本帖最后由 dlzxlsx 于 2025-4-11 22:42 编辑 有人说“千不怕,万不怕,就怕福建人讲土话",《明史》记载:“ 闽人入阁,自杨荣、陈山后,以语言难晓,垂二百年无人。” 确实如此。我生活闽北一个小县城,同栋楼的邻居操向不同方言;有建瓯方言、有顺昌方言(据说与将乐方言一样)、有闽南方言、有客家方言、有福州方言、有畲族方言、有古田方言、有屏南言。不同方言的人在一天聊天,对于我而言,他们的方言比英语还难懂。在农村,有相当一部分上岁数的老者不会讲普通话,根本用不了现代的语音控制的智能设备,因为当前的语音智能设备听不懂福建土话。 基于上述实际情况,该项目的目的就是尝试应用Edge impulse训练一个福建土话关键词识别的模型,实现用福建土话控制LED。 1.测试esp32S3AI模块麦克风功能 确保电脑安装了esP32开发板后,上传下面的代码,实现显示环境声音波形。 <font size="4">#include <ESP_I2S.h>
I2SClass I2S;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial) {
}
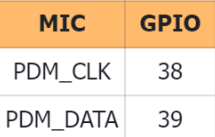
// setup 38 PDM clock and 39 PDM data pins
I2S.setPinsPdmRx(38, 39);
// start I2S at 16 kHz with 16-bits per sample
if (!I2S.begin(I2S_MODE_PDM_RX, 16000, I2S_DATA_BIT_WIDTH_16BIT, I2S_SLOT_MODE_MONO)) {
Serial.println("Failed to initialize I2S!");
while (1); // do nothing
}
}
void loop() {
// read a sample
int sample = I2S.read();
if (sample && sample != -1 && sample != 1) {
Serial.println(sample);
}
}</font> 复制代码 2.实现将录制的声音保存到 microSD 卡 <font size="4">#include "ESP_I2S.h"
#include "FS.h"
#include "SD.h"
#include "SPI.h"
void setup() {
I2SClass i2s;
uint8_t *wav_buffer;
size_t wav_size;
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial) {
delay(10);
}
Serial.println("Initializing I2S bus...");
i2s.setPinsPdmRx(38,39);
// start I2S at 16 kHz with 16-bits per sample
if (!i2s.begin(I2S_MODE_PDM_RX, 16000, I2S_DATA_BIT_WIDTH_16BIT, I2S_SLOT_MODE_MONO)) {
Serial.println("Failed to initialize I2S!");
while (1); // do nothing
}
Serial.println("I2S bus initialized.");
Serial.println("Initializing SD card...");
#ifdef REASSIGN_PINS
SPI.begin(sck, miso, mosi, cs);
if (!SD.begin(cs)) {
#else
if (!SD.begin()) {
#endif
Serial.println("Card Mount Failed");
return;
}
uint8_t cardType = SD.cardType();
if (cardType == CARD_NONE) {
Serial.println("No SD card attached");
return;
}
Serial.println("SD card initialized.");
Serial.println("Recording 20 seconds of audio data...");
// Record 20 seconds of audio data
wav_buffer = i2s.recordWAV(20, &wav_size);
// Create a file on the SD card
File file = SD.open("/Arduino r_rec.wav", FILE_WRITE);
if (!file) {
Serial.println("Failed to open file for writing!");
return;
}
Serial.println("Writing audio data to file...");
// Write the audio data to the file
if (file.write(wav_buffer, wav_size) != wav_size) {
Serial.println("Failed to write audio data to file!");
return;
}
// Close the file
file.close();
Serial.println("Application complete.");
}
void loop() {
delay(1000);
Serial.printf(".");
}</font> 复制代码 打开串口监视器,当串口输出信息”Recording 20 seconds of audio data... “时,模块开始录音,当串口显示”Writing audio data to file... “录音结束。随后出现............时,断电取下SD卡,用电脑查看音频文件arduinor_rec.wav,播放该文件,音量较小。 <font size="4">#include "ESP_I2S.h"
#include "FS.h"
#include "SD.h"
#include "SPI.h"
// make changes as needed
#define RECORD_TIME 10 // seconds, The maximum value is 240
#define WAV_FILE_NAME "data"
#define I2S_READ_CHUNK_SIZE 1920 // 添加到文件头部或全局作用域:ml-citation{ref="1,6" data="citationList"}
// do not change for best
#define SAMPLE_RATE 16000U
#define SAMPLE_BITS 16
#define WAV_HEADER_SIZE 44
#define VOLUME_GAIN 4 //取4音量较大,3应该更合适
I2SClass I2S;
String baseFileName;
int fileNumber = 1;
bool isRecording = false;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial) ;
// setup 38 PDM clock and 39 PDM data pins
I2S.setPinsPdmRx(38,39);
if (!I2S.begin(I2S_MODE_PDM_RX, 16000, I2S_DATA_BIT_WIDTH_16BIT, I2S_SLOT_MODE_MONO)) {
Serial.println("Failed to initialize I2S!");
while (1) ;
}
#ifdef REASSIGN_PINS
SPI.begin(sck, miso, mosi, cs);
if (!SD.begin(cs)) {
#else
if (!SD.begin()) {
#endif
Serial.println("Card Mount Failed");
return;
}
uint8_t cardType = SD.cardType();
if (cardType == CARD_NONE) {
Serial.println("No SD card attached");
return;
}
Serial.println("SD card initialized.");
Serial.printf("Enter with the label name\n");
//record_wav();
}
void loop() {
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
String command = Serial.readStringUntil('\n');
command.trim();
if (command == "rec") {
isRecording = true;
} else {
baseFileName = command;
fileNumber = 1; // reset file number each time a new base file name is set
Serial.printf("Send rec for starting recording label \n");
}
}
if (isRecording && baseFileName != "") {
String fileName = "/" + baseFileName + "." + String(fileNumber) + ".wav";
fileNumber++;
record_wav(fileName);
delay(1000); // delay to avoid recording multiple files at once
isRecording = false;
}
}
void record_wav(String fileName)
{
uint32_t sample_size = 0;
uint32_t record_size = (SAMPLE_RATE * SAMPLE_BITS / 8) * RECORD_TIME;
uint8_t *rec_buffer = NULL;
Serial.printf("Start recording ...\n");
File file = SD.open(fileName.c_str(), FILE_WRITE);
// Write the header to the WAV file
uint8_t wav_header[WAV_HEADER_SIZE];
generate_wav_header(wav_header, record_size, SAMPLE_RATE);
file.write(wav_header, WAV_HEADER_SIZE);
// PSRAM malloc for recording
rec_buffer = (uint8_t *)ps_malloc(record_size);
if (rec_buffer == NULL) {
Serial.printf("malloc failed!\n");
while(1) ;
}
Serial.printf("Buffer: %d bytes\n", ESP.getPsramSize() - ESP.getFreePsram());
// 开始录音
sample_size = 0;
sample_size = I2S.readBytes((char*)rec_buffer, record_size);
if (sample_size == 0) {
Serial.println("Record Failed!");
} else {
Serial.printf("Record %d bytes\n", sample_size);
}
// Increase volume
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < sample_size; i += SAMPLE_BITS/8) {
(*(uint16_t *)(rec_buffer+i)) <<= VOLUME_GAIN;
}
// Write data to the WAV file
Serial.printf("Writing to the file ...\n");
if (file.write(rec_buffer, record_size) != record_size)
Serial.printf("Write file Failed!\n");
free(rec_buffer);
file.close();
Serial.printf("Recording complete: \n");
Serial.printf("Send rec for a new sample or enter a new label\n\n");
}
void generate_wav_header(uint8_t *wav_header, uint32_t wav_size, uint32_t sample_rate)
{
// See this for reference: http://soundfile.sapp.org/doc/WaveFormat/
uint32_t file_size = wav_size + WAV_HEADER_SIZE - 8;
uint32_t byte_rate = SAMPLE_RATE * SAMPLE_BITS / 8;
const uint8_t set_wav_header[] = {
'R', 'I', 'F', 'F', // ChunkID
file_size, file_size >> 8, file_size >> 16, file_size >> 24, // ChunkSize
'W', 'A', 'V', 'E', // Format
'f', 'm', 't', ' ', // Subchunk1ID
0x10, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, // Subchunk1Size (16 for PCM)
0x01, 0x00, // AudioFormat (1 for PCM)
0x01, 0x00, // NumChannels (1 channel)
sample_rate, sample_rate >> 8, sample_rate >> 16, sample_rate >> 24, // SampleRate
byte_rate, byte_rate >> 8, byte_rate >> 16, byte_rate >> 24, // ByteRate
0x02, 0x00, // BlockAlign
0x10, 0x00, // BitsPerSample (16 bits)
'd', 'a', 't', 'a', // Subchunk2ID
wav_size, wav_size >> 8, wav_size >> 16, wav_size >> 24, // Subchunk2Size
};
memcpy(wav_header, set_wav_header, sizeof(set_wav_header));
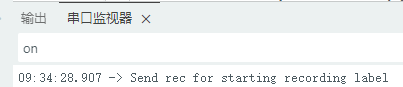
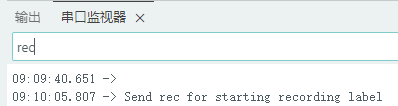
}</font> 复制代码 上传后,在串口输入“hello",该字串将是声音文件的名称前缀,根据串口信息提示,输入”rec",开始录音,如此循环。 DAY2
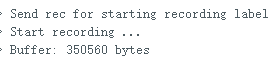
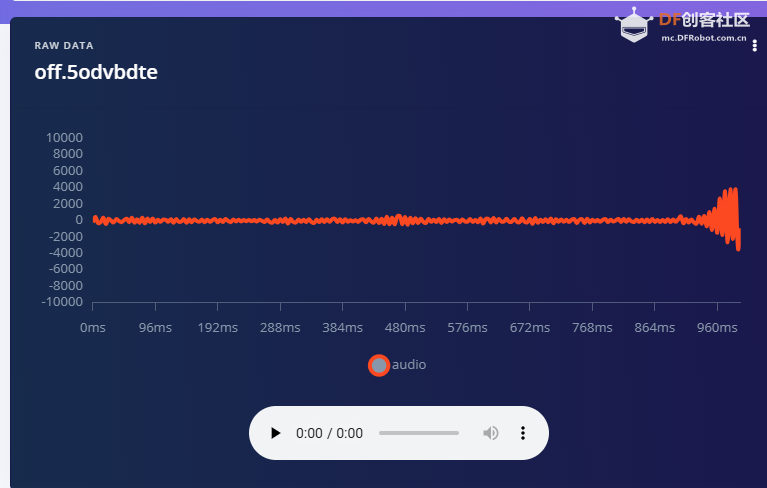
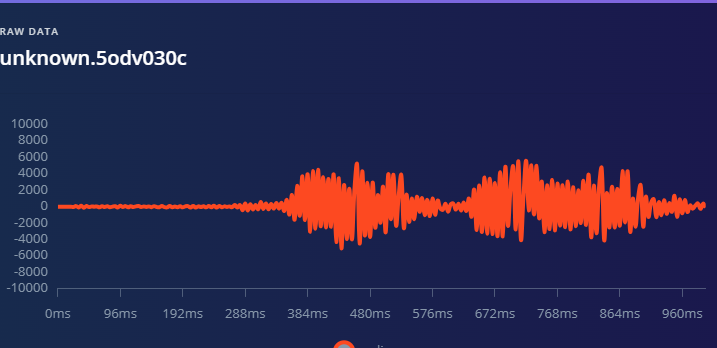
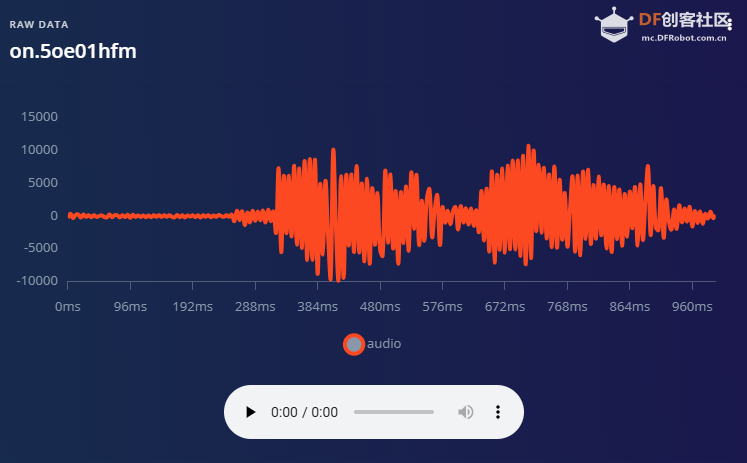
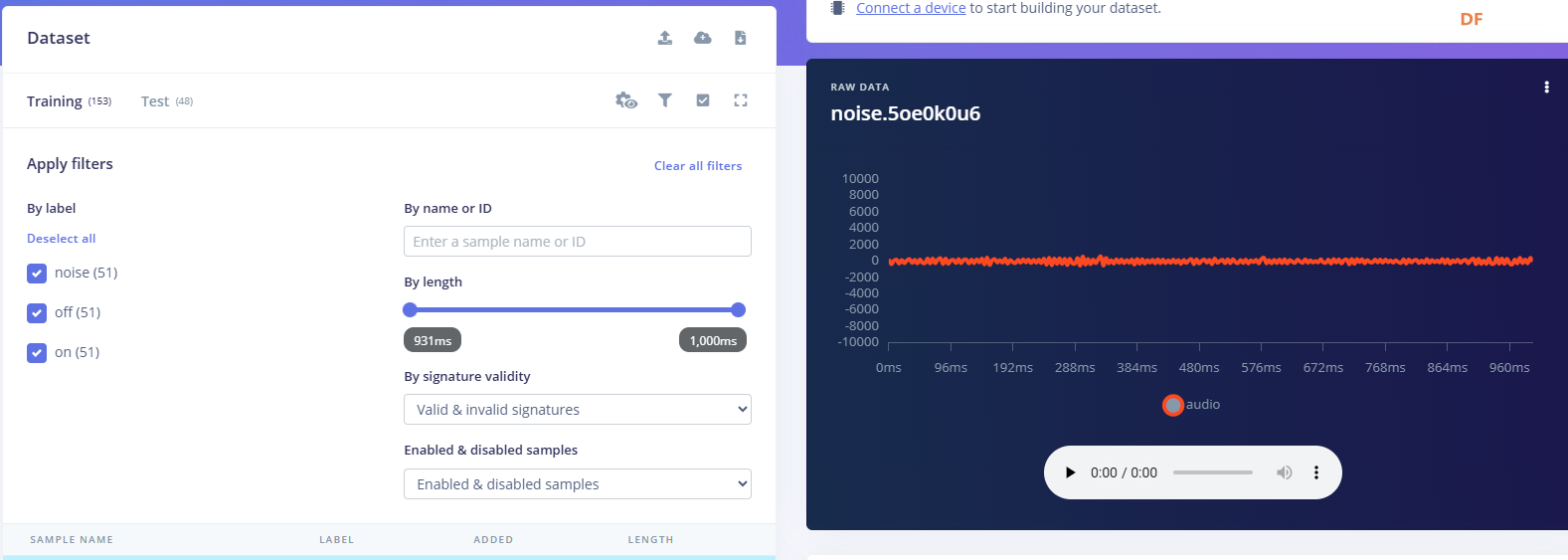
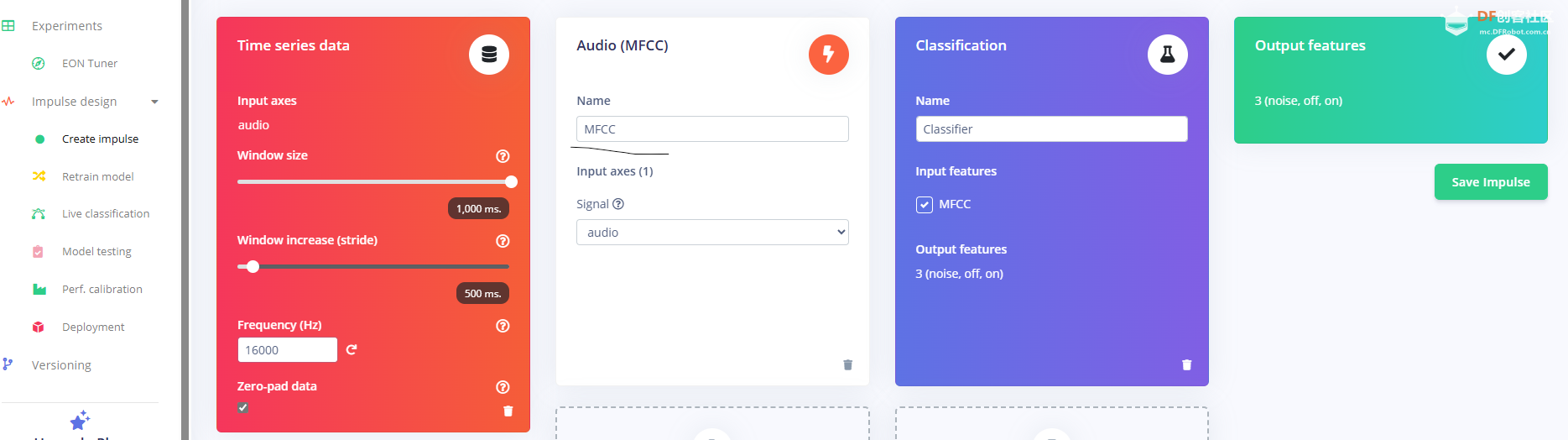
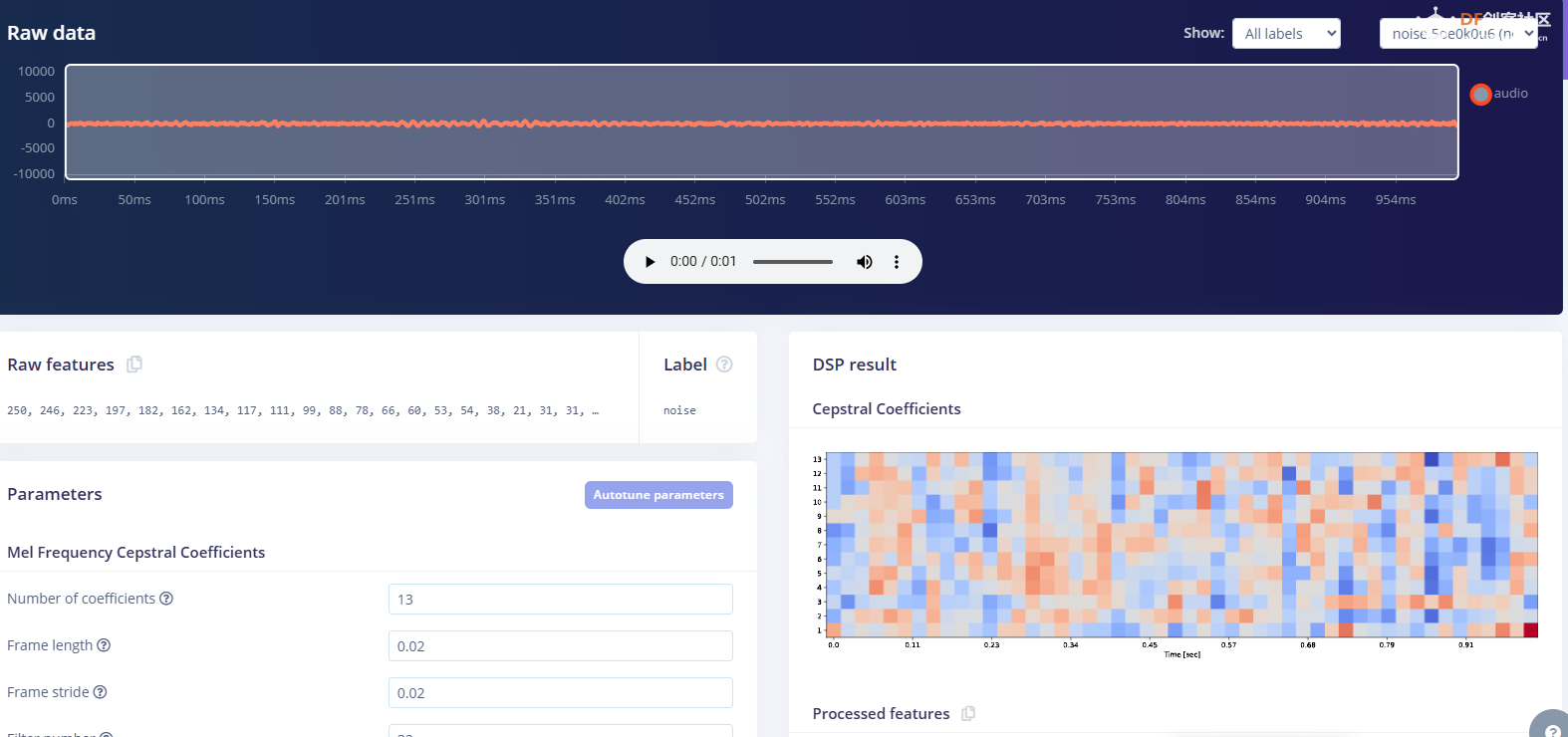
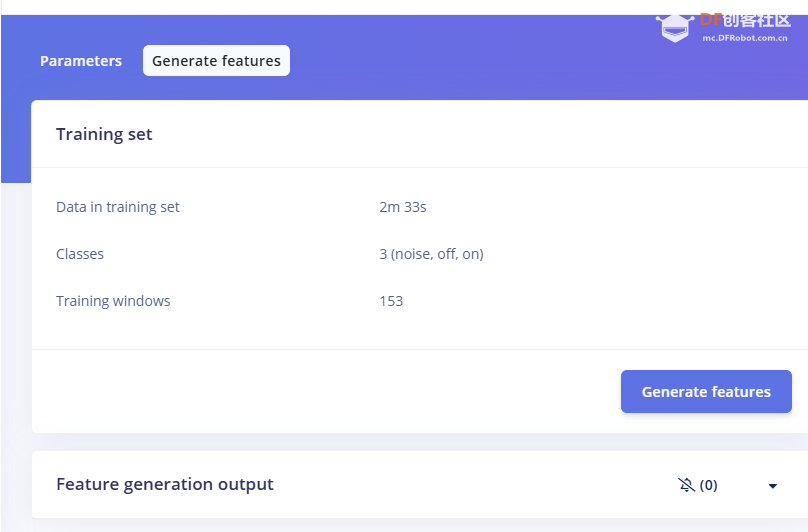
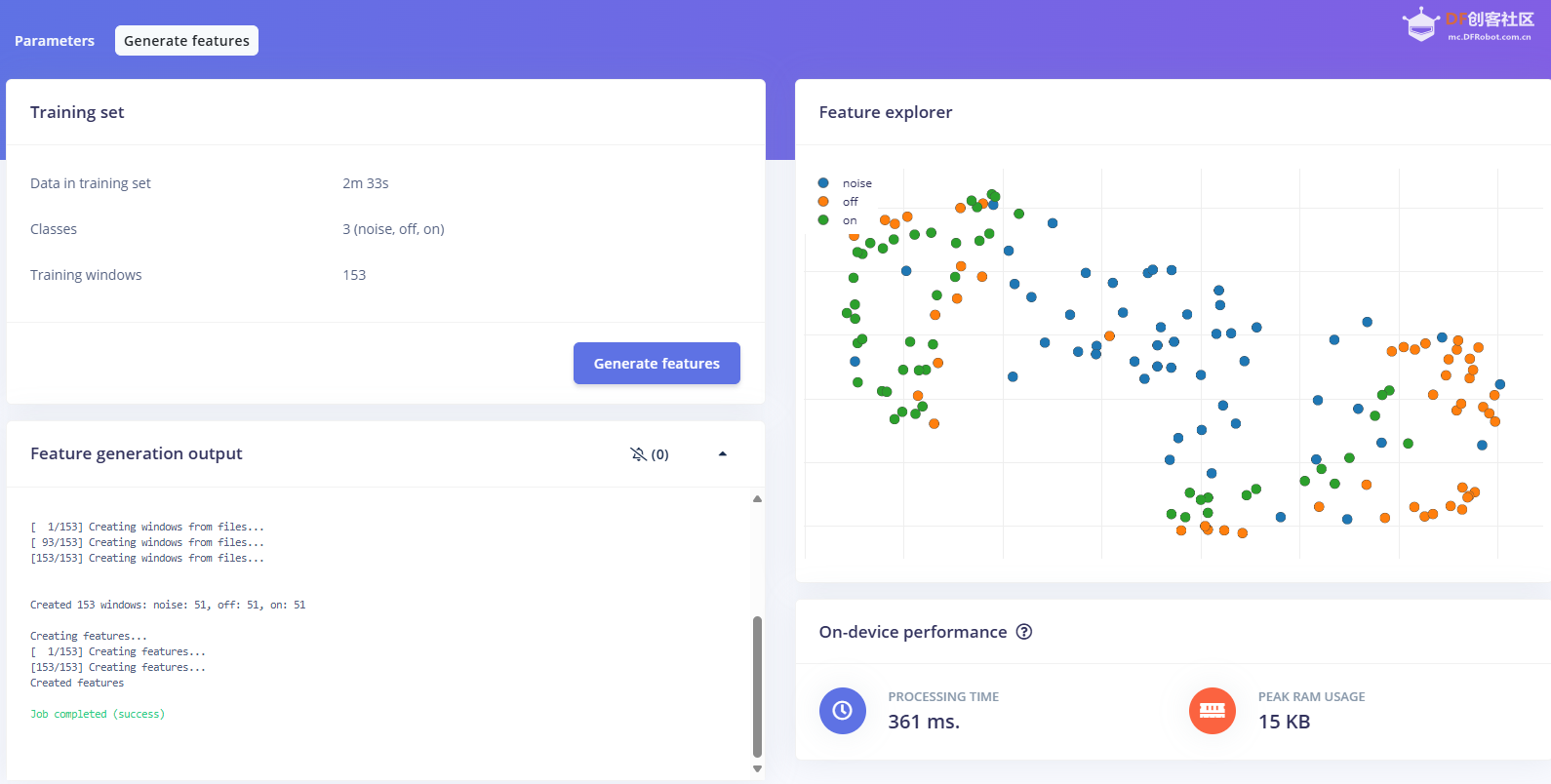
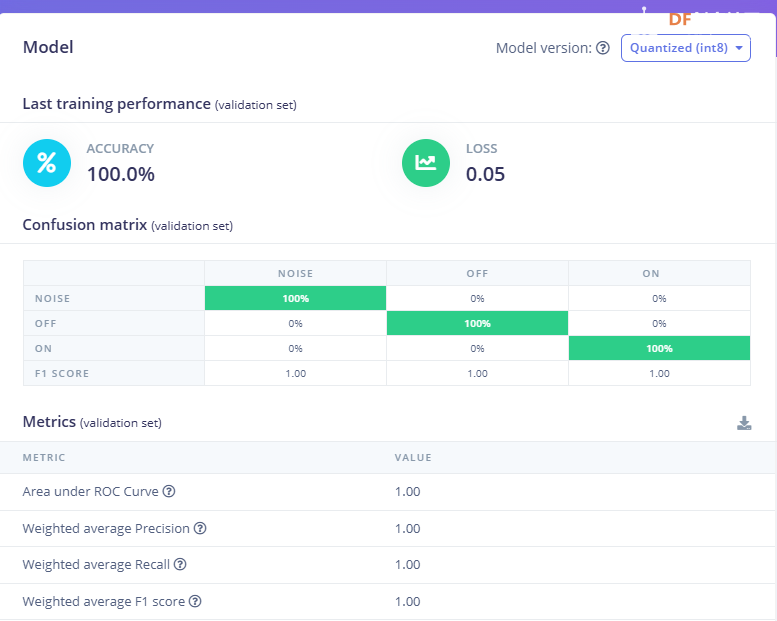
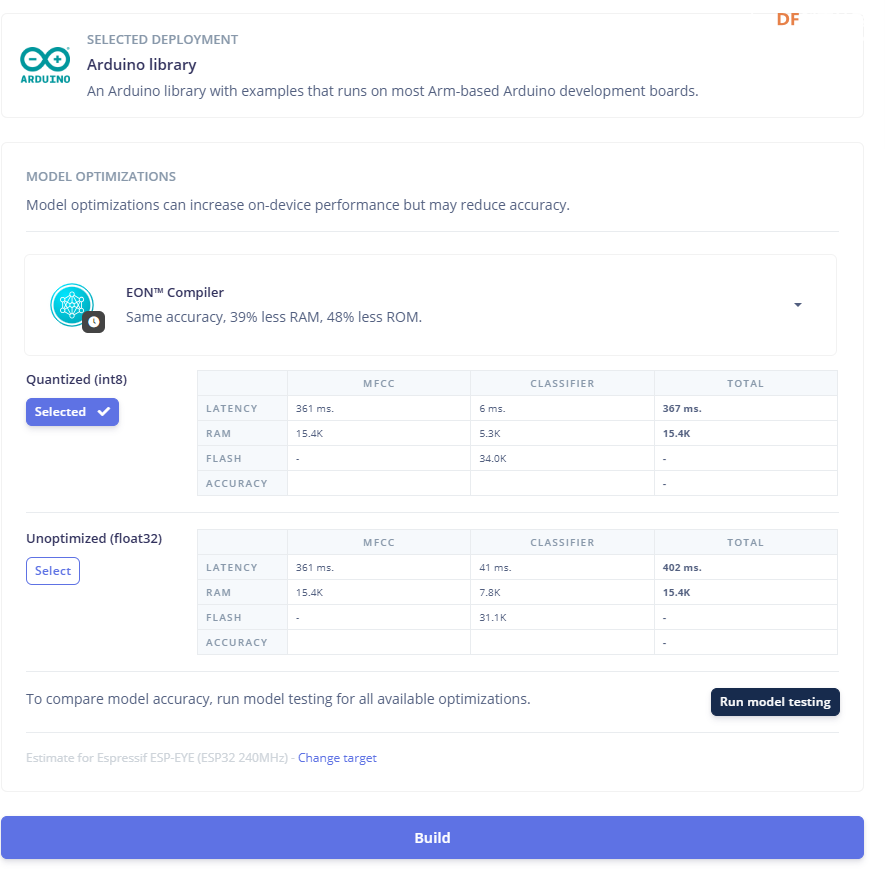
1.准备声音数据集 利用昨天最后一个程序实现声音收集。首先收集用建瓯方言(而且是乡村口音)说“开灯”关键词,方法是先格式化SD卡,插入ESP32S3AI模块SD卡槽,上电。打开Arduino IDE串口,等串口提示:“Send rec for a new sample or enter a new label”时,输入关键词的标签。由于每次录音只有10秒,我就多次采集该关键词,输入“on”,表示采集“开灯”语音录音文件。 2.用edge Impulse训练与生成模型 在edge impulse上创建一个名为“fj_dialect_detector"的工程,并把SD卡上的录音文件上传到平台数据集中。 用”split sample"把时长为10秒的文件分割成1秒的数据,方法如下图。 如果数据集数量太少,少于50个,可用平台上的收集数据功能,通过电脑或手机采集声音数据。 通过电脑麦克风采集的声音文件时,可以先标注收集数据的标签,如下图是将要采集的数据标签为off(关灯) 当三类声音的样本量都有60个时,观察每个声音数据的波形,删除一些不合格的文件,如下图 开关灯声音的正常的波形应该是下面这样的。 我的数据集分三个分类:开灯、关灯、背景音,每类51个样本。 3.准备好数据集,就可以进行设置Impulse 首先,impulse处理的音频文件为1秒窗口的数据点,每 500 毫秒滑动一次该窗口。 必须用小于 1 秒的零样本填充。另外,我们将每个 1 秒的音频样本经过预处理并转换为图像(例如,13 x 49 x 1)。因此,我使用 MFCC,它从音频信号中提取特征,这对分析人类的声音效果很好 。模型各类是 Classifier,使用卷积神经网络进行图像分类构建分类模型。 点击下面的按键后保存参数,此时左侧多出了MFCC 和 Classifier两个条目 点击”autotun parameters"(自动调节参数) 点击 “save parameters”保存参数按键 现在要设置训练模型的超参数。4.部署模型,首先要先生成Arduino 库文件 解压下载的模型文件 把 该文件安装到Arduino libraries中,打开“ esp32_microphone ”文件,并做适合的修改,修改后的文件如下: <font size="4">#include <fj_dialect_detector_inferencing.h>
#include "ESP_I2S.h"
#define SAMPLE_RATE 16000U
#define SAMPLE_BITS 16
/** Audio buffers, pointers and selectors */
typedef struct {
int16_t *buffer;
uint8_t buf_ready;
uint32_t buf_count;
uint32_t n_samples;
} inference_t;
static inference_t inference;
static const uint32_t sample_buffer_size = 2048;
static signed short sampleBuffer[sample_buffer_size];
static bool debug_nn = false; // Set this to true to see e.g. features generated from the raw signal
static bool record_status = true;
I2SClass I2S;
/**
* @brief Arduino setup function
*/
void setup()
{
// put your setup code here, to run once:
Serial.begin(115200);
// comment out the below line to cancel the wait for USB connection (needed for native USB)
while (!Serial);
Serial.println("Edge Impulse Inferencing Demo");
pinMode(3, OUTPUT); // Set the pin as output
digitalWrite(3, LOW); //Turn off
// setup 38 PDM clock and 39 PDM data pins
I2S.setPinsPdmRx(38, 39);
if (!I2S.begin(I2S_MODE_PDM_RX, 16000, I2S_DATA_BIT_WIDTH_16BIT, I2S_SLOT_MODE_MONO)) {
Serial.println("Failed to initialize I2S!");
while (1) ;
}
// summary of inferencing settings (from model_metadata.h)
ei_printf("Inferencing settings:\n");
ei_printf("\tInterval: ");
ei_printf_float((float)EI_CLASSIFIER_INTERVAL_MS);
ei_printf(" ms.\n");
ei_printf("\tFrame size: %d\n", EI_CLASSIFIER_DSP_INPUT_FRAME_SIZE);
ei_printf("\tSample length: %d ms.\n", EI_CLASSIFIER_RAW_SAMPLE_COUNT / 16);
ei_printf("\tNo. of classes: %d\n", sizeof(ei_classifier_inferencing_categories) / sizeof(ei_classifier_inferencing_categories[0]));
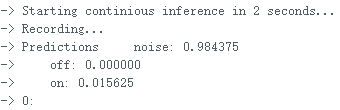
ei_printf("\nStarting continious inference in 2 seconds...\n");
ei_sleep(2000);
if (microphone_inference_start(EI_CLASSIFIER_RAW_SAMPLE_COUNT) == false) {
ei_printf("ERR: Could not allocate audio buffer (size %d), this could be due to the window length of your model\r\n", EI_CLASSIFIER_RAW_SAMPLE_COUNT);
return;
}
ei_printf("Recording...\n");
}
/**
* @brief Arduino main function. Runs the inferencing loop.
*/
void loop()
{
bool m = microphone_inference_record();
if (!m) {
ei_printf("ERR: Failed to record audio...\n");
return;
}
signal_t signal;
signal.total_length = EI_CLASSIFIER_RAW_SAMPLE_COUNT;
signal.get_data = µphone_audio_signal_get_data;
ei_impulse_result_t result = { 0 };
EI_IMPULSE_ERROR r = run_classifier(&signal, &result, debug_nn);
if (r != EI_IMPULSE_OK) {
ei_printf("ERR: Failed to run classifier (%d)\n", r);
return;
}
int pred_index = 0; // Initialize pred_index
float pred_value = 0; // Initialize pred_value
// print the predictions
ei_printf("Predictions ");
//ei_printf("(DSP: %d ms., Classification: %d ms., Anomaly: %d ms.)",
// result.timing.dsp, result.timing.classification, result.timing.anomaly);
// ei_printf(": \n");
for (size_t ix = 0; ix < EI_CLASSIFIER_LABEL_COUNT; ix++) {
ei_printf(" %s: ", result.classification[ix].label);
ei_printf_float(result.classification[ix].value);
ei_printf("\n");
if (result.classification[ix].value > pred_value){
pred_index = ix;
pred_value = result.classification[ix].value;
}
}
ei_printf("%d: ",pred_index);
ei_printf("\n");
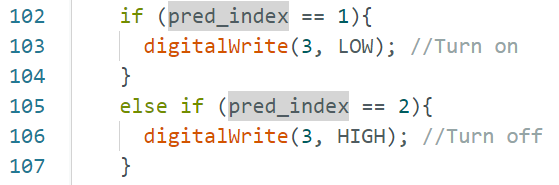
if (pred_index == 1){
digitalWrite(3, LOW); //Turn on
}
else if (pred_index == 2){
digitalWrite(3, HIGH); //Turn off
}
#if EI_CLASSIFIER_HAS_ANOMALY == 1
ei_printf(" anomaly score: ");
ei_printf_float(result.anomaly);
ei_printf("\n");
#endif
}
static void audio_inference_callback(uint32_t n_bytes)
{
for(int i = 0; i < n_bytes>>1; i++) {
inference.buffer[inference.buf_count++] = sampleBuffer[i];
if(inference.buf_count >= inference.n_samples) {
inference.buf_count = 0;
inference.buf_ready = 1;
}
}
}
static void capture_samples(void* arg) {
const int32_t i2s_bytes_to_read = (uint32_t)arg;
size_t bytes_read = i2s_bytes_to_read;
while (record_status) {
/* read data at once from i2s */
//i2s_read((i2s_port_t)1, (void*)sampleBuffer, i2s_bytes_to_read, &bytes_read, 100);
//I2S.i2s_read(esp_i2s::I2S_NUM_0, (void*)sampleBuffer, i2s_bytes_to_read, &bytes_read, 100);
//从 I2S 接口中读取 i2s_bytes_to_read 字节到 sampleBuffer 中,读取结果保存在 bytes_read 中。
bytes_read = I2S.readBytes((char*)sampleBuffer, i2s_bytes_to_read);
if (bytes_read <= 0) {
ei_printf("Error in I2S read : %d", bytes_read);
}
else {
if (bytes_read < i2s_bytes_to_read) {
ei_printf("Partial I2S read");
}
// scale the data (otherwise the sound is too quiet)
for (int x = 0; x < i2s_bytes_to_read/2; x++) {
sampleBuffer[x] = (int16_t)(sampleBuffer[x]) * 8;
}
if (record_status) {
audio_inference_callback(i2s_bytes_to_read);
}
else {
break;
}
}
}
vTaskDelete(NULL);
}
/**
* @brief Init inferencing struct and setup/start PDM
*
* @param[in] n_samples The n samples
*
* @return { description_of_the_return_value }
*/
static bool microphone_inference_start(uint32_t n_samples)
{
inference.buffer = (int16_t *)malloc(n_samples * sizeof(int16_t));
if(inference.buffer == NULL) {
return false;
}
inference.buf_count = 0;
inference.n_samples = n_samples;
inference.buf_ready = 0;
// if (i2s_init(EI_CLASSIFIER_FREQUENCY)) {
// ei_printf("Failed to start I2S!");
// }
ei_sleep(100);
record_status = true;
xTaskCreate(capture_samples, "CaptureSamples", 1024 * 32, (void*)sample_buffer_size, 10, NULL);
return true;
}
/**
* @brief Wait on new data
*
* @return True when finished
*/
static bool microphone_inference_record(void)
{
bool ret = true;
while (inference.buf_ready == 0) {
delay(10);
}
inference.buf_ready = 0;
return ret;
}
/**
* Get raw audio signal data
*/
static int microphone_audio_signal_get_data(size_t offset, size_t length, float *out_ptr)
{
numpy::int16_to_float(&inference.buffer[offset], out_ptr, length);
return 0;
}
/**
* @brief Stop PDM and release buffers
*/
static void microphone_inference_end(void)
{
free(sampleBuffer);
ei_free(inference.buffer);
}
// static int i2s_init(uint32_t sampling_rate) {
// // Start listening for audio: MONO @ 8/16KHz
// i2s_config_t i2s_config = {
// .mode = (i2s_mode_t)(I2S_MODE_MASTER | I2S_MODE_RX | I2S_MODE_TX),
// .sample_rate = sampling_rate,
// .bits_per_sample = (i2s_bits_per_sample_t)16,
// .channel_format = I2S_CHANNEL_FMT_ONLY_RIGHT,
// .communication_format = I2S_COMM_FORMAT_I2S,
// .intr_alloc_flags = 0,
// .dma_buf_count = 8,
// .dma_buf_len = 512,
// .use_apll = false,
// .tx_desc_auto_clear = false,
// .fixed_mclk = -1,
// };
// i2s_pin_config_t pin_config = {
// .bck_io_num = 26, // IIS_SCLK
// .ws_io_num = 32, // IIS_LCLK
// .data_out_num = -1, // IIS_DSIN
// .data_in_num = 33, // IIS_DOUT
// };
// esp_err_t ret = 0;
// ret = i2s_driver_install((i2s_port_t)1, &i2s_config, 0, NULL);
// if (ret != ESP_OK) {
// ei_printf("Error in i2s_driver_install");
// }
// ret = i2s_set_pin((i2s_port_t)1, &pin_config);
// if (ret != ESP_OK) {
// ei_printf("Error in i2s_set_pin");
// }
// ret = i2s_zero_dma_buffer((i2s_port_t)1);
// if (ret != ESP_OK) {
// ei_printf("Error in initializing dma buffer with 0");
// }
// return int(ret);
// }
// static int i2s_deinit(void) {
// i2s_driver_uninstall((i2s_port_t)1); //stop & destroy i2s driver
// return 0;
// }
#if !defined(EI_CLASSIFIER_SENSOR) || EI_CLASSIFIER_SENSOR != EI_CLASSIFIER_SENSOR_MICROPHONE
#error "Invalid model for current sensor."
#endif
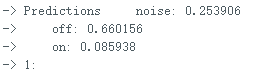
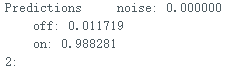
</font> 复制代码 文件上传后,打开串口,输出的信息如下: 输出该信息对应的代码部分为对该段代码的变量说明: result.classification[ix].label是标签名(noise,off,on); result.classification[ix].value是当前声音为三个标签的可能性; pred_index是最大可能标签的序号,noise--0,off--1,on--2. 全文完
感谢:Solomon Githu的文章“Environment audio monitoring wearable with XIAO ESP32S3 - Hackster.io ”对本项目的顺利完成帮助巨大 



 ,
,

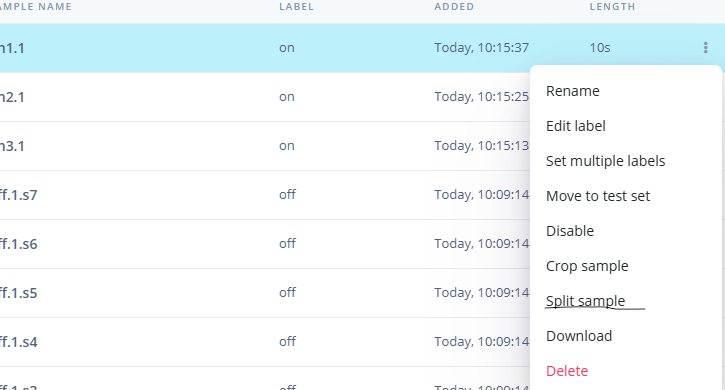 用”split sample"把时长为10秒的文件分割成1秒的数据,方法如下图。
用”split sample"把时长为10秒的文件分割成1秒的数据,方法如下图。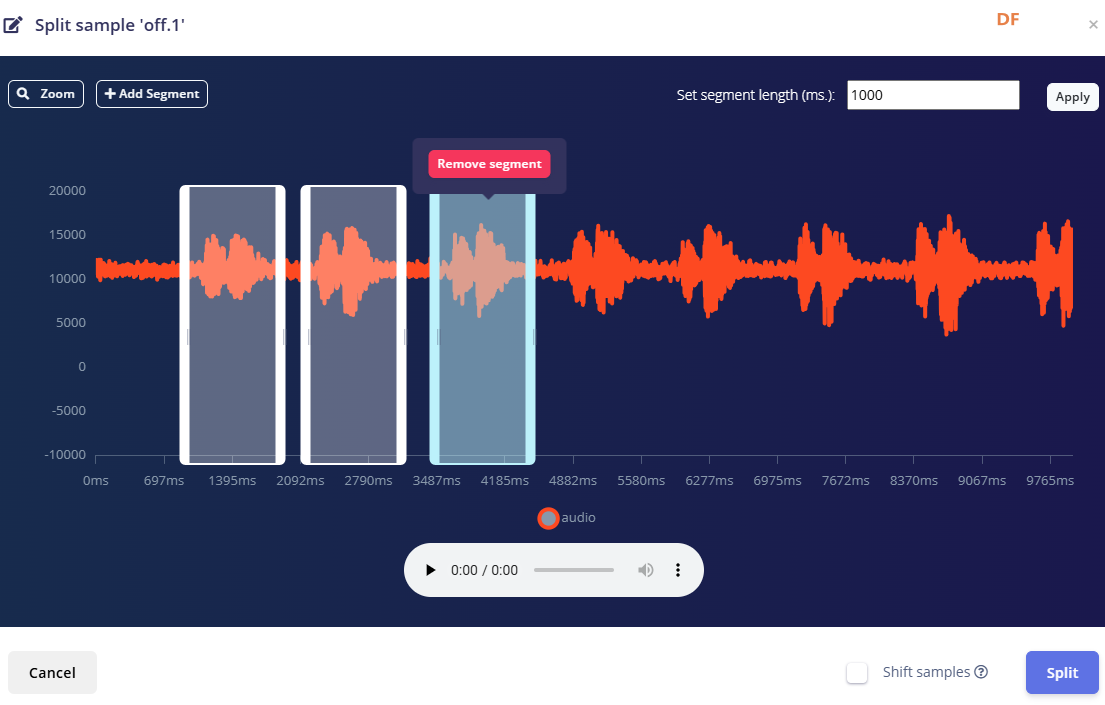








 沪公网安备31011502402448
沪公网安备31011502402448