上一次我们对Beetle ESP32 C3进行了亮灯操作,初试尝试了对该主控板进行MicroPython编程。
这次我们将在原来点灯的基础上,增加一点点难度,利用物联网控制板载LED灯的开关。
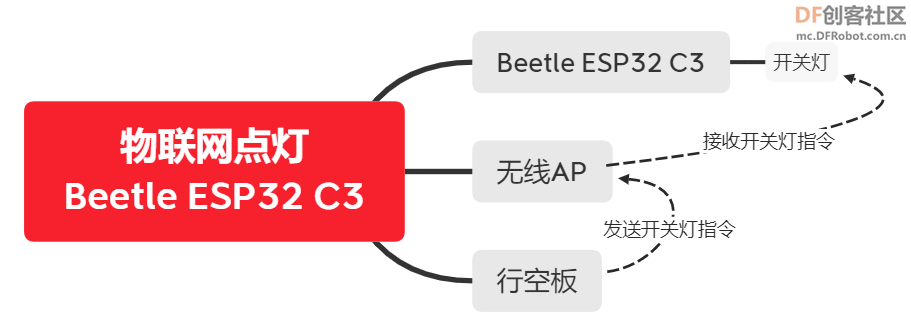
通过上图我们发现,行空板作为物联网服务器,发送开关灯指令,然后将指令通过无线网络发送给ESP32 C3,从而实现板载灯的开或关。
一、物联网服务器的选择
本例采用行空板自带的Siot服务器,因上次测试云雀气象仪,已经将行空板上的Siot版本升级成V2,当然也可以利用一台电脑作为Siot服务器。此外,由于已经使用Siot V2,因此适于用MicroPython的siot.py文件可能会出现一些差异。
行空板通过USB连接电脑,在电脑上打开浏览器,地址栏输入10.1.2.3,然后单击左侧的**应用开关**,在右侧确定将SIoT服务打开,然后单击**打开页面**按钮进入SIoT服务器管理界面。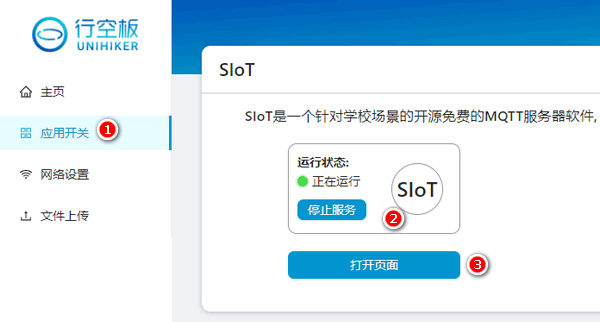
输入账号和密码,默认是siot和dfrobot,单击登录。
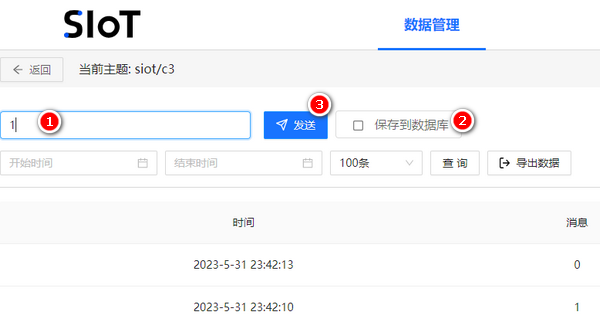
然后创建一个名为**c3**的主题,设备名称为siot,注意在编程时,需要输入"**siot/c3**"
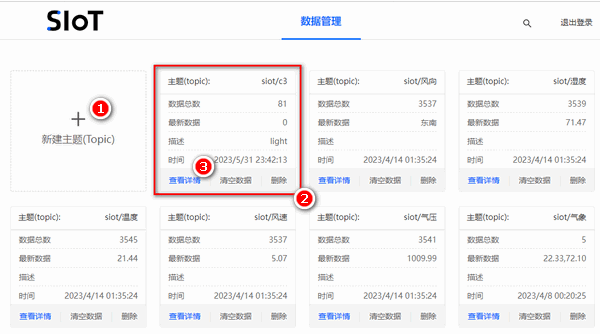
单击**查看详情**进入该主题,通过输入信息字符串,勾选**保存到数据库**,然后单击**发送**按钮将消息发送。后面我们可以通过发送1来点灯,发送0实现灭灯。
二、无线AP
由于ESP32对无线和蓝牙的支持,因此本例通过无线网络进行物联网数据交换,我们可以直接使用家庭无线网络,将行空板(所在电脑)与Beetle ESP32 C3接入同一网络,如没有网络环境,也可以打开手机热点,将行空板和ESP32 C3连上手机热点。
1. 行空板连接无线网络
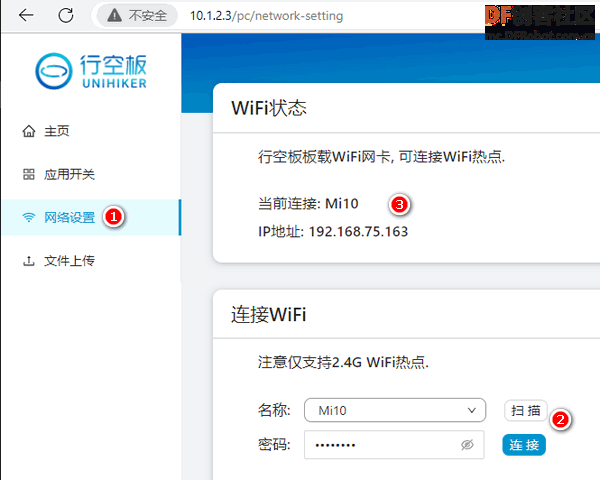
行空板通过USB连接电脑,在电脑上打开浏览器,地址栏输入10.1.2.3,然后单击左侧的**网络设置**,在右侧通过选择无线网络的名称,并输入密码进行连接,连接成功后,WiFi状态会显示相关信息,需要将IP地址记下来,供后面使用。
2. ESP32 C3连接无线网络
MicroPython中默认提供了network模块用于无线网络的通信,我们Python程序中定义一个函数用于无线网络连接。
- def WIFIconnect():
- import network
- ssid='Mi10' #无线网络名称
- password='********' #填写自己的无线网络密码
- station=network.WLAN(network.STA_IF)
- if station.isconnected() == True:
- print("WiFi already connected")
- print(station.ifconfig()) #这里显示一下ESP C3连接无线网络后的动态IP地址
- return
- station.active(True)
- station.connect(ssid,password)
- while station.isconnected() == False:
- pass
- print("Connection successful")
- print(station.ifconfig())
三、ESP32 C3上编程
使用Thonny为ESP32 C3编写程序,用于接收SIoT服务器发送过来的消息,并根据消息实现开灯和关灯。要使ESP32 C3能使用SIoT,我们需要将soit.py库文件上传到ESP32 C3上去。
在Thonny中新建文件,并将下面的代码复制到Thonny中,保存时选择**保存到MicroPython设备**。
- # file siot.py
-
- # brief download into mpython and run the demo
- # Copyright Copyright (c) 2010 DFRobot Co.Ltd (http://www.dfrobot.com)
- # licence The MIT License (MIT)
- # author [LuoYufeng](yufeng.luo@dfrobot.com)
- # version V1.0
- # date 2019-10-8
- '''
-
- import usocket as socket
- import ustruct as struct
- from machine import Timer
- #from ubinascii import hexlify
-
- class MQTTException(Exception):
- pass
-
- tim = None
- _sock = None
- _pid = 0
- _cb = None
- lw_topic = None
- lw_msg = None
- lw_qos = 0
- lw_retain = False
-
- def init(client_id, server, port=0, user=None, password=None, keepalive=0,ssl=False, ssl_params={}):
- global _client_id, _addr, _ssl, _ssl_params, _user, _pswd, _keepalive
- if port == 0:
- port = 8883 if ssl else 1883
- _client_id = client_id
- _addr = socket.getaddrinfo(server, port)[0][-1]
- _ssl = ssl
- _ssl_params = ssl_params
- _user = user
- _pswd = password
- _keepalive = keepalive
-
- def _send_str(s):
- global _sock
- _sock.write(struct.pack("!H", len(s)))
- _sock.write(s)
-
- def _recv_len():
- global _sock
- n = 0
- sh = 0
- while 1:
- b = _sock.read(1)[0]
- n |= (b & 0x7f) << sh
- if not b & 0x80:
- return n
- sh += 7
-
-
-
- def set_callback(f):
- global _cb
- _cb = f
-
- def subscribe(topic, callback):
- global _cb
- _cb = callback
- getsubscribe(topic)
-
- def loop():
- global tim
- if tim !=None:
- tim.deinit()
- tim = Timer(1)
- tim.init(period=50,mode=Timer.PERIODIC, callback=check_msg)
-
- def set_last_will(topic, msg, retain=False, qos=0):
- global lw_topic, lw_msg, lw_qos, lw_retain
- assert 0 <= qos <= 2
- assert topic
- lw_topic = topic
- lw_msg = msg
- lw_qos = qos
- lw_retain = retain
-
- def connect(clean_session=True):
- global _sock, _ssl, _user, _keepalive, lw_topic
- _sock = socket.socket()
- _sock.connect(_addr)
- if _ssl:
- import ussl
- _sock = ussl.wrap_socket(_sock, **_ssl_params)
- msg = bytearray(b"\x10\0\0\x04MQTT\x04\x02\0\0")
- msg[1] = 10 + 2 + len(_client_id)
- msg[9] = clean_session << 1
- if _user is not None:
- msg[1] += 2 + len(_user) + 2 + len(_pswd)
- msg[9] |= 0xC0
- if _keepalive:
- assert _keepalive < 65536
- msg[10] |= _keepalive >> 8
- msg[11] |= _keepalive & 0x00FF
- if lw_topic:
- msg[1] += 2 + len(lw_topic) + 2 + len(lw_msg)
- msg[9] |= 0x4 | (lw_qos & 0x1) << 3 | (lw_qos & 0x2) << 3
- msg[9] |= lw_retain << 5
- _sock.write(msg)
- #print(hex(len(msg)), hexlify(msg, ":"))
- _send_str(_client_id)
- if lw_topic:
- _send_str(lw_topic)
- _send_str(lw_msg)
- if _user is not None:
- _send_str(_user)
- _send_str(_pswd)
- resp = _sock.read(4)
- assert resp[0] == 0x20 and resp[1] == 0x02
- if resp[3] != 0:
- raise MQTTException(resp[3])
- return resp[2] & 1
-
- def stop():
- global _sock, tim
- _sock.write(b"\xe0\0")
- _sock.close()
- if tim !=None:
- tim.deinit()
-
- def ping():
- global _sock
- _sock.write(b"\xc0\0")
-
- def publish(topic, msg, retain=False, qos=0):
- global _sock, _pid
- pkt = bytearray(b"\x30\0\0\0")
- pkt[0] |= qos << 1 | retain
- sz = 2 + len(topic) + len(msg)
- if qos > 0:
- sz += 2
- assert sz < 2097152
- i = 1
- while sz > 0x7f:
- pkt[i] = (sz & 0x7f) | 0x80
- sz >>= 7
- i += 1
- pkt[i] = sz
- #print(hex(len(pkt)), hexlify(pkt, ":"))
- _sock.write(pkt, i + 1)
- _send_str(topic)
- if qos > 0:
- _pid += 1
- pid = _pid
- struct.pack_into("!H", pkt, 0, pid)
- _sock.write(pkt, 2)
- _sock.write(msg)
- if qos == 1:
- while 1:
- op = wait_msg()
- if op == 0x40:
- sz = _sock.read(1)
- assert sz == b"\x02"
- rcv_pid = _sock.read(2)
- rcv_pid = rcv_pid[0] << 8 | rcv_pid[1]
- if pid == rcv_pid:
- return
- elif qos == 2:
- assert 0
-
- def getsubscribe(topic, qos=0):
- global _sock, _pid
- assert _cb is not None, "getsubscribe callback is not set"
- pkt = bytearray(b"\x82\0\0\0")
- _pid += 1
- struct.pack_into("!BH", pkt, 1, 2 + 2 + len(topic) + 1, _pid)
- #print(hex(len(pkt)), hexlify(pkt, ":"))
- _sock.write(pkt)
- _send_str(topic)
- _sock.write(qos.to_bytes(1, "little"))
- while 1:
- op = wait_msg()
- if op == 0x90:
- resp = _sock.read(4)
- #print(resp)
- assert resp[1] == pkt[2] and resp[2] == pkt[3]
- if resp[3] == 0x80:
- raise MQTTException(resp[3])
- return
-
- # Wait for a single incoming MQTT message and process it.
- # Subscribed messages are delivered to a callback previously
- # set by .set_callback() method. Other (internal) MQTT
- # messages processed internally.
- def wait_msg():
- global _sock
- res = _sock.read(1)
- _sock.setblocking(True)
- if res is None:
- return None
- if res == b"":
- raise OSError(-1)
- if res == b"\xd0": # PINGRESP
- sz = _sock.read(1)[0]
- assert sz == 0
- return None
- op = res[0]
- if op & 0xf0 != 0x30:
- return op
- sz = _recv_len()
- topic_len = _sock.read(2)
- topic_len = (topic_len[0] << 8) | topic_len[1]
- topic = _sock.read(topic_len)
- sz -= topic_len + 2
- if op & 6:
- pid = _sock.read(2)
- pid = pid[0] << 8 | pid[1]
- sz -= 2
- msg = _sock.read(sz)
- _cb(topic, msg)
- if op & 6 == 2:
- pkt = bytearray(b"\x40\x02\0\0")
- struct.pack_into("!H", pkt, 2, pid)
- _sock.write(pkt)
- elif op & 6 == 4:
- assert 0
-
- # Checks whether a pending message from server is available.
- # If not, returns immediately with None. Otherwise, does
- # the same processing as wait_msg.
- def check_msg(msg = ""):
- global _sock
- _sock.setblocking(False)
- return wait_msg()
下面是ESP32 C3上保存的main.py程序代码:
- import time
- from machine import Pin
- import siot #导入同目录下的siot.py
-
- led=Pin(10,Pin.OUT)
-
- SERVER="192.168.75.163" #行空板的IP地址
- CLIENT_ID=""
- IOT_pubTopic='siot/c3'
- IOT_UserName='siot'
- IOT_PassWord='dfrobot'
-
- siot.init(CLIENT_ID,SERVER,user=IOT_UserName,password=IOT_PassWord)
-
- def WIFIconnect(): #无线链接
- import network
- ssid='Mi10' #无线名称
- password='********' #修改为无线密码
- station=network.WLAN(network.STA_IF)
- if station.isconnected() == True:
- print("WiFi already connected")
- print(station.ifconfig())
- return
- station.active(True)
- station.connect(ssid,password)
- while station.isconnected() == False:
- pass
- print("Connection successful")
- print(station.ifconfig())
-
- def sub_cp(topic,msg): # 回调函数
- s=msg.decode() #对接收到的信息解码
- print(s)
- if s=='1': #接收的消息1就亮灯
- led.value(1)
- else:
- led.value(0)
-
- WIFIconnect()
- siot.connect()
- siot.set_callback(sub_cp)
- siot.subscribe(IOT_pubTopic,sub_cp)
-
- while True:
- time.sleep(1)
- siot.check_msg()
此时,我们可能通过向行空板上的SIoT发送1或0,实现ESP32 C3板载灯的亮或灭。我们也可以进一步在行空板上编写一个控制程序,如设置2个按钮,一个按钮是亮灯,另一个是关灯,实现消息的发送。[/md]
|







 编辑选择奖
编辑选择奖
 沪公网安备31011502402448
沪公网安备31011502402448