本帖最后由 RRoy 于 2024-10-10 08:47 编辑
这个项目介绍了如何制作和控制一只仿生手。作者最初受到Instagram上一个视频的启发,该视频展示了使用MPU6050传感器追踪手部动作并在屏幕上显示3D模型。作者决定将这个想法进一步发展,使用OpenCV来控制一只真实的仿生手。
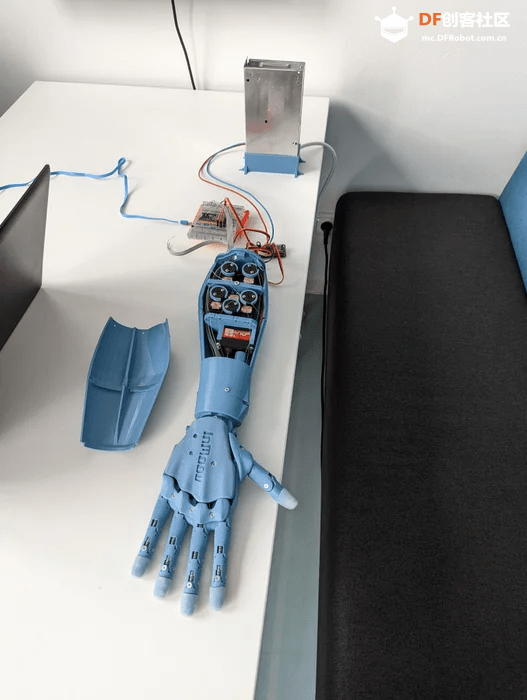
大家好,在这篇教程中,我想和大家分享一下如何制作并控制一只自己的仿生手。这个想法源于我在无意中刷Instagram时,看到一段短视频:一个人通过MPU6050传感器来跟踪手部运动,并在屏幕上显示手的3D模型。因为我之前也使用过这个传感器,所以觉得这个我也能完成。我一直喜欢将编程与现实世界结合起来,于是我想,为什么不将这些测量数据传输到一个真实的仿生手上呢?后来我决定,使用OpenCV代替MPU6050会更加高效,部分原因也是我想借此机会学习另一种技能。
特别感谢Gaël Langevin,他在InMoov项目[1]中设计了这个手的模型,并慷慨地分享了出来。
效果展示
所需材料InMoov手及前臂- 3D打印机
- 焊接工具
- 约1公斤的耗材(PETG 或 ABS 或 PLA)
- 3米钓鱼线(能承重约20公斤)
- 5根扩展弹簧(3/16″ x 1-3/4)
- RTV硅胶 Ecoflex™ 00-10
螺丝、螺母和螺栓- 10个M2x4平头木螺丝
- 10个M3x4mm平头螺丝
- 4个M3x12mm平头木螺丝
- 20个M3x12mm平头螺丝
- 25个M3x16mm平头螺丝
- 10个M3x20mm平头螺丝
- 35个M3螺母
电子元件- 1块ESP32 38-pin 开发模块
- 1根micro USB数据线
- 5个线性霍尔传感器(49E)
- 5个直径2.5mm x 1mm的磁盘磁铁
- 1根16芯彩排线
- 5个1k电阻
- 5个2k电阻
- 6个伺服电机(JX PDI-6225MG-300)
- 1块定制PCB(可选)
- 1个电源(理想情况下为6V或5V,功率约100W,因为每个伺服电机的电流可达3A)
步骤1:3D打印手部
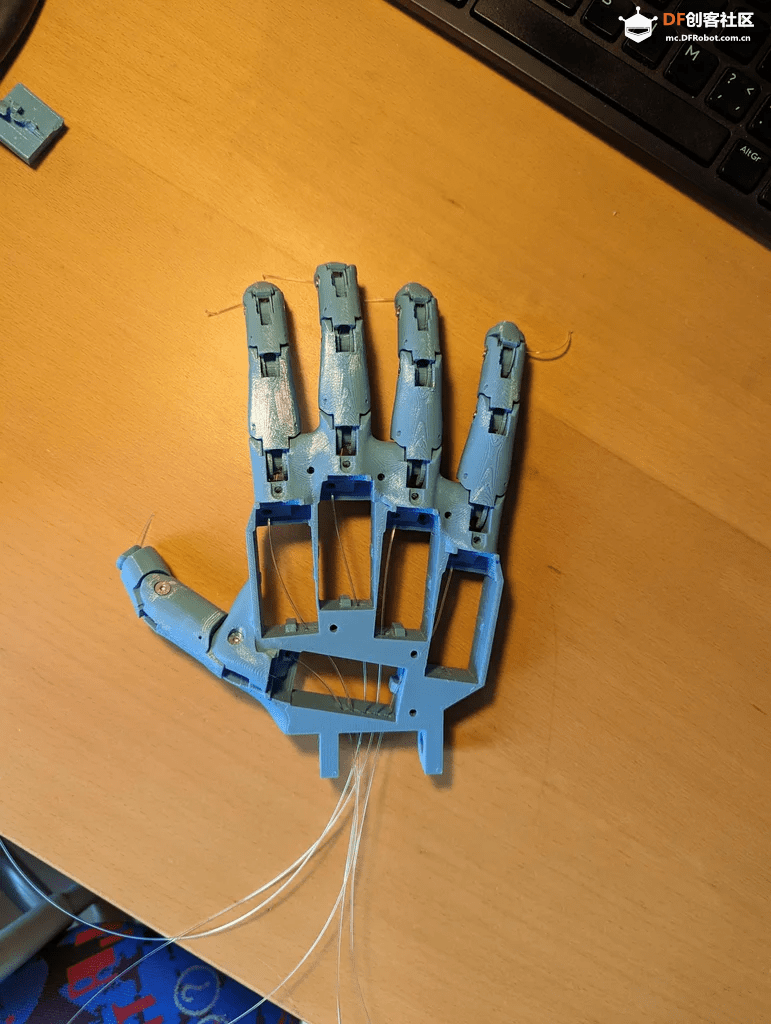

3D打印文件见文末。
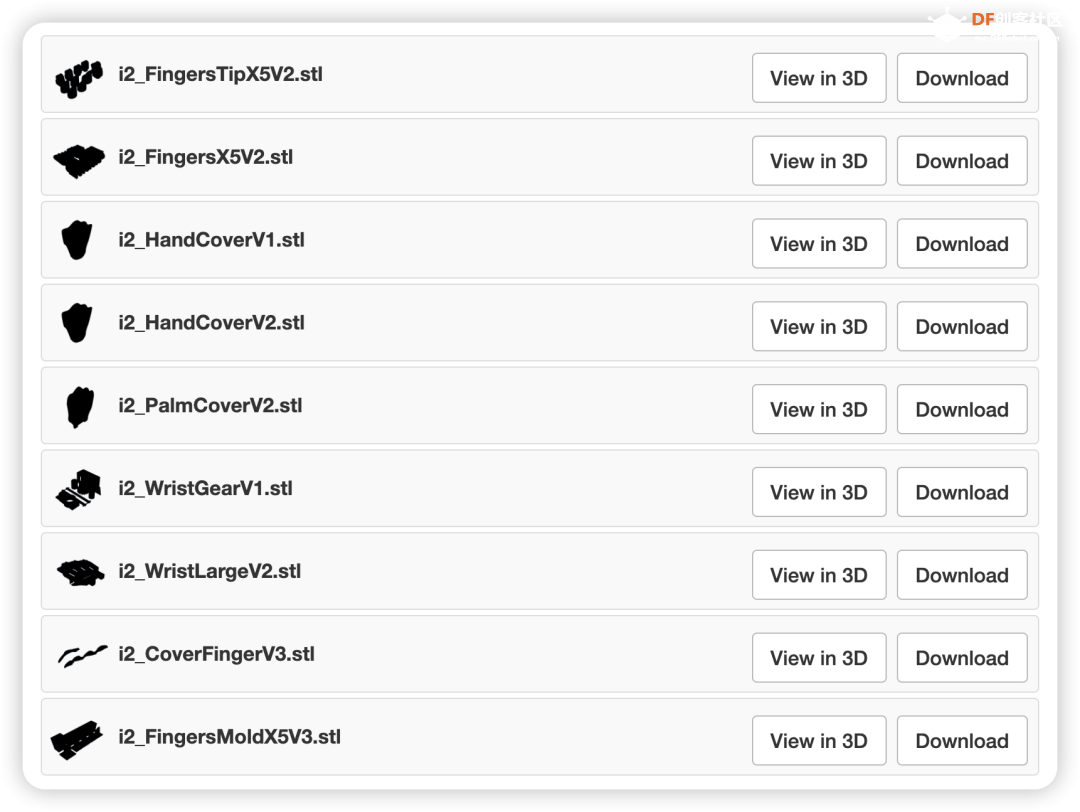
打印时,建议使用稍高的填充率(约30%),以提高部件的耐用性。关于材料,InMoov使用的是ABS,不过如果你没有稳定打印ABS的设备,PETG或PLA同样可以使用。
步骤2:3D打印前臂
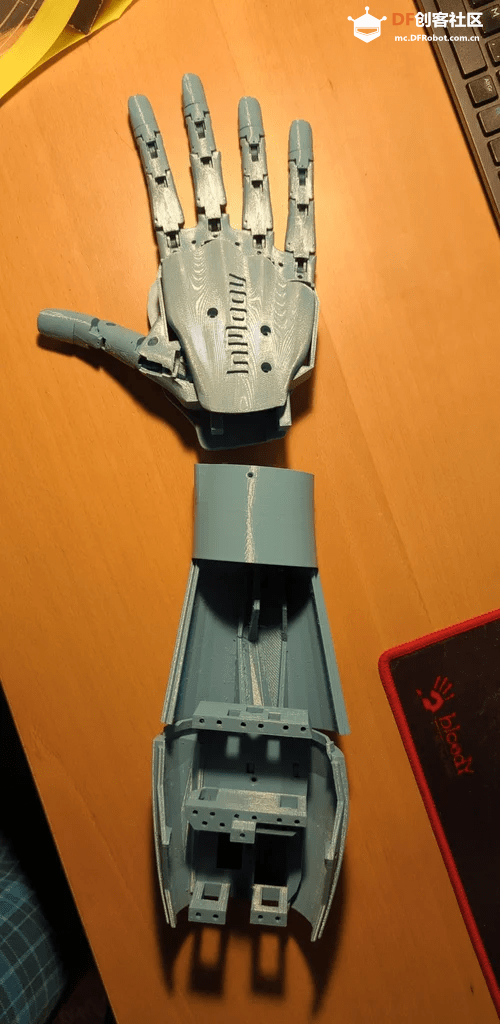

同样地,手部所需的文件如下,并且也在inmoov STL零件库[2]中。请注意,在inmoov零件库中有原版inmoov机器人的文件。这个手是i2版本,因此你只需要前臂部分的一些零件。另外一个需要注意的是,当打印Bolt_entretoise7时,你只需要中间的螺栓和夹子(其他部分是为旧版手设计的)。
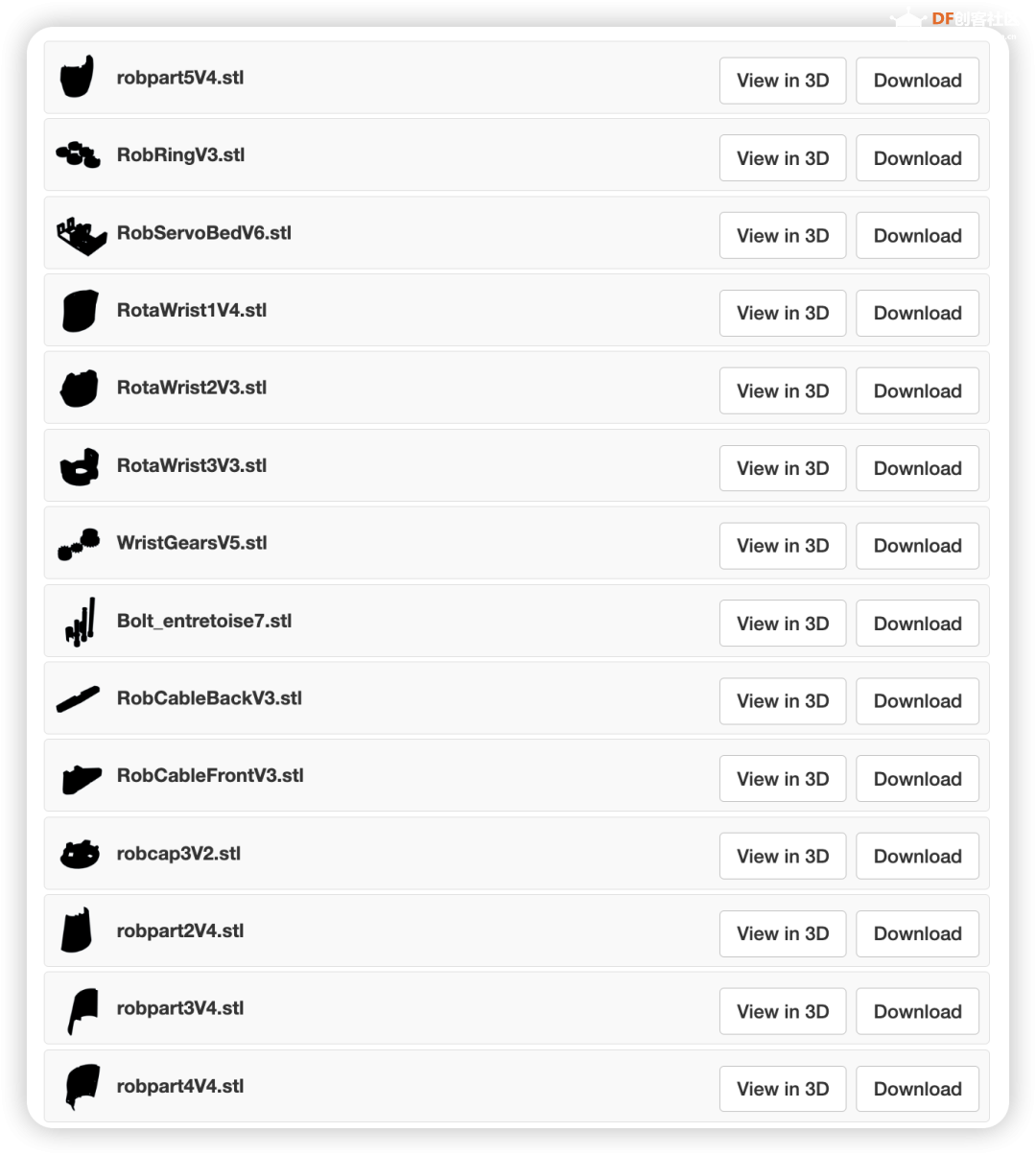
3D打印文件文末下载。
你还可以打印一个我自己在Fusion 360中设计的小展示支架。
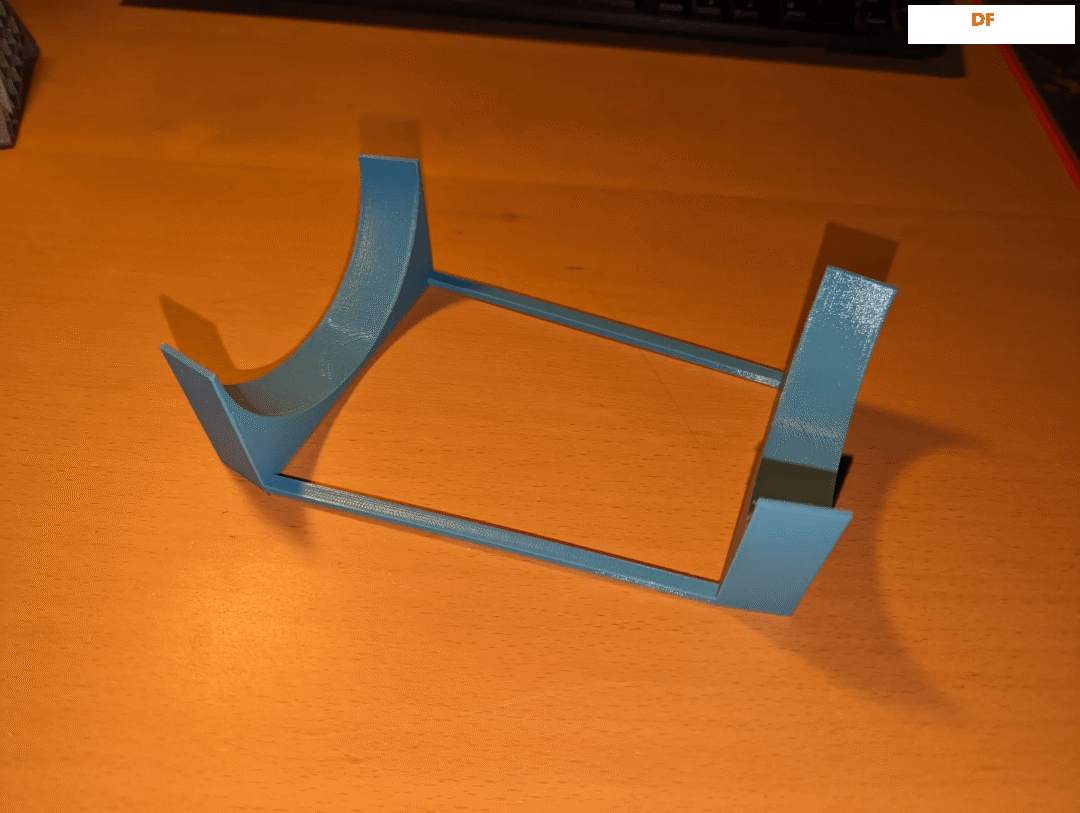
链接:https://www.printables.com/model/593999-inmoov-hand-stand?lang=cs
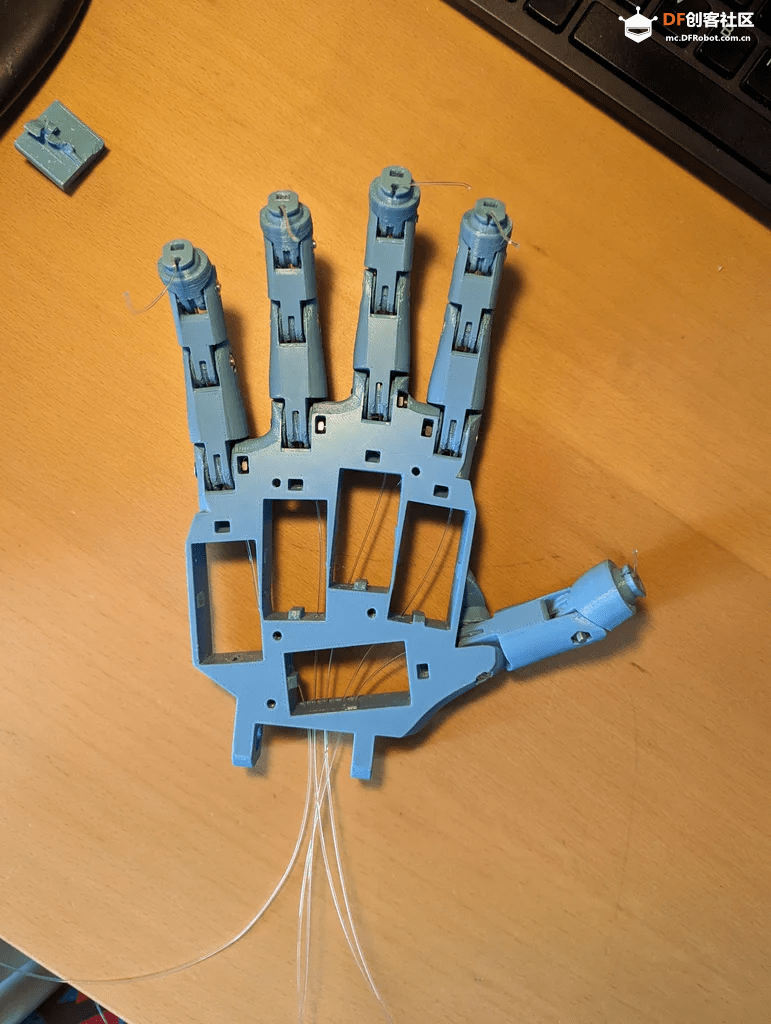
步骤3:组装
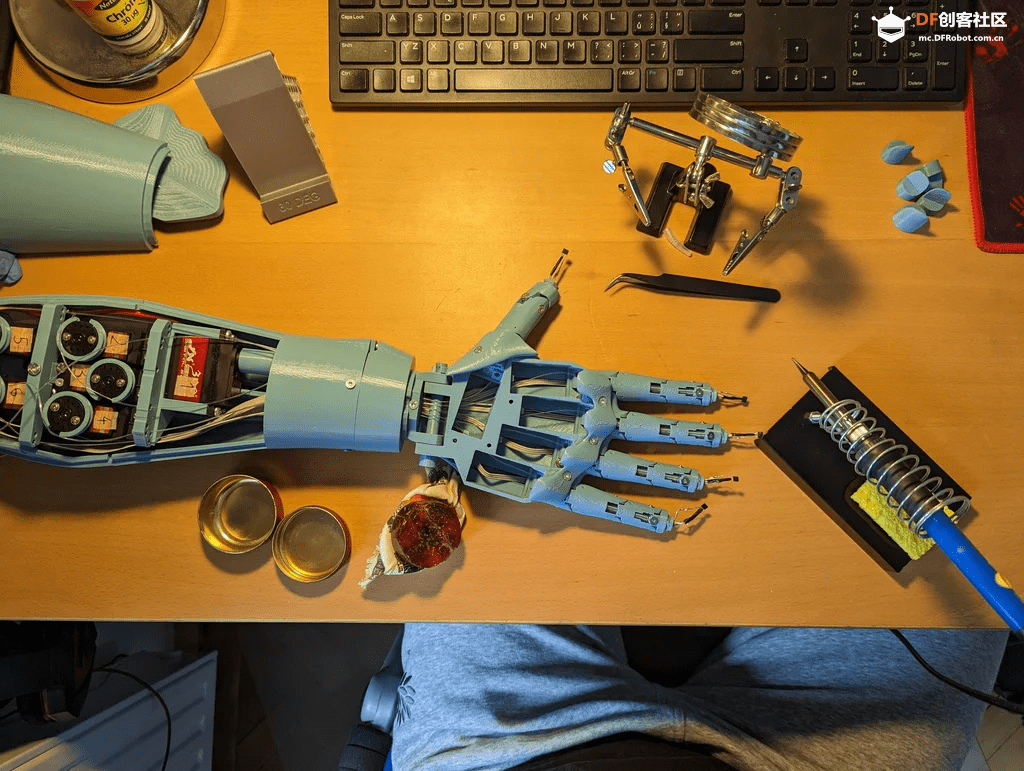

在组装时,可以参考InMoov提供的hand i2[3]与前臂[4]的教程,这些教程非常详细,提供了所有必要的信息。
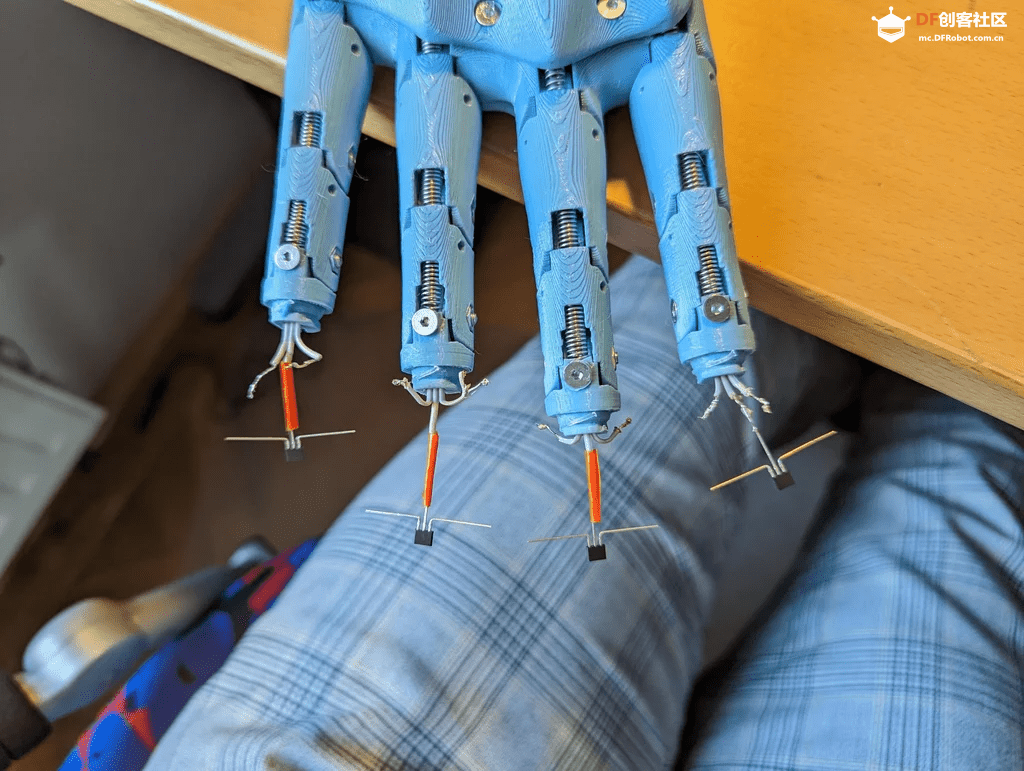


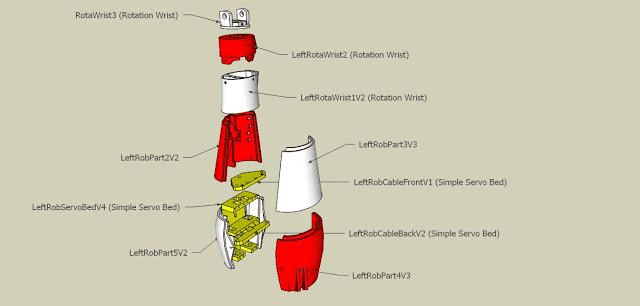
初始部件的组装相对简单,只需用螺丝将整个设计固定在一起。稍微复杂的部分是确保钓鱼线的布置不打结,以及将霍尔传感器正确安装在指尖。
步骤4:硅胶指尖
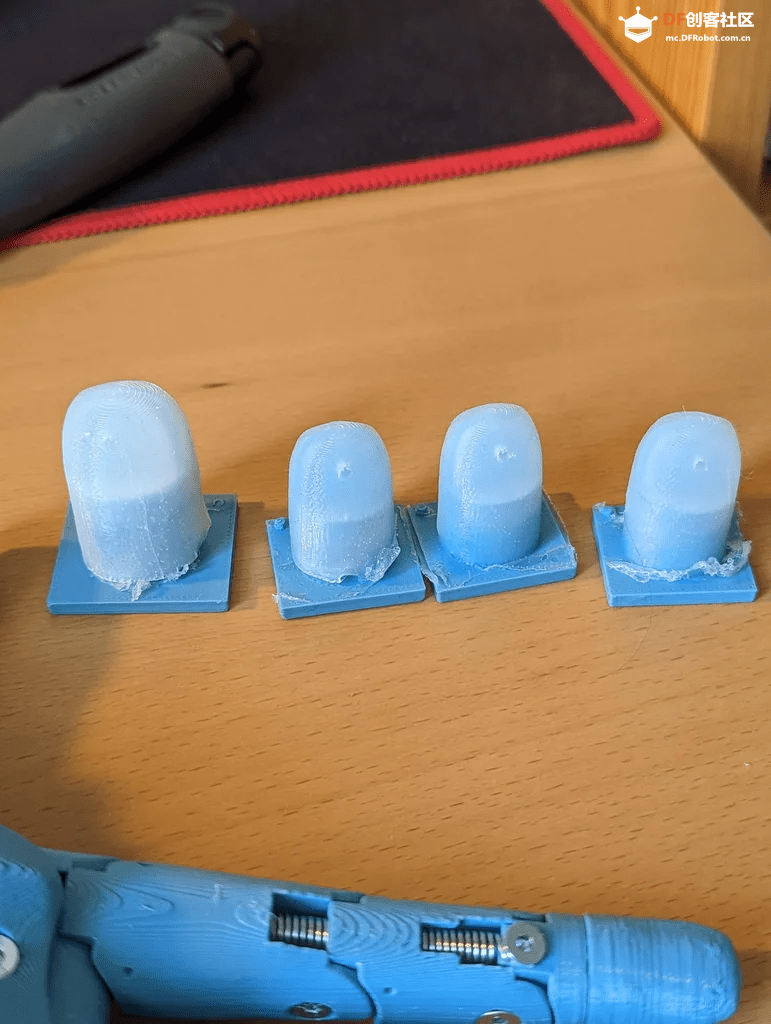
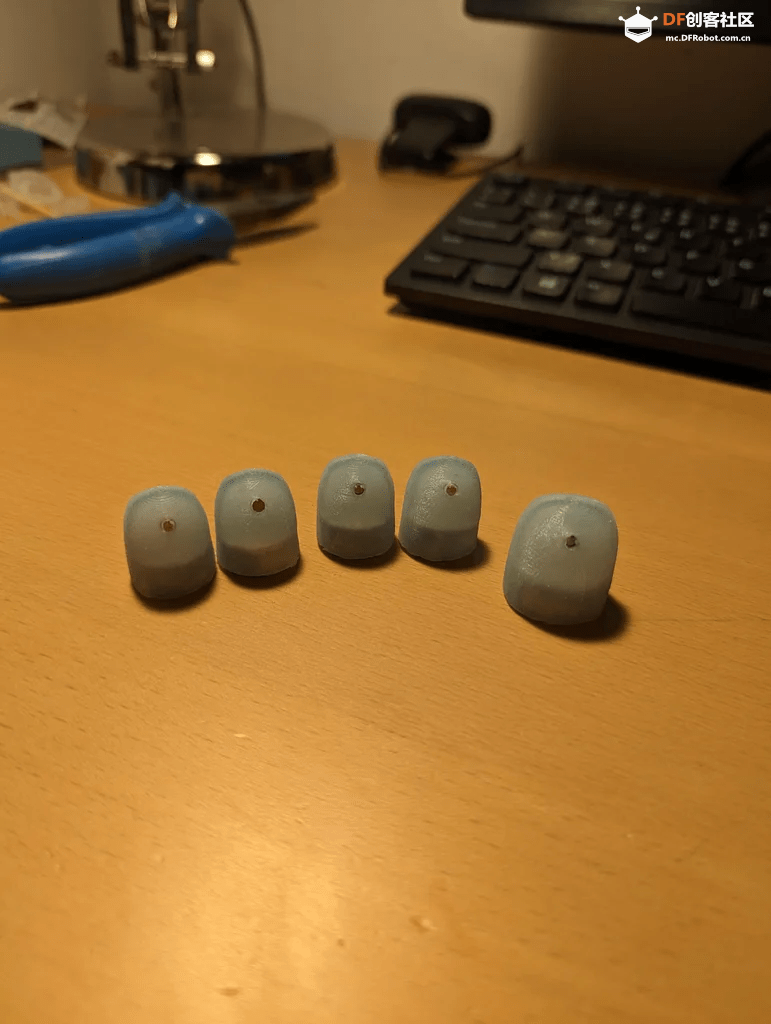
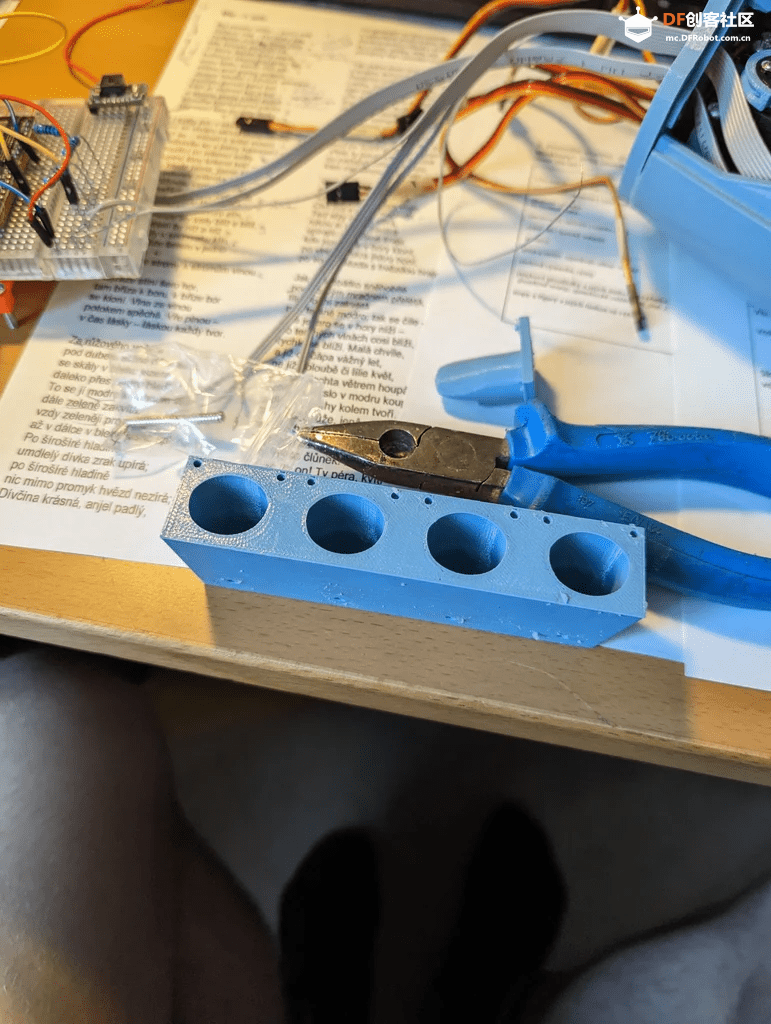


对于指尖来说,使用非常柔软的硅胶是很重要的,因为霍尔传感器的读取有一定的不确定性。硅胶越软,内部的磁铁运动幅度越大,从而更容易从数据中识别。将硅胶部分粘到3D打印出的部件上之后,可以用它来调整霍尔传感器的突出程度。
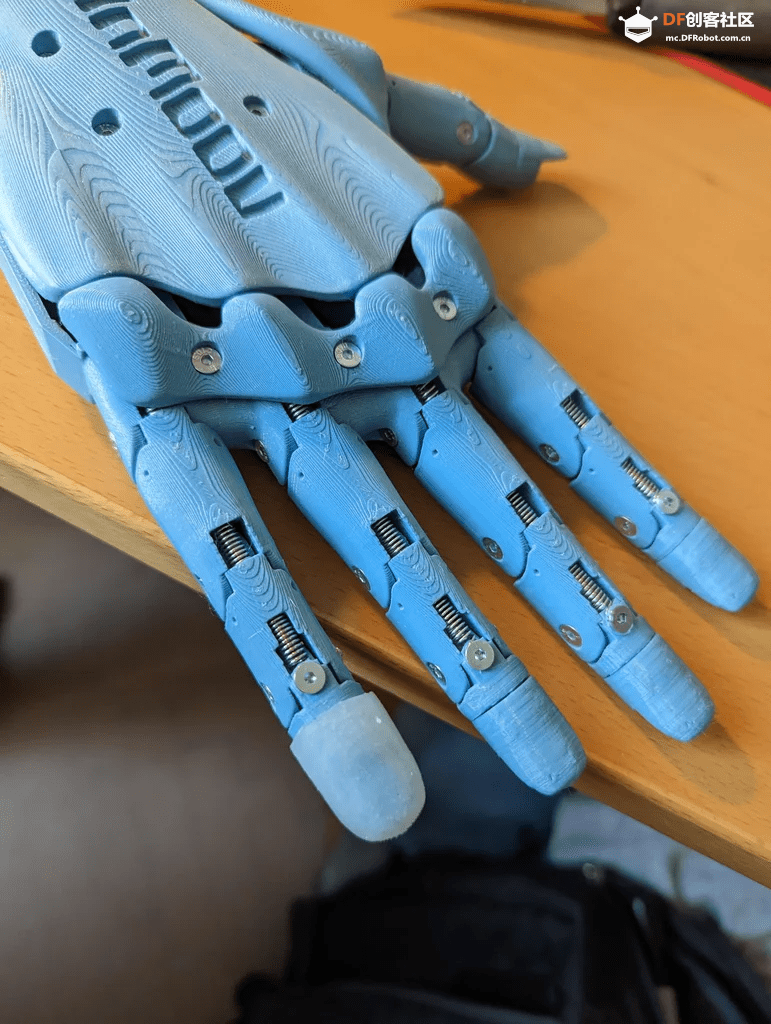

在这一切设置好之后,强烈建议将霍尔传感器固定在手指的末端,否则在手指运动过程中,霍尔传感器可能会稍微移动,从而影响测量结果。
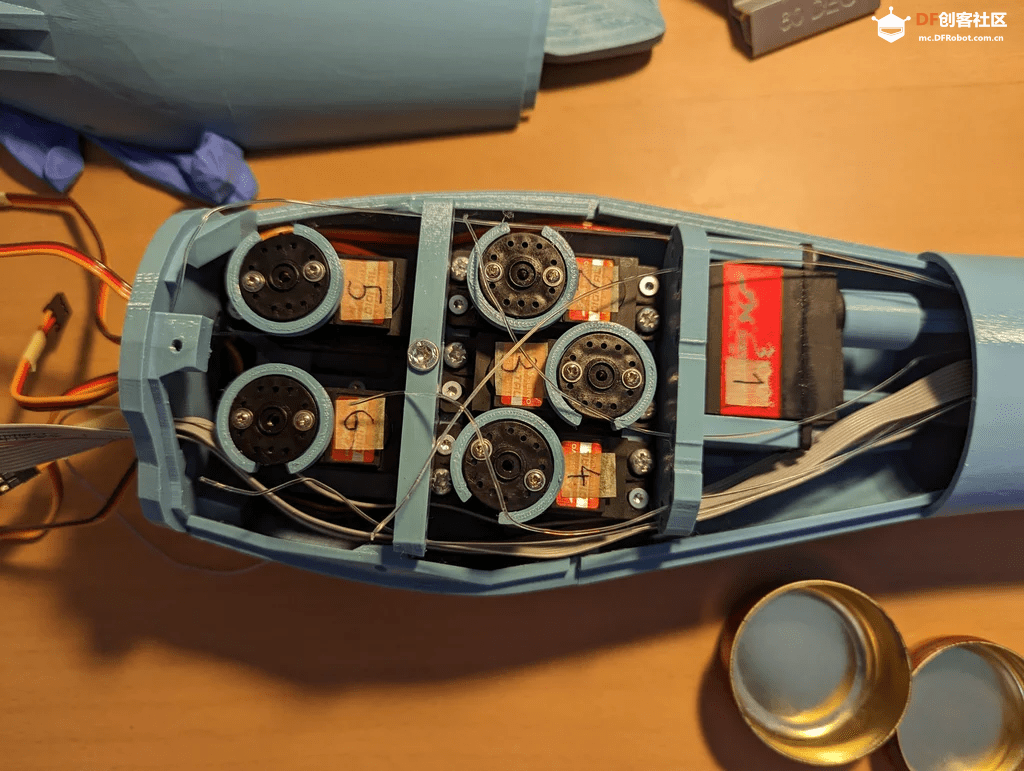
步骤5:电路
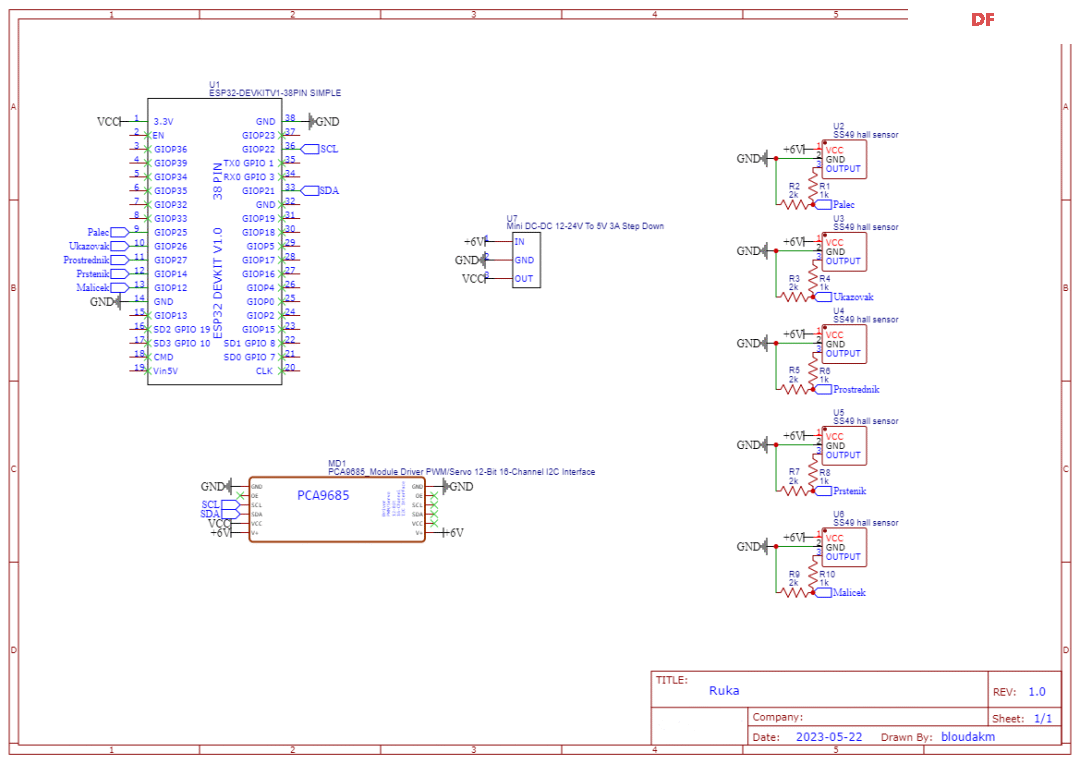
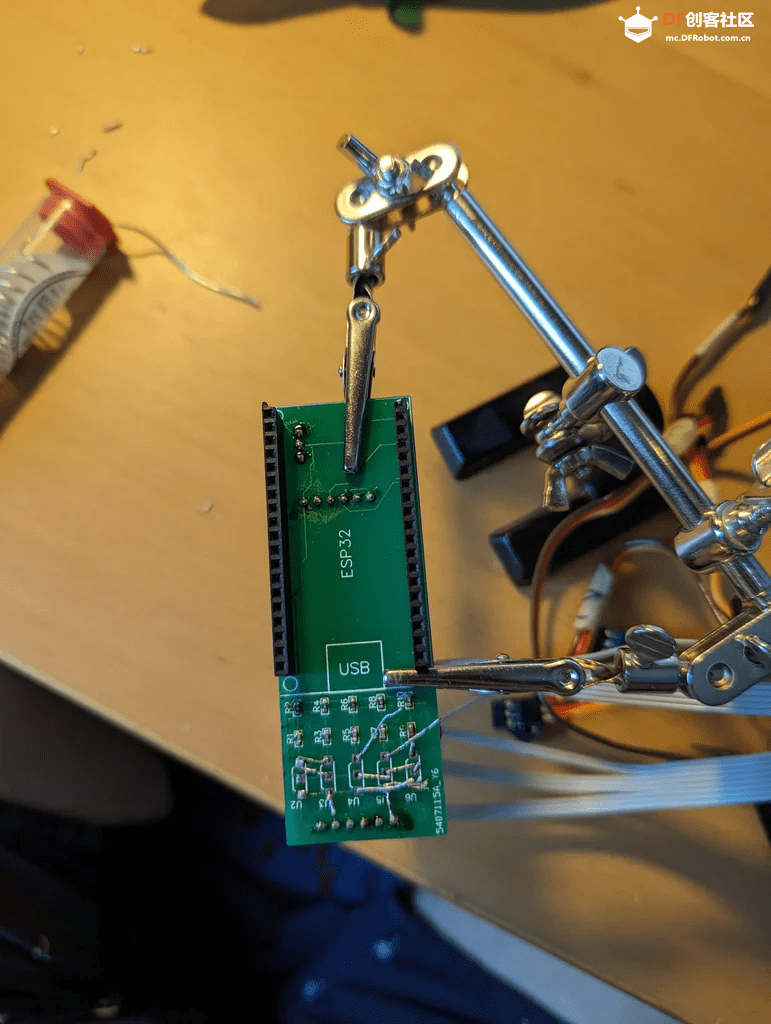
电路方面,使用16路舵机驱动模块会带来显著的效果,但也存在一些缺点。该驱动模块有两种不同的版本,虽然它们几乎相同,但在反极性保护电路(用于电容)所使用的晶体管上有区别,一个版本可承受约8A电流,而另一个版本仅可承受约0.5A,这远低于舵机实际需要的电流。因此,最好不要让伺服电机通过驱动模块供电,或者按照视频[5]中所述进行小改动,并在使用电容时要格外小心。
关于霍尔传感器,我们需要使用一个电压分压器,因为它输出的电压范围在0V到5V之间,而ESP32只能正确读取0V到3.3V的ADC值。
对于整个电路,可以选择使用面包板,或者更好的是使用定制PCB(作者版本的GitHub链接[6])。
步骤6:测试
▲ 在仿生手上测试霍尔传感器
▲ 在仿生手上测试电机
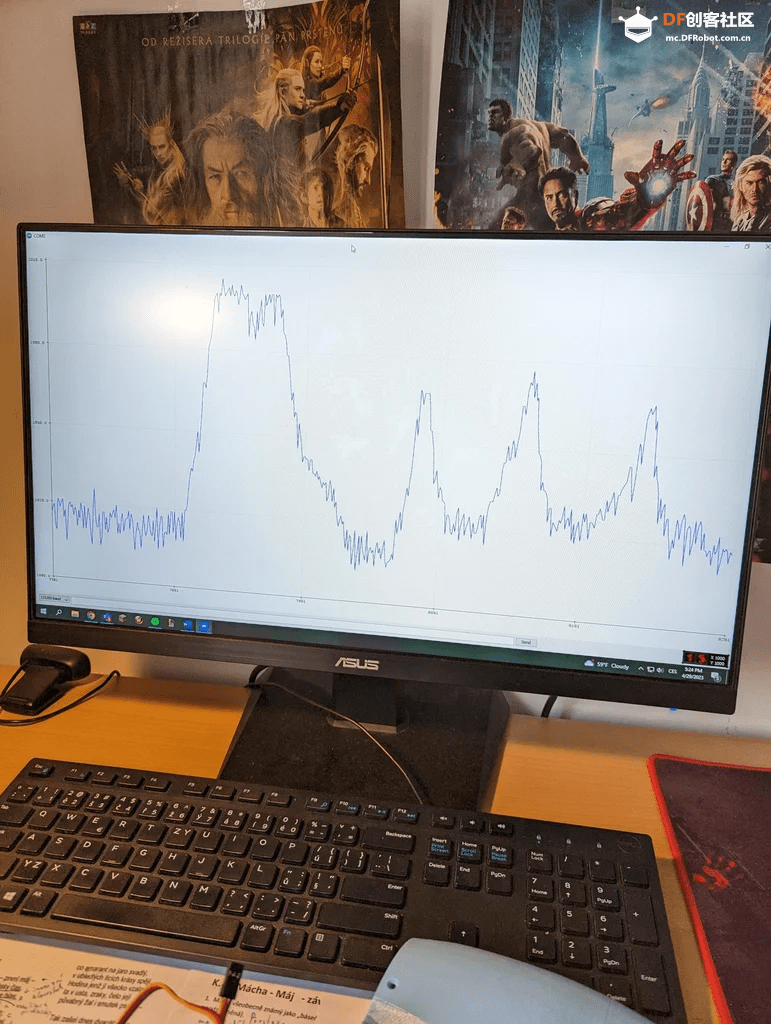
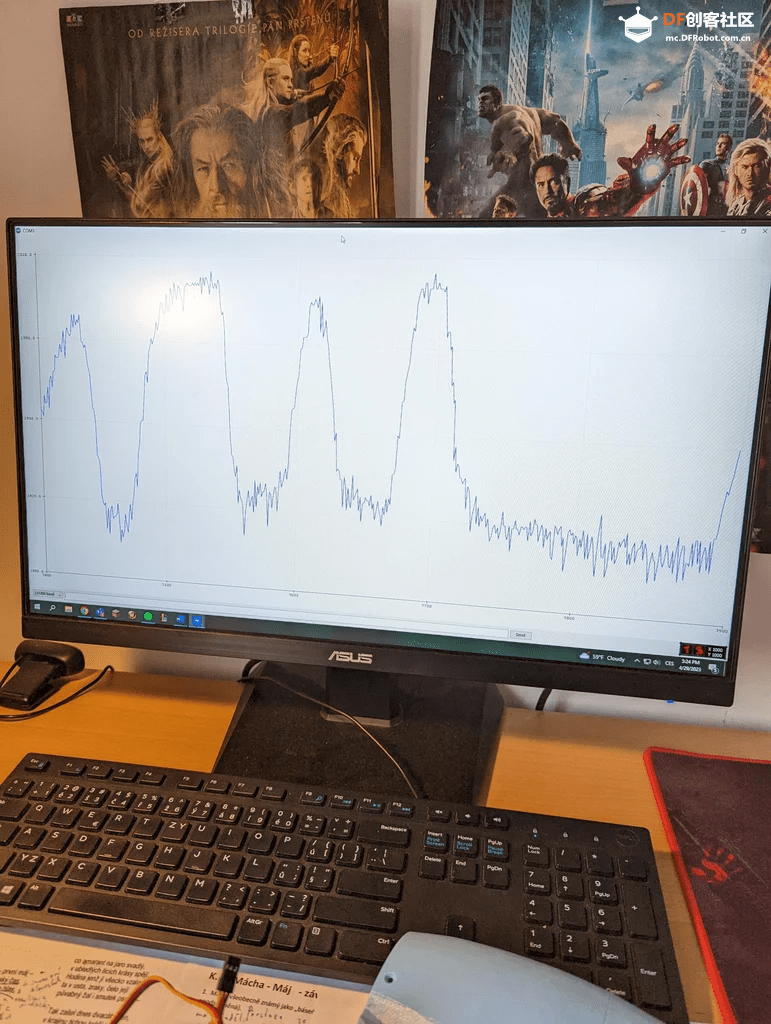
由于每个伺服电机和霍尔传感器都略有不同,所以需要对它们进行测试。
最重要的是测试霍尔传感器,因为它们测量的值将决定仿生手是否施加了足够的压力。我建议使用Arduino IDE的绘图功能来绘制数据,以观察数值何时超过自然不确定性范围。
为此,我们可以使用这个非常简单的代码片段:
- int hall = "Pin number your hall sensor is connected to";
-
- void setup() {
- Serial.begin(115200);
- pinMode(hall, INPUT);
- }
-
- void loop() {
- Serial.println(analogRead(hall));
- delay(10);
- }
步骤7:代码OpenCV(在VSCode中运行的Python代码)
就运行在带有网络摄像头的PC上的代码而言,我们需要完成两个主要任务:
第一个任务是使用OpenCV追踪手部及其元素。基于这些元素我们可以计算每根手指的位置。
第二个任务是通过串口将数据发送到ESP32,以便控制伺服电机。这些数据可以相对简化,因为我们不需要发送精确的角度值,而只需发送每个手指是否弯曲的信息。因此,我们可以发送五个0或1,并在末尾加一个符号以便后续识别每个数字的索引。
这种方法将手部追踪和数据传输简化为一个二进制状态系统,使得数据处理和传输更加高效,同时仍能提供足够的信息来控制仿生手的动作。
首先,我们需要为Python代码导入以下库:
- import cv2
- import mediapipe as mp
- import time
- import serial
然后,我们需要创建一个用于处理摄像头数据的类:
- class HandDetector():
- # Constructor of the class with parameters for the measurement
- def __init__(self, mode=False, maxHands=1, detectionCon=0.5, trackCon=0.5):
- self.mode = mode
- self.maxHands = maxHands
- self.detectionCon = detectionCon
- self.trackCon = trackCon
-
- self.mpHands = mp.solutions.hands
- self.hands = self.mpHands.Hands()
- self.mpDraw = mp.solutions.drawing_utils
-
- # Function for finding and drawing the hand
- def findHands(self, frame, draw=True):
- imgRGB = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
- self.results = self.hands.process(imgRGB)
-
- if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
- for handLms in self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
- if draw:
- self.mpDraw.draw_landmarks(frame, handLms, self.mpHands.HAND_CONNECTIONS)
- return frame
-
- # Function for finding each hand landmark and drawing its position
- def findPosition(self, frame, handNo=0, draw=False):
- lmList = []
-
- if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
- myHand = self.results.multi_hand_landmarks[handNo]
-
- for id, lm in enumerate(myHand.landmark):
- h, w, c = frame.shape
- cx, cy = int(lm.x * w), int(lm.y * h)
-
- lmList.append([id, cx, cy])
-
- if draw and id == 0:
- cv2.circle(frame, (cx, cy), 15, (255, 0, 255), -1)
- return lmList
接下来定义主函数:
- def main():
- # The prevTime and currentTime are used to calculate the FPS later
- prevTime = 0
- currentTime = 0
-
- # Array for storing the info about the hand
- hand = [["Wrist", False], ["Index", False], ["Middle", False],
- ["Ring", False], ["Thumb", False], ["Pinky", False]]
-
- # Initializing the Serial and opencv
- ser = serial.Serial(port="The name of the port the ESP32 is connected to")
- # I had to include the "cv2.CAP_DSHOW" because I had issues with the webcam loading on my linux machine
- cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0, cv2.CAP_DSHOW)
- detector = HandDetector()
-
- #MAIN LOOP OF THE CODE#
-
- # Releasing the stuff allocated for opencv
- cap.release()
- cv2.destroyAllWindows()
-
- main()
以及代码的主循环:
- while (True):
- # Finding the hands and reading the position of hte landmarks
- ret, frame = cap.read()
- frame = detector.findHands(frame)
- lmList = detector.findPosition(frame)
-
- if len(lmList) > 0:
-
- j = 1
- change = False
- # Loop which checks if the top of the finger is below the second most top
- for i in range(1, 6):
- if i == 1 and lmList[4][1] < lmList[3][1] and not hand[4][1]:
- # In case that it is true it changes all the needed data
- hand[4][1] = True
- change = True
- print(hand[4][0], hand[4][1])
- elif i == 1 and lmList[4][1] > lmList[3][1] and hand[4][1]:
- hand[4][1] = False
- change = True
- print(hand[4][0], hand[4][1])
- elif i != 1:
- if lmList[i*4][2] > lmList[(i*4)-2][2] and not hand[j][1]:
- hand[j][1] = True
- change = True
- print(hand[j][0], hand[j][0])
- elif lmList[i*4][2] < lmList[(i*4)-2][2] and hand[j][1]:
- hand[j][1] = False
- change = True
- print(hand[j][0], hand[j][0])
- if j == 3:
- j += 2
- else:
- j += 1
-
- # If there has been any change in the state of the hand this code block will run
- if change:
- msg = ""
- # Converts the boolean values to 0s and 1s
- for i in range(6):
- if hand[i][1]:
- msg += "1"
- else:
- msg += "0"
-
- # Adds the ending symbol and sends the data over to the ESP32
- msg += '\n'
- print(msg)
- ser.write(msg.encode("Ascii"))
-
- # Calculates the FPS and displays it on the frame
- currentTime = time.time()
- fps = 1/(currentTime-prevTime)
- prevTime = currentTime
- cv2.putText(frame, str(int(fps)), (10, 70), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3, (255, 0, 255), 3)
-
- # Shows what the webcam sees on a frame
- cv2.imshow("frame", frame)
-
- # If we press "q" it quits running the program
- if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord("q"):
- break
整个代码 OpenCV:
- import cv2
- import mediapipe as mp
- import time
- import serial
-
- class HandDetector():
- def __init__(self, mode=False, maxHands=2, detectionCon=0.5, trackCon=0.5):
- self.mode = mode
- self.maxHands = maxHands
- self.detectionCon = detectionCon
- self.trackCon = trackCon
-
- self.mpHands = mp.solutions.hands
- self.hands = self.mpHands.Hands()
- self.mpDraw = mp.solutions.drawing_utils
-
- def findHands(self, frame, draw=True):
- imgRGB = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
- self.results = self.hands.process(imgRGB)
-
- if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
- for handLms in self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
- if draw:
- self.mpDraw.draw_landmarks(frame, handLms, self.mpHands.HAND_CONNECTIONS)
- return frame
-
- def findPosition(self, frame, handNo=0, draw=False):
- lmList = []
-
- if self.results.multi_hand_landmarks:
- myHand = self.results.multi_hand_landmarks[handNo]
-
- for id, lm in enumerate(myHand.landmark):
- h, w, c = frame.shape
- cx, cy = int(lm.x * w), int(lm.y * h)
-
- lmList.append([id, cx, cy])
-
- if draw and id == 0:
- cv2.circle(frame, (cx, cy), 15, (255, 0, 255), -1)
- return lmList
-
- def main():
- prevTime = 0
- currentTime = 0
- hand = [["Wrist", False], ["Index", False], ["Middle", False],
- ["Ring", False], ["Thumb", False], ["Pinky", False]]
-
-
- ser = serial.Serial(port="COM3")
- cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0, cv2.CAP_DSHOW)
- detector = HandDetector()
-
- while (True):
- ret, frame = cap.read()
- frame = detector.findHands(frame)
- lmList = detector.findPosition(frame)
-
- if len(lmList) > 0:
-
- j = 1
- change = False
- for i in range(1, 6):
- if i == 1 and lmList[4][1] < lmList[3][1] and not hand[4][1]:
- hand[4][1] = True
- change = True
- print(hand[4][0], hand[4][1])
- elif i == 1 and lmList[4][1] > lmList[3][1] and hand[4][1]:
- hand[4][1] = False
- change = True
- print(hand[4][0], hand[4][1])
- elif i != 1:
- if lmList[i*4][2] > lmList[(i*4)-2][2] and not hand[j][1]:
- hand[j][1] = True
- change = True
- print(hand[j][0], hand[j][0])
- elif lmList[i*4][2] < lmList[(i*4)-2][2] and hand[j][1]:
- hand[j][1] = False
- change = True
- print(hand[j][0], hand[j][0])
- if j == 3:
- j += 2
- else:
- j += 1
-
- if change:
- msg = ""
- for i in range(6):
- if hand[i][1]:
- msg += "1"
- else:
- msg += "0"
-
- msg += '\n'
- print(msg)
- ser.write(msg.encode("Ascii"))
-
- currentTime = time.time()
- fps = 1/(currentTime-prevTime)
- prevTime = currentTime
-
- cv2.putText(frame, str(int(fps)), (10, 70), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 3, (255, 0, 255), 3)
-
- cv2.imshow("frame", frame)
-
- if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord("q"):
- break
-
- cap.release()
- cv2.destroyAllWindows()
-
- main()
ESP32(Arduino IDE)
我们可以充分利用ESP32是双核这一特点,类似于PC的代码,我们同样需要完成两项主要工作。
首先是接收来自PC的数据。正如前面提到的,数据基本上是一个带有六位二进制数和结束符的字符串。此外,由于只有在状态变化时才会传输数据,我们可以立即将这些值(转换为true或false)分配给相应的变量。将这个任务分配给核心0,而主循环则在核心1上运行。
第二项工作就是控制手部运动。为此,我们需要不停地检查这些变量的状态是否发生变化,一旦有变化,伺服电机就会按小步长进行线性移动。在每一步后,首先需要检查变量是否没有再次变化,并且还要测量霍尔传感器读取的值。如果霍尔传感器的值过高,意味着磁铁距离手指核心太近,此时也要停止伺服电机的运动。
最初,我们需要用于伺服驱动的库,并且还将包含用于I2C通信的Wire库:
- #include <Wire.h>
- #include <Adafruit_PWMServoDriver.h>
之后,我们需要定义脉冲长度的值,这些值因伺服类型而异,所以强烈建议查找特定伺服的信息或者像这样测试[7]它们。
- // Operating Speed of my Servo (6V): 0.21 sec/60°
-
- #define SERVOMIN "Your value (mine was 70)" // This is the 'minimum' pulse length count (out of 4096)
- #define SERVOMAX "Your value (mine was 510)" // This is the 'maximum' pulse length count (out of 4096)
- #define SERVO_FREQ 50 // Analog servos run at ~50 Hz updates
现在我们必须定义其余要使用到的变量:
- // Initializing servo driver object
- Adafruit_PWMServoDriver pwm = Adafruit_PWMServoDriver();
-
- // Index, Middle, Ring, Thumb, Pinky
- // "state0" is the state the hand on the webcam is in and "state"
- // is the stuff happening on the actual hand
- bool state0[6] = {false, false, false, false, false, false};
- bool state[6] = {false, false, false, false, false, false};
-
- // Variable which indicates if there has been any change made to the state
- bool change = false;
-
- // Variables needed for reading the data from Serial
- char sData;
- String state;
-
- // Variable for the hall sensor
- // Index, Middle, Ring, Thumb, Pinky
- // {pin, measured value, maximum value}
- // ALL OF THE MAX VALUES WERE MEASURED BY ME THUS THEY WILL MOST LIKELY NOT BE SAME FOR YOU
- int hall[5][3] = {{26, 0, 2200}, {27, 0, 2400}, {14, 0, 2300}, {25, 0, 2200}, {12, 0, 2300}};
-
- // Setting the index numbers of each motor
- int wrist = 0;
- int thumb = 4;
- int index = 1;
- int middle = 2;
- int ring = 3; // IMPORTANT this motor will rotate in the oposite direction
- int pinky = 5; // IMPORTANT this motor will rotate in the oposite direction
-
- // Function for calculating the PWM based on the degree you want
- int degToPwm(int degree) {
- return map(degree, 0, 320, SERVOMIN, SERVOMAX);
- }
-
- // Setting the degree thresholds used
- int deg = degToPwm(75);
- int deg1 = degToPwm(95);
- int deg2 = degToPwm(85);
- int startDeg = degToPwm(180);
接下来,需要定义我们将要使用的函数:
- // Initialization of the task
- TaskHandle_t recieveData;
-
- // Function which reads the data from Serial
- void recieveDataCode(void * parameter) {
- for(;;) {
- // Loop which runs when there is a message sent
- while(Serial.available()) {
- // Reading by each character
- sData = Serial.read();
-
- // If the character is the line ending symbol we know it is the end of the message
- if(sData == '\n') {
- // Loop for converting the string 0s and 1s to boolean
- for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
- state0[i] = state.substring(i, i+1).toInt();
- }
-
- // Reseting the state temporary variable
- state = "";
- // Showing a change in state happened
- change = true;
- break;
- } else { // If the character is not the line ending symbol we add it to the temporary state
- state += sData;
- }
- }
- delay(10);
- }
- }
-
- // Function for actually moving the servos
- void moveFinger(int fingerId, bool flex, int iteration) {
- // Because the ring and pinky motors move in opposite direction
- // we have to check which motors we are moving
- if(fingerId != ring && fingerId != pinky) {
- // We also need to check if we want the finger to flex or straighten
- if(flex) {
- // Moreover the thumb moves a little less so we also check for that
- if(fingerId == thumb) {
- // Because we want to be able to control the movement throughout we have to
- // divide it into smaller parts
- float fPwm = SERVOMIN + (float(103)*float(iteration))/float(130);
- // But we also have to make sure to convert back to int because float would
- // not be accepted by pwm function
- int iPwm = round(fPwm);
- pwm.setPWM(fingerId, 0, iPwm);
- } else { // If the finger is not the thumb we just move it
- pwm.setPWM(fingerId, 0, SERVOMIN + iteration);
- }
- } else { // For the case that is retracting we have to just do the opposite
- if(fingerId == thumb) {
- float fPwm = deg - (float(103)*float(iteration))/float(130);
- int iPwm = round(fPwm);
- pwm.setPWM(fingerId, 0, iPwm);
- } else {
- pwm.setPWM(fingerId, 0, deg1 - iteration);
- }
- }
- } else if(fingerId == ring || fingerId == pinky) {
- // In the case of the ring or pinky finger we do again the same
- if(flex) {
- pwm.setPWM(fingerId, 0, startDeg - iteration);
- } else {
- pwm.setPWM(fingerId, 0, deg2 + iteration);
- }
- }
- }
补上设置和循环功能:
- void setup() {
- // Starting Serial on the same frequency as on the PC
- Serial.begin(9600);
-
- // Assigning the pinMode to all pins connected to hall sensor
- for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
- pinMode(hall[i][0], INPUT);
- }
-
- // Setup and starting the servo driver
- pwm.begin();
- pwm.setOscillatorFrequency(27000000);
- pwm.setPWMFreq(SERVO_FREQ);
-
- delay(10);
-
- // Pinning the created task to core 0
- xTaskCreatePinnedToCore(
- recieveDataCode,
- "recieveData",
- 10000,
- NULL,
- 0,
- &recieveData,
- 0);
- delay(500);
- }
-
- void loop() {
- // Once there has been a change in the state this code block will run
- if(change) {
- // Looping firstly through the total steps of the servos
- for(int i = 5; i < 135; i += 5) {
-
- // Secondly through all of the hall sensors and reading the values
- for(int k = 0; k < 5; k++) {
- hall[k][1] = analogRead(hall[k][0]);
- // If the measured value is greater than maximum value we stop the movement
- if(hall[k][1] > hall[k][2]) {
- state1[k+1] = state0[k+1];
- }
- }
-
- // Thirdly through all the servo motors
- for(int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
- if(state0[j] != state1[j]) {
- // If the state on the PC does not match the one on the esp32 we
- // call the function for moving the respective finger
- moveFinger(j, state0[j], i);
- }
- }
- // This delay is very important as it sets the speed of the movements
- delay(17);
- }
-
- // At the and we make the state variables equal again
- for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
- state1[i] = state0[i];
- }
- }
-
- delay(100);
- }
ESP32的完整代码:
- #include <Wire.h>
- #include <Adafruit_PWMServoDriver.h>
-
- #define SERVOMIN "Your value"
- #define SERVOMAX "Your value"
- #define SERVO_FREQ 50
-
- Adafruit_PWMServoDriver pwm = Adafruit_PWMServoDriver();
-
- bool state0[6] = {false, false, false, false, false, false};
- bool state1[6] = {false, false, false, false, false, false};
-
- bool change = false;
-
- char sData;
- String state;
-
- int hall[5][3] = {{26, 0, 2200}, {27, 0, 2400}, {14, 0, 2300}, {25, 0, 2200}, {12, 0, 2300}};
-
- int wrist = 0;
- int thumb = 4;
- int index = 1;
- int middle = 2;
- int ring = 3;
- int pinky = 5;
-
- int degToPwm(int degree) {
- return map(degree, 0, 320, SERVOMIN, SERVOMAX);
- }
-
- int deg = degToPwm(75);
- int deg1 = degToPwm(95);
- int deg2 = degToPwm(85);
- int startDeg = degToPwm(180);
-
- TaskHandle_t recieveData;
-
- void recieveDataCode(void * parameter) {
- for(;;) {
- while(Serial.available()) {
- sData = Serial.read();
- if(sData == '\n') {
- for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
- state0[i] = state.substring(i, i+1).toInt();
- }
- state = "";
- change = true;
- break;
- } else {
- state += sData;
- }
- }
- delay(10);
- }
- }
-
- void moveFinger(int fingerId, bool flex, int iteration) {
- if(fingerId != ring && fingerId != pinky) {
- if(flex) {
- if(fingerId == thumb) {
- float fPwm = SERVOMIN + (float(103)*float(iteration))/float(130);
- int iPwm = round(fPwm);
- pwm.setPWM(fingerId, 0, iPwm);
- } else {
- pwm.setPWM(fingerId, 0, SERVOMIN + iteration);
- }
- } else {
- if(fingerId == thumb) {
- float fPwm = deg - (float(103)*float(iteration))/float(130);
- int iPwm = round(fPwm);
- pwm.setPWM(fingerId, 0, iPwm);
- } else {
- pwm.setPWM(fingerId, 0, deg1 - iteration);
- }
- }
- } else /*if(fingerId == ring || fingerId == pinky)*/ {
- if(flex) {
- pwm.setPWM(fingerId, 0, startDeg - iteration);
- } else {
- pwm.setPWM(fingerId, 0, deg2 + iteration);
- }
- }
- }
-
- void setup() {
- Serial.begin(9600);
-
- for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
- pinMode(hall[i][0], INPUT);
- }
-
- pwm.begin();
- pwm.setOscillatorFrequency(27000000);
- pwm.setPWMFreq(SERVO_FREQ);
-
- delay(10);
-
- xTaskCreatePinnedToCore(
- recieveDataCode,
- "recieveData",
- 10000,
- NULL,
- 0,
- &recieveData,
- 0);
- delay(500);
- }
-
- void loop() {
- if(change) {
- for(int i = 5; i < 135; i += 5) {
- for(int k = 0; k < 5; k++) {
- hall[k][1] = analogRead(hall[k][0]);
- if(hall[k][1] > hall[k][2]) {
- state1[k+1] = state0[k+1];
- }
- }
- for(int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
- if(state0[j] != state1[j]) {
- moveFinger(j, state0[j], i);
- }
- }
- delay(17);
- }
-
- for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
- state1[i] = state0[i];
- }
- }
-
- delay(100);}
参考资料
[1]InMoov项目: https://inmoov.fr/?doing_wp_cron ... 7699527740478515625
[2]inmoov STL零件库: https://inmoov.fr/inmoov-stl-parts-viewer/
[3]i2手: https://inmoov.fr/hand-i2/
[4]前臂: https://inmoov.fr/hand-and-forarm/
[5]视频: https://youtu.be/EqVhpilm3sw?si=hGODLQO_kjNtr1q0
[6]作者版本的GitHub链接: https://github.com/Bloudakm/Blou ... hand_Gerber_PCB.zip
[7]测试: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y8X9X10Tn1k&t=941s
原文地址:https://www.instructables.com/Bionic-Hand-Controlled-by-OpenCV/
项目作者:bloudakm
译文首发于:DF创客社区
转载请注明来源信息
|





















 沪公网安备31011502402448
沪公网安备31011502402448