本帖最后由 无垠的广袤 于 2025-5-6 21:21 编辑
Beetle 树莓派RP2350 - 桌面时钟摆件本文介绍了 DFRobot Beetle RP2350 开发板结合 DS1307 - RTC 时钟模块实现桌面时钟的项目设计。
项目介绍
包括 RTC 时钟模块(关键部件,用以存储时间数据)、DS1307 芯片介绍、工作原理、参数特点等信息,在此基础上实现工程代码编写、硬件测试等流程,最终实现桌面时钟显示摆件的项目设计。
方案设计
调用 MicroPython 的 RTC 库,获取系统时间,并实现OLED显示; 使用 IIC 通信连接 DS1307 模块,并实现时间的获取和校准; 读取校准后的时钟数据,并完成 OLED 显示; 断电测试,主控重新上电,观察 OLED 显示结果,和系统时间对比,确保 DS1307 模块有效记录时间。
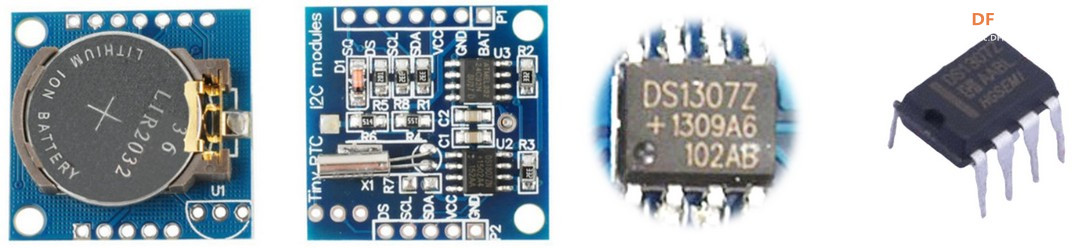
DS1307
DS1307 是一款由美信 Maxim Integrated 公司生产的低功耗、带56字节非易失性 RAM 的实时时钟(RTC)芯片,广泛应用于需要精确时间管理的电子设备和嵌入式系统。
工作原理
DS1307 通过 32.768 kHz 晶振产生时钟脉冲,追踪时间信息。通过 IIC 总线与主控设备通信,支持读写操作,用户可以通过配置寄存器来设置和调整时间。
参数特点
时钟/日历功能:提供秒、分、时、日、月、年、星期信息,自动闰年补偿,有效期至2100年 时间格式:支持 12 小时制和 24 小时制,在 12 小时制下具有 AM/PM 指示 IIC接口:通过两线制 IIC 总线与 MCU 通信 56字节、电池备份、通用 RAM,写次数不受限制 可编程方波输出 低功耗:工作电流小于 500nA (电池备份模式),适合电池供电的便携设备 电源感应电路:具有内置的电源感应电路,能够检测主电源的断电情况,并自动切换到备用电池供电 宽工作电压:4.5V 至 5.5V 工作温度:-40°C 至 +85°C 封装: 8 引脚 DIP 、贴片
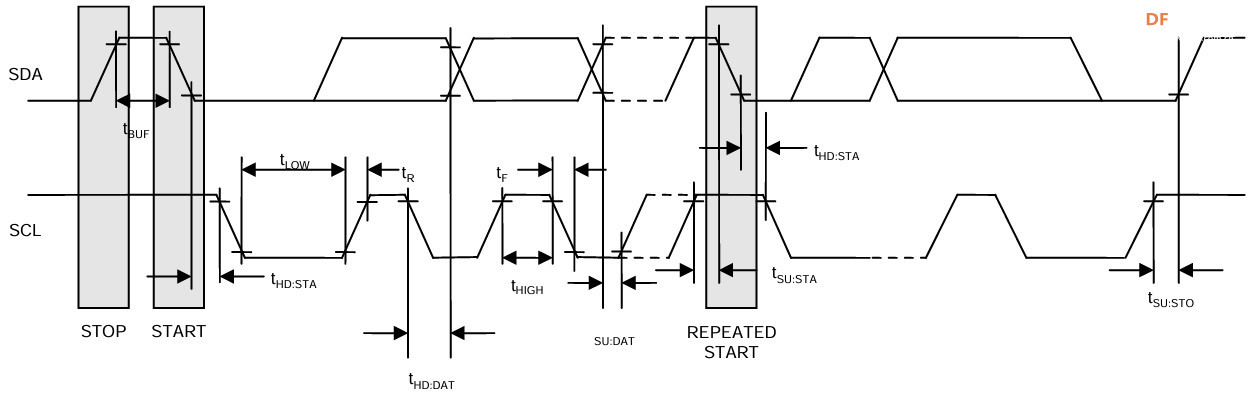
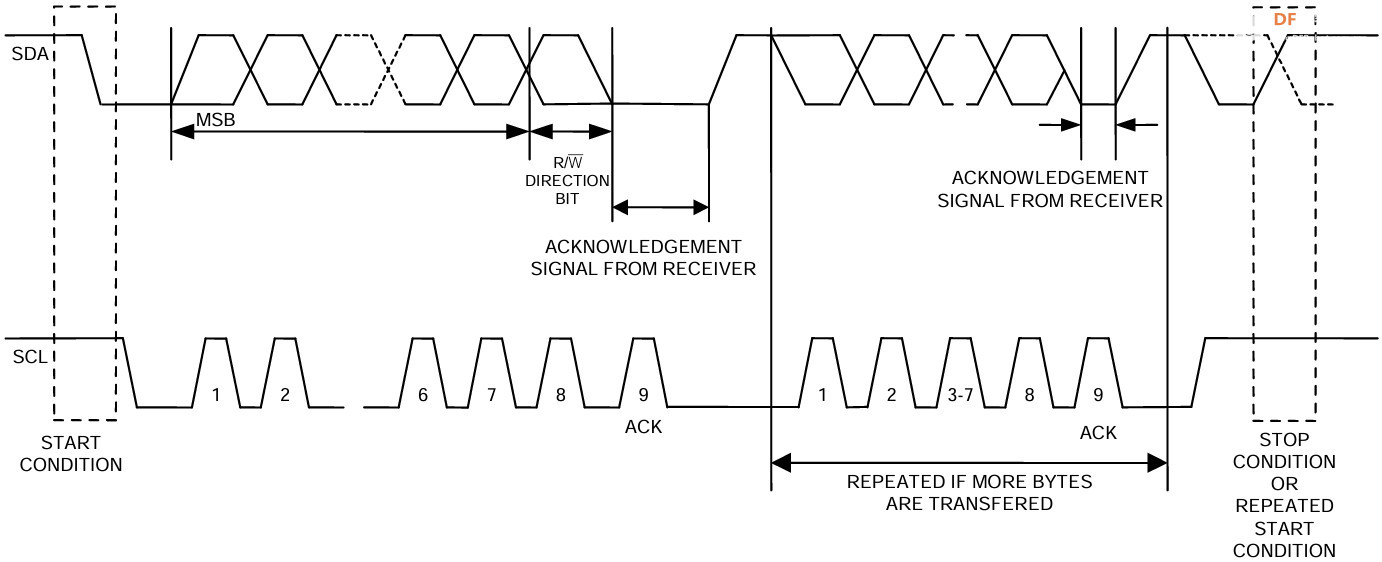
时序图
IIC 总线数据通信
注意事项
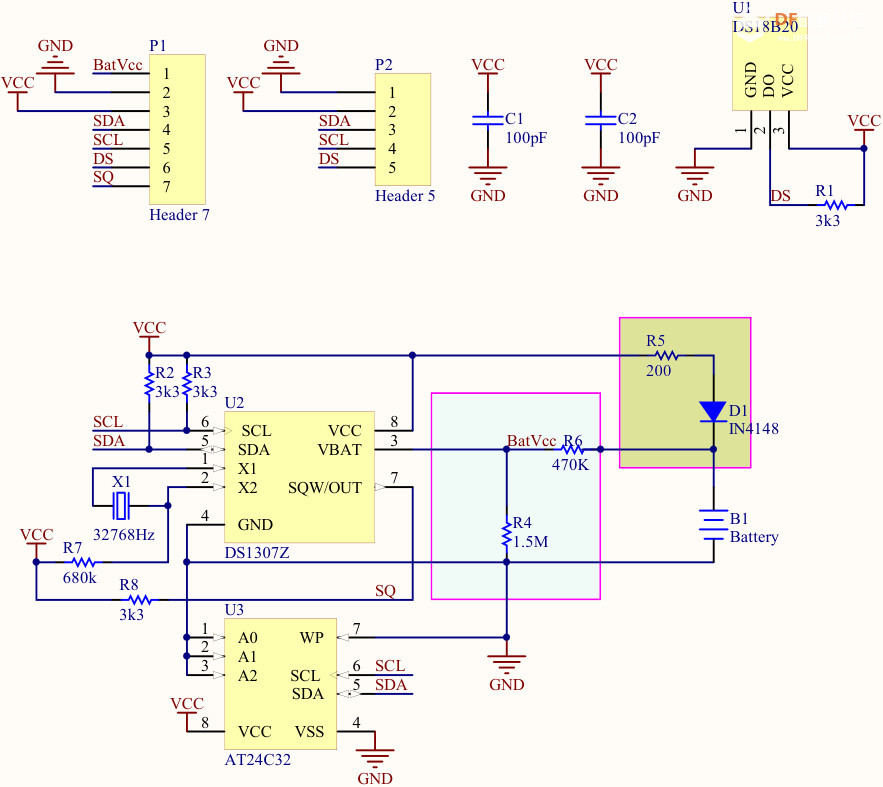
原理图
引脚定义
DS1307 RTC 模块引脚输出定义 [td]
| Pin | Name | Describe | SQ | Square Wave | Optional square wave or logic level output | DS | DS18B20 | Output for temperature readings if DS18B20 is connected (we won’t use) | SCL | I2C Clock | I2C clock for DS1307 and EEPROM | SDA | I2C Data | I2C data for DS1307 and EEPROM | VCC | Input Supply | 3.3V or 5V power for module and to charge coin cell battery | GND | Ground | Ground | BAT | Battery Voltage | For monitoring battery voltage |
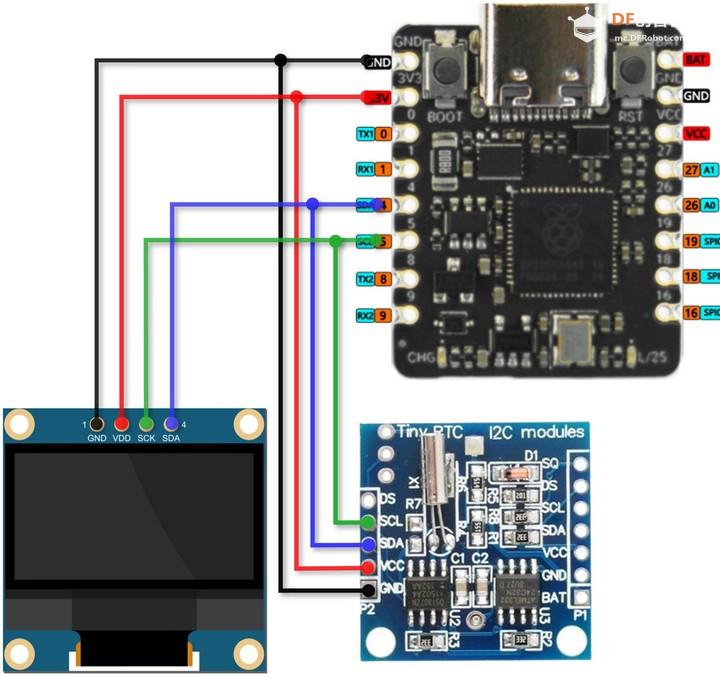
硬件连接
- GP5 ---- SCL (DS1307)
- GP4 ---- SDA (DS1307)
- GP5 ---- SCL(OLED)
- GP4 ---- SDA(OLED)
这里复用了硬件 IIC 引脚 GPIO5(IIC_SCL)和 GPIO4(IIC_SDA).
工程项目
介绍了系统时间显示测试、DS1307 模块的测试和校准、时钟显示、桌面摆件的项目设计。
系统时间显示
在使用 DS1307 模块获取和记录时间之前,通过系统时间的 OLED 显示项目对硬件连接进行测试。
代码
- '''
- Name: System time display on OLED screen
- Version: v1.0
- Date: 2025.05
- Author: ljl
- Other: System time is displayed on OLED screen.
- Hardware connect:
- 5 ---- SCL(OLED)
- 4 ---- SDA(OLED)
- Shell print.
- '''
-
- from machine import Pin, I2C
- from ssd1306 import SSD1306_I2C
- import time
-
- i2c = I2C(0, sda=Pin(4), scl=Pin(5), freq=400000)
- days_of_week = ['Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Wednesday', 'Thursday', 'Friday', 'Saturday', 'Sunday']
-
- devices = i2c.scan()
- # scan iic devices and print address name
- if len(devices) == 0:
- print("No i2c device found.")
- else:
- print("i2c devices found:", len(devices))
-
- for device in devices:
- print("i2c scan:", hex(device))
-
- rtc_pico = machine.RTC() # datetime (2025, 5, 6, 1, 16, 30, 23, 0)
- print("System time: ", rtc_pico.datetime())
- oled_width = 128
- oled_height = 64
- oled = SSD1306_I2C(oled_width, oled_height, i2c, addr=devices[0])
-
- while True:
- # Get current time from system
- current_datetime = rtc_pico.datetime()
- # Format the date and time as strings
- formatted_date = '{:04d}-{:02d}-{:02d}'.format(current_datetime[0], current_datetime[1], current_datetime[2]) # year, month, day
- formatted_time = '{:02d}:{:02d}:{:02d}:{:02d}'.format(current_datetime[4], current_datetime[5], current_datetime[6], current_datetime[7]) # hour, minute, second
- formatted_day_week = days_of_week[current_datetime[3]] # week
- try:
- oled.fill(0)
- oled.text('Date:' + formatted_date, 0, 0)
- oled.text('Week:' + formatted_day_week, 0, 16)
- oled.text('Time:' + formatted_time, 0, 32)
- oled.show()
-
- # Print the formatted date and time to the shell
- print(formatted_date + ' ' + formatted_day_week + ' ' + formatted_time)
- except Exception as err:
- print(f"Unable to initialize oled: {err}")
-
- # Wait for 1 second
- time.sleep(1)
效果
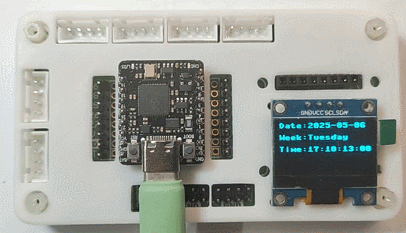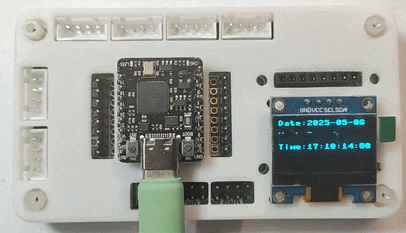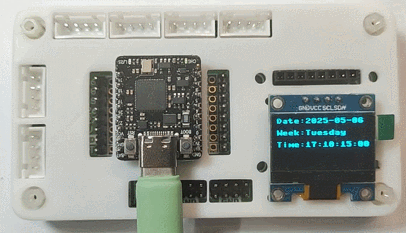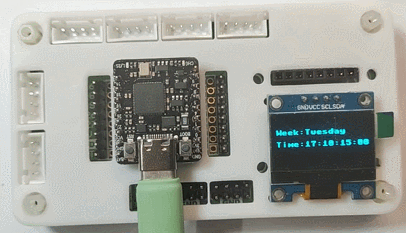
同时终端打印时间(间隔 1 秒)
DS1307 模块
测试 DS1307 模块,调用模块时间并实现终端打印。
代码
- '''
- Name: RTC DS1307 demo
- Author: ljl
- Date: 2025.05
- Other: Connect ds1307 module and print ds1307 time.
- Ref:https://randomnerdtutorials.com/ ... canner-micropython/
- '''
-
- from machine import Pin, I2C
- import ds1307
-
- rtc_pico = machine.RTC()
- print("System time: ", rtc_pico.datetime())
-
- # scan i2c devices
- i2c = machine.I2C(id=0, scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4), freq = 400000)
- devices = i2c.scan()
-
- # print i2c devices address
- if len(devices) == 0:
- print("No i2c device found.")
- else:
- print("i2c devices found:", len(devices))
-
- for device in devices:
- print("i2c scan:", hex(device))
-
- # the adress of ds1307 is 0x68
- rtc_ds1307 = ds1307.DS1307(i2c)
- print("DS1307 time: ", rtc_ds1307.datetime())
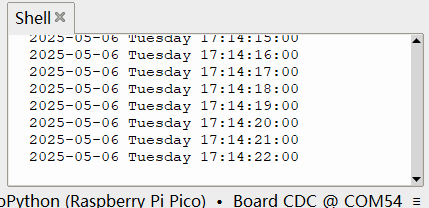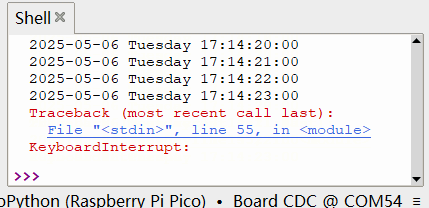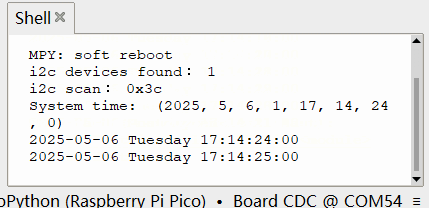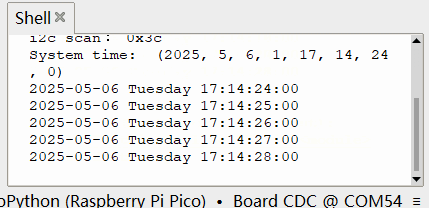
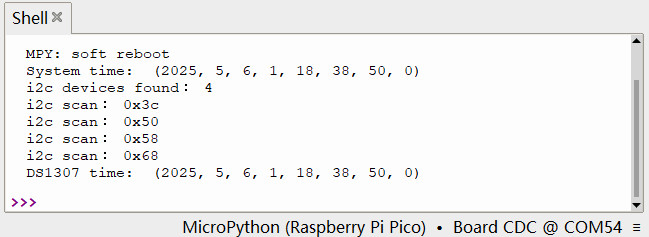
效果
初始时间为 2000 年 1 月 1 日, 0 时 0 分 0 秒
校准
DS1307 模块在首次上电、断电情况下时钟会初始化,因此 时钟校准 是该模块实现具体应用的重要环节。 代码
在上述代码后面添加 update_time() 函数并执行
- def update_time():
- ''' --- custom time --- '''
- #str_time = input("Please input [year month day week hour minute second]: ")
- #if str_time == '': return
- #str_time = rtc_pico.datetime()
- #givenTime = tuple(map(int, tuple(str_time.split(' '))))
- #print(givenTime)
- #rtc_ds1307.datetime(givenTime)
- ''' --- use system time --- '''
- givenTime = rtc_pico.datetime()
- rtc_ds1307.datetime(givenTime)
-
- update_time()
- print("DS1307 time corrected: ", rtc_ds1307.datetime())
时钟校正后的结果为
此时,断电重新上电,读取 DS1307 时钟模块,可获得正确的时间。
时钟显示
在完成前面的 OLED 显示和 DS1307 时钟读取及校准流程的基础上,进一步将从模块读取的时间数据显示在 OLED 屏幕即可。
代码
- '''
- Name: Time display on OLED screen by DS1307 RTC module
- Version: v1.0
- Date: 2025.05
- Author: ljl
- Other: DS1307 RTC module is used to obtain time and display it on OLED screen.
- Hardware connect:
- 5 ---- SCL (DS1307)
- 4 ---- SDA (DS1307)
- 5 ---- SCL(OLED)
- 4 ---- SDA(OLED)
- Shell print.
- '''
-
- from machine import Pin, I2C
- import ds1307
- from ssd1306 import SSD1306_I2C
- import utime
-
- i2c = I2C(0, sda=Pin(4), scl=Pin(5), freq=400000)
- days_of_week = ['Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Wednesday', 'Thursday', 'Friday', 'Saturday', 'Sunday']
-
- devices = i2c.scan()
- # scan iic devices and print address name
- if len(devices) == 0:
- print("No i2c device found.")
- else:
- print("i2c devices found:", len(devices))
-
- for device in devices:
- print("i2c scan:", hex(device))
-
- # define OLED module
- oled = SSD1306_I2C(128, 64, i2c,addr=devices[0])
-
- # define RTC DS1307 module
- rtc_pico = machine.RTC() # datetime (2025, 5, 6, 1, 16, 30, 23, 0)
- print("System time: ", rtc_pico.datetime())
-
- rtc_ds1307 = ds1307.DS1307(i2c)
- #print(dir(rtc_ds1307)) # dir --- print objects class values ...
- print("DS1307 time: ", rtc_ds1307.datetime())
-
- def update_time():
- ''' --- custom time --- '''
- #str_time = input("Please input [year month day week hour minute second]: ")
- #if str_time == '': return
- #str_time = rtc_pico.datetime()
- #givenTime = tuple(map(int, tuple(str_time.split(' '))))
- #print(givenTime)
- #rtc_ds1307.datetime(givenTime)
- ''' --- use system auto time --- '''
- givenTime = rtc_pico.datetime()
- rtc_ds1307.datetime(givenTime)
-
- #update_time() # run this code when DS1307 module need time correction
-
- while True:
- # Get current time from the RTC module
- current_datetime = rtc_ds1307.datetime()
- # Format the date and time as strings
- formatted_date = '{:04d}-{:02d}-{:02d}'.format(current_datetime[0], current_datetime[1], current_datetime[2]) # year, month, day
- formatted_time = '{:02d}:{:02d}:{:02d}:{:02d}'.format(current_datetime[4], current_datetime[5], current_datetime[6], current_datetime[7]) # hour, minute, second
- formatted_day_week = days_of_week[current_datetime[3]] # week
- try:
- oled.fill(0)
- oled.text('Date:' + formatted_date, 0, 0)
- oled.text('Week:' + formatted_day_week, 0, 16)
- oled.text('Time:' + formatted_time, 0, 32)
- oled.show()
-
- # Print the formatted date and time to the shell
- print(formatted_date + ' ' + formatted_day_week + ' ' + formatted_time)
- except Exception as err:
- print(f"Unable to initialize oled: {err}")
-
- # Wait for 1 second
- utime.sleep(1)
效果
将 Type-C 数据线拔掉,维持系统断电一段时间,重新上电并执行程序,可见此时时钟读数依然准确,并与系统时间保持一致
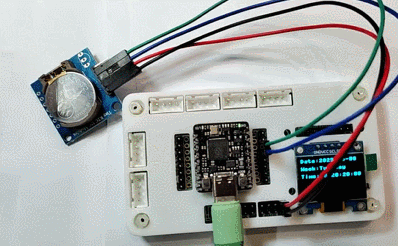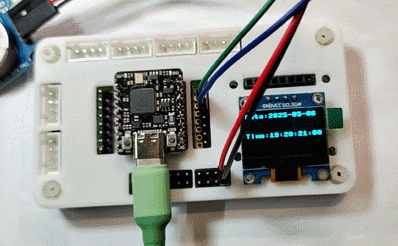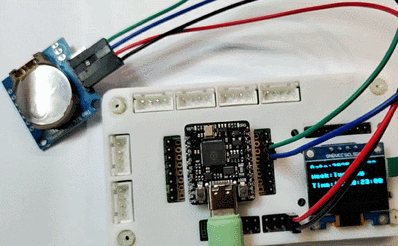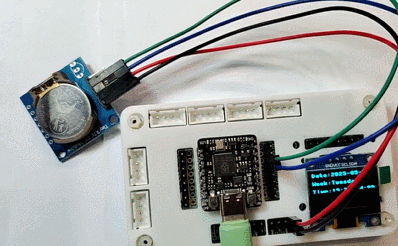
增加外置电池,通过快接插头连接至 BAT 接口,即可制成桌面时钟摆件。
总结
本文介绍了 DFRobot Beetle RP2350 开发板结合 DS1307 时钟模块实现时间记忆,扩展板配合 3D 外壳实现桌面时钟摆件的项目设计,为 Beetle RP2350 开发板的开发设计和产品应用提供了参考。
| 


 沪公网安备31011502402448
沪公网安备31011502402448