection4, LOW);
digitalWrite(motorDirection1, LOW);
digitalWrite(motorDirection2, HIGH);
} else if (direction == "left") {
// 控制右转逻辑
digitalWrite(motorDirection3, LOW);
digitalWrite(motorDirection4, HIGH);
digitalWrite(motorDirection1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(motorDirection2, LOW);
}
// 可以添加其他控制逻辑,例如速度控制等
request->send(200, "text/plain", "Motor " + direction); // 发送文本响应,表示控制成功
}
void handleStopMotor(AsyncWebServerRequest* request) {
// 停止电机
digitalWrite(motorDirection1, LOW);
digitalWrite(motorDirection2, LOW);
digitalWrite(motorDirection3, LOW);
digitalWrite(motorDirection4, LOW);
request->send(200, "text/plain", "Motor Stopped"); // 发送文本响应,表示电机已停止
}
void setup() {
pinMode(motorDirection1, OUTPUT); // 设置电机方向引脚1为输出
pinMode(motorDirection2, OUTPUT); // 设置电机方向引脚2为输出
pinMode(motorDirection3, OUTPUT); // 设置电机方向引脚3为输出
pinMode(motorDirection4, OUTPUT); // 设置电机方向引脚4为输出
Serial.begin(115200); // 初始化串口通信,波特率为115200
// 循环检查电源管理模块初始化是否成功
while (axp.begin() != 0) {
Serial.println("Initialization error. Retrying..."); // 打印初始化错误消息
delay(1000); // 等待1秒
}
axp.enableCameraPower(axp.eOV2640); // 启用摄像头电源
configInitCamera(); // 初始化摄像头配置
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA); // 设置WiFi模式为站点模式(连接到现有网络)
WiFi.begin(ssid, password); // 连接到WiFi网络,使用提供的SSID和密码
WiFi.setSleep(false); // 禁用WiFi休眠模式
// 循环检查WiFi连接状态,直到连接成功
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
Serial.print("."); // 打印连接指示符
delay(500); // 等待0.5秒
}
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); // 打印本地IP地址
server.on("/", HTTP_GET, handleRoot); // 处理根路径的GET请求,调用handleRoot函数
server.on("/image", HTTP_GET, handleImage); // 处理图像路径的GET请求,调用handleImage函数
server.on("/startMotor", HTTP_GET, handleMotorRequest); // 处理启动电机的GET请求,调用handleMotorRequest函数
server.on("/stopMotor", HTTP_GET, handleStopMotor); // 处理停止电机的GET请求,调用handleStopMotor函数
server.begin(); // 启动Web服务器
}
void loop() {
// 这里可以放置与摄像头相关的代码,用于持续获取和处理摄像头图像
}
代码说明
当你看这段代码时,可以按照以下步骤来理解它:
步骤 1:导入库和声明全局变量
在这一步,首先导入所需的库,包括WiFi、异步Web服务器、ESP32摄像头以及电源管理模块。然后,创建一个DFRobot_AXP313A对象(axp),定义WiFi的名称和密码,以及电机和摄像头的引脚。
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <ESPAsyncWebServer.h>
#include "esp_camera.h"
#include "DFRobot_AXP313A.h"
DFRobot_AXP313A axp;
const char* ssid = "eva";
const char* password = "12345678";
const int motorDirection1 = 21;
const int motorDirection2 = 12;
const int motorDirection3 = 13;
const int motorDirection4 = 14;
// 定义摄像头引脚
const int XCLK_GPIO_NUM = 45;
const int PWDN_GPIO_NUM = -1;
const int RESET_GPIO_NUM = -1;
// ... (其他摄像头引脚的定义)
步骤 2:初始化摄像头配置
这一步创建了一个函数configInitCamera,用于配置摄像头的各项参数,并初始化摄像头。如果初始化失败,会打印错误消息并重启ESP32。
void configInitCamera() {
// ... (摄像头配置参数的设置)
esp_err_t err = esp_camera_init(&config);
if (err != ESP_OK) {
// 处理摄像头初始化失败的情况
Serial.printf("Camera initialization failed, error code 0x%x", err);
delay(1000);
ESP.restart();
}
}
步骤 3:定义HTML模板
在这一步,定义了一个HTML模板,用于创建包含摄像头图像和控制按钮的Web页面。CSS样式和HTML内容都包含在模板中。
const char* htmlTemplate = R"(
<html>
<head>
<!-- (CSS样式的定义省略) -->
</head>
<body>
<!-- (HTML内容的定义省略) -->
</body>
</html>
)";
步骤 4:处理Web请求
这一步定义了两个函数,handleImage用于处理获取摄像头图像的请求,而handleRoot处理根路径的请求,返回包含控制按钮的HTML页面。
void handleImage(AsyncWebServerRequest* request) {
// 处理获取摄像头图像的请求
camera_fb_t* fb = esp_camera_fb_get();
if (fb) {
AsyncWebServerResponse* response = request->beginResponse_P(200, "image/jpeg", fb->buf, fb->len);
request->send(response);
esp_camera_fb_return(fb);
}
}
void handleRoot(AsyncWebServerRequest* request) {
// 处理根路径的请求,返回包含控制按钮的HTML页面
// ... (HTML内容的生成省略)
}
步骤 5:设置电机方向引脚
在setup函数中,设置电机方向引脚为输出,并进行其他初始化操作,包括串口通信、电源管理模块的初始化、摄像头电源的启用,以及摄像头配置的初始化。
void setup() {
// ... (其他初始化代码省略)
pinMode(motorDirection1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(motorDirection2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(motorDirection3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(motorDirection4, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(115200);
while (axp.begin() != 0) {
// 循环检查电源管理模块初始化是否成功
Serial.println("Initialization error. Retrying...");
delay(1000);
}
axp.enableCameraPower(axp.eOV2640);
configInitCamera();
// ... (WiFi连接和Web服务器的初始化省略)
}
步骤 6:循环主程序
最后,在loop函数中,可以添加与摄像头相关的代码,用于持续获取和处理摄像头图像。目前这部分的代码是空的,可以根据需要添加额外的功能。
通过按照这些步骤逐一阅读代码,你可以更好地理解代码的结构和功能。

 沪公网安备31011502402448
沪公网安备31011502402448