项目代码/* ****NOTES****
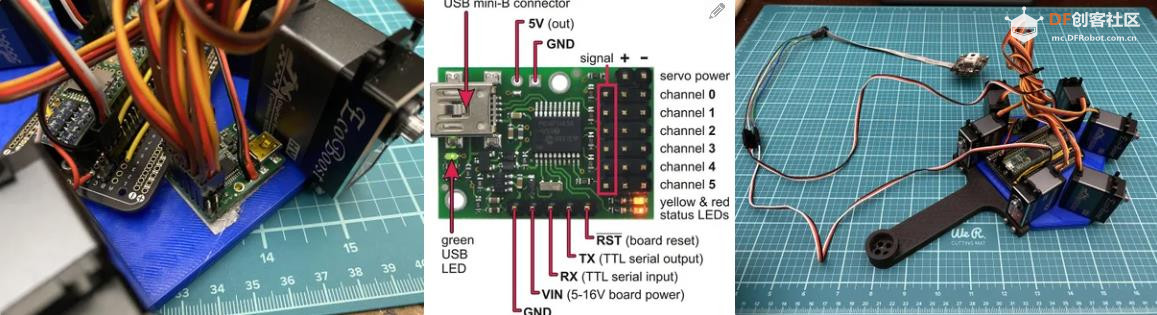
Before using this, go to the Serial Settings
tab in the Maestro Control Center and apply these settings:
Serial mode: UART, fixed baud rate
Baud rate: 9600
CRC disabled
Be sure to click "Apply Settings" after making any changes.
Array Indexes
-------------
a1 = 0
a2 = 1
b1 = 2
b2 = 3
c1 = 4
c2 = 5
range for hz (105, 140)
*/
// libraries
#include "PololuMaestro.h"
#include "math.h"
#include <Pixy2SPI_SS.h>
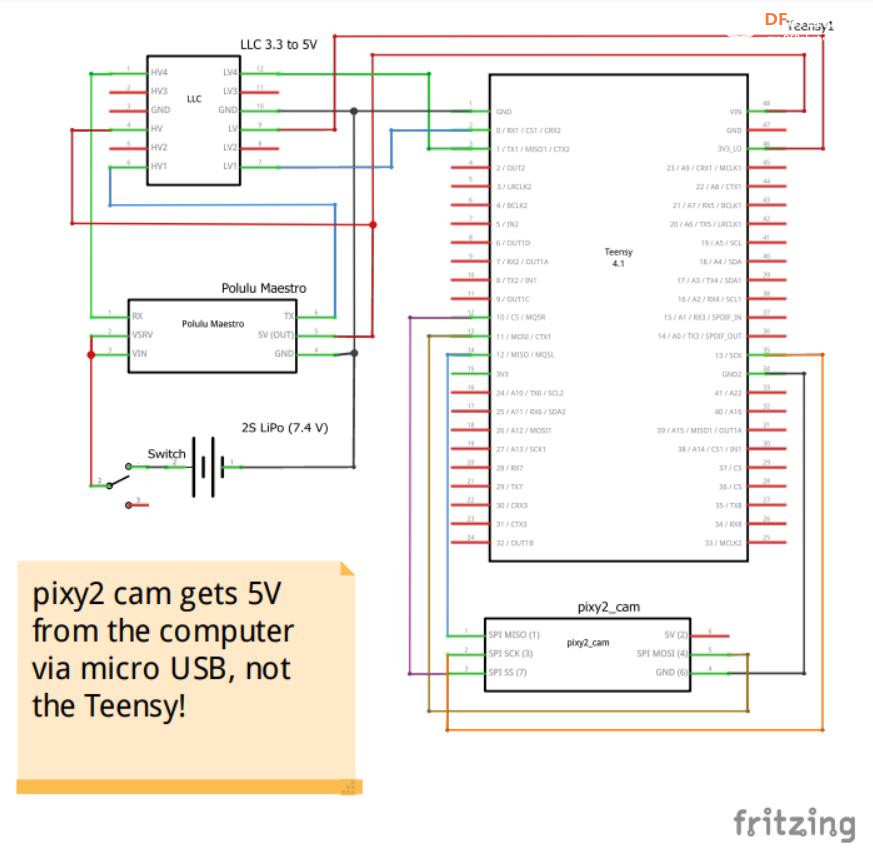
#define maestroSerial SERIAL_PORT_HARDWARE_OPEN //for teensy
// objects
Pixy2SPI_SS pixy;
MicroMaestro maestro(maestroSerial); // if using the Maestro Micro controller
//**CONSTANTS**
//-------------
float abs_0 = 4000; //ms position of absolute 0 degrees
float abs_90 = 8000; //ms position of absolute 90 degrees
float toDeg = 180 / PI; // radians to degrees conversion factor
int x = 0, y = 1, z = 2; // defines x, y, and z array indexes to be used
String ID[6] = { "a1", "a2", "b1", "b2", "c1", "c2" }; //servo ID's
//**USER DEFINED VALUES**
//----------------------
// angle range for each servo going CCW
// each servo can move from absolute 0 to absolute 90 degrees
// this defines a different range such as 90 to 180 degrees
float range[6][2] = { { -45, 45 }, { 45, -45 }, // a1, a2
{ -45, 45 },
{ 45, -45 }, // b1, b2
{ -45, 45 },
{ 45, -45 } }; // c1, c2
// angle offset value for each servo (should be less than 14 degrees since there are 25 teeth on the servo)
// redefines the position of the lower range of each servo
// Example: a servo with a range [0, 90] and an offset value of 5 would have its new 0 degree position where the old 5 degree position was
float offset[6] = { 0, 0, // channel #0 and channel #1
0, 0, // channel #2 and channel #3
0, 0 }; // channel #4 and channel #5
//**INVERSE KINEMATICS**
//----------------------
// user defined lengths (in mm)
float l0 = 73.025;
float lf = 67.775;
float d1 = 36.8893;
float d2 = 38.1;
float m = 12.7;
float p1 = 31.75;
float p2 = 129;
//calculates normal vectors nab, nac, and nbc for each side of the triangle
float nab[3] = { sqrt(3) * 0.5, -0.5, 0 };
float nac[3] = { sqrt(3) * 0.5, 0.5, 0 };
float nbc[3] = { 0, 1, 0 };
// intermediate variables
float t = (pow(lf, 2) * sqrt(3)) / 2;
float u = sqrt(pow(l0, 2) + pow(d1, 2)) * sin((2 * PI / 3) - atan(l0 / d1)); //(2*pi/3 is 120 degrees)
// calculates points a10, a20, b10, b20, c10, and c20
float a10[3] = { (d2 - u * sqrt(3)) / 2, (-u - d2 * sqrt(3)) / 2, 0 };
float a20[3] = { -a10[x], a10[y], 0 };
float b10[3] = { (u * sqrt(3) + d2) / 2, (d2 * sqrt(3) - u) / 2, 0 };
float b20[3] = { d2, u, 0 };
float c10[3] = { -b20[x], b20[y], 0 };
float c20[3] = { -b10[x], b10[y], 0 };
// calculates vectors, ab, ac, and bc
float ab[3] = { a20[x] - b10[x], a20[y] - b10[y], a20[z] - b10[z] };
float ac[3] = { a10[x] - c20[x], a10[y] - c20[y], a10[z] - c20[z] };
float bc[3] = { b20[x] - c10[x], b20[y] - c10[y], b20[z] - c10[z] };
float theta[6]; //array for calculated theta values a1, a2, b1, b2, c1, c2 respectively
float nz = 1; //nz is predefined
float hz_norm = 118.19374266158451; //normal hz value (at this height all servos are at 0 degrees)
float r_max = 0.25; // max radius of the nx and ny graph when nz = 1
//pixy2 cam
//----------------------
float origin[2] = { 0, 0 }; // X and Y co-ords of the origin
float r_platform = 0; // the distance from the center of the platform to the corner of the platform seen from the pixy2 cam
float ball[2]; // X and Y co-ords of the ball
// PID
//----------------------
float error[2]; // error of the ball
float error_prev[2]; // previous error value used to calculate derivative. Derivative = (error-previous_error)/(change in time)
float deriv[2]; // derivative of the error
float deriv_prev[2]; // previous derivative value
float kp = 6e-4; // proportional constant
float kd = 0.56; // derivative constant
float out[2]; // output values (nx and ny)
float time_i; // initial time
float time_f; // final time
float time; //change in time
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
maestroSerial.begin(9600);
pixy.init();
}
void loop() {
findBall(); // finds the location of the ball
if (ball[x] == 4004 && ball[y] == 4004) {
// sees if ball position (x and y) is 4004, if so then the ball is not detected and platform should be in home position
InverseKinematics(0, 0, hz_norm, 0, 0, 0); //hx, hy, hz, nx, ny, ax
moveServos(20, 20);
} else {
PD(); // calculates the proportional and derivative terms and outputs them to the platform
}
//Serial.println((String)"BALL LOCATION: [" + ball[x]+", "+ball[y]+"]"); //prints location of the ball
//Serial.println((String)"OUTPUT: [" + out[x]+", "+ out[y]+"]"); //prints the output values
}
//Functions
void moveServo(int i, float pos, int spd, int acc) { //moves servo i to an input position at a certain speed and acceleration value
pos = pos + offset[i]; //adds offset amount to the input position
pos = map(pos, range[i][0], range[i][1], abs_0, abs_90); //converts input pos to ms position
maestro.setSpeed(i, spd); //sets input speed to servo i
maestro.setAcceleration(i, spd); //sets input acceleration to servo i
maestro.setTarget(i, pos); //drives motor to calculated position
}
void moveServos(int spd, int acc) { //moves servos to their calculated positions at a certain speed and acceleration value
float pos;
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
maestro.setSpeed(i, spd); //sets input speed to servo i
maestro.setAcceleration(i, acc); //sets input acceleration to servo i
pos = theta[i] + offset[i]; //adds offset amount to the calculated angle
pos = map(pos, range[i][0], range[i][1], abs_0, abs_90); //converts input pos to ms position
maestro.setTarget(i, pos); //drives motor to calculated position
}
}
void stop() { //ends the program and stops all of the servos
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
maestro.setTarget(i, 0); //stops servo i
}
while (1) {}
}
void findBall() { // find the location of the ball using the pixy2 cam
// grab blocks!
pixy.ccc.getBlocks();
// If there is 1 ball detected then collect and print the data
if (pixy.ccc.numBlocks == 1) {
//sets current X and Y co-ords
ball[x] = pixy.ccc.blocks[0].m_x; // absolute X location of the ball
ball[y] = pixy.ccc.blocks[0].m_y; // absolute Y location of the ball
}
// If there are multiple balls detected, then print so
else if (pixy.ccc.numBlocks > 1) {
Serial.println("MULTIPLE BALLS DETECTED");
ball[x] = 4004; // X component of the ball
ball[y] = 4004; // Y component of the ball
}
// If there is no ball detected, then print so
else {
//Serial.println("NO BALL DETECTED");
ball[x] = 4004; // X component of the ball
ball[y] = 4004; // Y component of the ball
}
}
void PD() { // calculates the Proportional and Derivative values and moves the servos
// calculates the error of the ball
// the error is the difference of the location of the center of the ball and the center of the platform
// it is essentially a vector pointing from the center of the platform to the center of the ball
error[x] = origin[x] - ball[x]; // x component of error
error[y] = ball[y] - origin[y]; // y component of error
time_f = millis(); // sets final time
time = time_f - time_i; // change in time
time_i = millis();
// sets initial time
deriv[x] = (error[x] - error_prev[x]) / time; // x component of derivative
deriv[y] = (error[y] - error_prev[y]) / time; // y component of derivative
// checks if derivative is NaN or INF. If so, set to zero
if (isnan(deriv[x]) || isinf(deriv[x])) { // x component of derivative
deriv[x] = 0;
}
if (isnan(deriv[y]) || isinf(deriv[y])) { // y component of derivative
deriv[y] = 0;
}
// sets previous error to current error
error_prev[x] = error[x]; // x component of previous error
error_prev[y] = error[y]; // x component of previous error
float r_ball = sqrt(pow(error[x], 2) + pow(error[y], 2)); // calculates the distance from the center of the platfrom to the ball
if (r_ball > r_platform) {
// checks to see if the platform should be moved to the home position
// checks if the ball is on the platform by comparing r_ball and r_platform. If r_ball is greater than r_platform, the ball is off the platform and the platform should be in the home position
InverseKinematics(0, 0, hz_norm, 0, 0, 0); //hx, hy, hz, nx, ny, ax
moveServos(20, 20);
}
else { //if the ball should not be in the home position then calculate PD outputs
// output values
out[x] = (error[x] * kp) + (deriv[x] * kd); // calculates output x by adding proportional*kp and derivative*kd terms
out[y] = (error[y] * kp) + (deriv[y] * kd); // calculates output y by adding proportional*kp and derivative*kd terms
// error prevention
float r_out = sqrt(pow(out[x], 2) + pow(out[y], 2)); //calculates magnitude of the out vector
if (r_out > r_max) { // if the magnitude of the out vector is greater than r_max, then scale the out vector to have a magnitude of r
out[x] = out[x] * (r_max / r_out);
out[y] = out[y] * (r_max / r_out);
}
//move platform
InverseKinematics(0, 0, hz_norm, out[x], out[y], 0); //hx, hy, hz, nx, ny, ax
moveServos(0, 0);
}
}
void InverseKinematics(float hx, float hy, float hz, float nx, float ny, float ax) { // calculates theta values given hx, hy, hz, nx, ny, and ax (nz = 1 always)
//define vectors and points
float a[3] = { ax, 0, 0 }, a1f[3], a2f[3];
float b[3], b1f[3], b2f[3];
float c[3], c1f[3], c2f[3];
float n[3] = { nx, ny, nz }; // defines normal vector
n[x] = nx / mag(n);
n[y] = ny / mag(n);
n[z] = nz / mag(n); // converts vector 'n' to a unit vector
float h[3] = { hx, hy, hz }; // defined point h (center point of platform)
// **STAGE 1 CALCULATIONS**
//-------------------------
// in regards to e, g, and k indexes 0, 1, and 2 are a, b, and c respectively
float e[3], g[3], k[3];
// af components
e[0] = a[x] - h[x]; // 'ea'
a[z] = ((n[y] * sqrt(pow(lf, 2) * (1 - pow(n[x], 2)) - pow(e[0], 2)) - n[z] * n[x] * e[0]) / (1 - pow(n[x], 2))) + h[z]; // 'az'
g[0] = a[z] - h[z]; // calculates 'ga'
a[y] = h[y] - sqrt(pow(lf, 2) - pow(g[0], 2) - pow(e[0], 2)); // 'ay'
k[0] = a[y] - h[y]; // 'ka'
float w = sqrt(3) * (n[x] * g[0] - n[z] * e[0]); // intermediate variable
// bf components
b[y] = h[y] + ((sqrt(pow(w, 2) - 3 * pow(lf, 2) * (1 - pow(n[y], 2)) + pow(2 * k[0], 2)) - w) / 2); // 'by'
k[1] = b[y] - h[y]; // 'kb'
b[x] = ((e[0] * k[1] - n[z] * t) / k[0]) + h[x]; // 'bx'
e[1] = b[x] - h[x]; // 'eb'
b[z] = ((n[x] * t + g[0] * k[1]) / k[0]) + h[z]; //'bz'
g[1] = b[z] - h[z]; // 'gb'
// cf components
c[y] = h[y] + ((w + sqrt(pow(w, 2) - 3 * pow(lf, 2) * (1 - pow(n[y], 2)) + pow(2 * k[0], 2))) / 2); // 'cy'
k[2] = c[y] - h[y]; // 'kc'
c[x] = ((e[0] * k[2] + n[z] * t) / k[0]) + h[x]; // 'cx'
e[2] = c[x] - h[x]; // 'ec'
c[z] = ((g[0] * k[2] - n[x] * t) / k[0]) + h[z]; // 'cz'
g[2] = c[z] - h[z]; // 'gc'
// STAGE 2 CALCULATIONS
//---------------------
// a1
a1f[x] = a[x] + (m / lf) * (n[z] * k[0] - n[y] * g[0]); // a1fx
if (e[0] == 0) { //if e[0] is 0 then there will be a divide by zero error
a1f[y] = a[y]; // a1fy
a1f[z] = a[z]; // a1fz
} else {
a1f[y] = a[y] + ((a1f[x] - a[x]) * k[0] - n[z] * lf * m) / e[0]; // a1fy
a1f[z] = a[z] + (n[y] * lf * m + (a1f[x] - a[x]) * g[0]) / e[0]; // a1fz
}
float a1[3] = { a1f[x] - a10[x], a1f[y] - a10[y], a1f[z] - a10[z] }; // vector 'a1'
// a2
a2f[x] = 2 * a[x] - a1f[x]; // a2fx
a2f[y] = 2 * a[y] - a1f[y]; // a2fy
a2f[z] = 2 * a[z] - a1f[z]; // a2fz
float a2[3] = { a2f[x] - a20[x], a2f[y] - a20[y], a2f[z] - a20[z] }; // vector 'a2'
// b1
b1f[x] = b[x] + (m / lf) * (n[z] * k[1] - n[y] * g[1]); // b1fx
b1f[y] = b[y] + ((b1f[x] - b[x]) * k[1] - n[z] * lf * m) / e[1]; // b1fy
b1f[z] = b[z] + (n[y] * lf * m + (b1f[x] - b[x]) * g[1]) / e[1]; // b1fz
float b1[3] = { b1f[x] - b10[x], b1f[y] - b10[y], b1f[z] - b10[z] }; // vector 'b1'
// b2
b2f[x] = 2 * b[x] - b1f[x]; // b2fx
b2f[y] = 2 * b[y] - b1f[y]; // b2fy
b2f[z] = 2 * b[z] - b1f[z]; // b2fz
float b2[3] = { b2f[x] - b20[x], b2f[y] - b20[y], b2f[z] - b20[z] }; // vector 'b2'
// c1
c1f[x] = c[x] + (m / lf) * (n[z] * k[2] - n[y] * g[2]); // c1fx
c1f[y] = c[y] + ((c1f[x] - c[x]) * k[2] - n[z] * lf * m) / e[2]; // c1fy
c1f[z] = c[z] + (n[y] * lf * m + (c1f[x] - c[x]) * g[2]) / e[2]; // c1fz
float c1[3] = { c1f[x] - c10[x], c1f[y] - c10[y], c1f[z] - c10[z] }; // vector 'c1'
// c2
c2f[x] = 2 * c[x] - c1f[x]; // c2fx
c2f[y] = 2 * c[y] - c1f[y]; // c2fy
c2f[z] = 2 * c[z] - c1f[z]; // c2fzSerial.println("-----------------------");
float c2[3] = { c2f[x] - c20[x], c2f[y] - c20[y], c2f[z] - c20[z] }; // vector 'c2'
//**STAGE 3 CALCULATIONS**
//------------------------
// theta_a1
float a1s[3] = { nac[x] * dot(a1, nac), nac[y] * dot(a1, nac), nac[z] * dot(a1, nac) }; // vector 'a1s'
float mag_a1s = mag(a1s); // magnitude of vector 'a1s'
float a1_proj[3] = { a1[x] - a1s[x], a1[y] - a1s[y], a1[z] - a1s[z] }; // projection of vector 'a1' onto the ac plane
float mag_a1_proj = mag(a1_proj); // magnitude of vector 'a1' projected on the ac plane
float mag_p2a1 = sqrt(pow(p2, 2) - pow(mag_a1s, 2)); // magnitude of link p2 projected on the ac plane
theta[0] = acos(-dot(a1_proj, ac) / (2 * d2 * mag_a1_proj)); // theta a1
theta[0] = (theta[0] - acos((pow(mag_a1_proj, 2) + pow(p1, 2) - pow(mag_p2a1, 2)) / (2 * mag_a1_proj * p1))) * toDeg; // theta a1 continued calculation
// theta_a2
float a2s[3] = { nab[x] * dot(a2, nab), nab[y] * dot(a2, nab), nab[z] * dot(a2, nab) }; // vector 'a2s'
float mag_a2s = mag(a2s); // magnitude of vector 'a2s'
float a2_proj[3] = { a2[x] - a2s[x], a2[y] - a2s[y], a2[z] - a2s[z] }; // projection of vector 'a2' onto the ab plane
float mag_a2_proj = mag(a2_proj); // magnitude of vector 'a2' projected on the ab plane
float mag_p2a2 = sqrt(pow(p2, 2) - pow(mag_a2s, 2)); // magnitude of link p2 projected on the ab plane
theta[1] = acos(-dot(a2_proj, ab) / (2 * d2 * mag_a2_proj)); // theta a2
theta[1] = (theta[1] - acos((pow(mag_a2_proj, 2) + pow(p1, 2) - pow(mag_p2a2, 2)) / (2 * mag_a2_proj * p1))) * toDeg; // theta a2 continued calculation
// theta_b1
float b1s[3] = { nab[x] * dot(b1, nab), nab[y] * dot(b1, nab), nab[z] * dot(b1, nab) }; // vector 'b1s'
float mag_b1s = mag(b1s); // magnitude of vector 'b1s'
float b1_proj[3] = { b1[x] - b1s[x], b1[y] - b1s[y], b1[z] - b1s[z] }; // projection of vector 'b1' onto the ab plane
float mag_b1_proj = mag(b1_proj); // magnitude of vector 'b1' projected on the ab plane
float mag_p2b1 = sqrt(pow(p2, 2) - pow(mag_b1s, 2)); // magnitude of link p2 projected on the ab plane
theta[2] = acos(dot(b1_proj, ab) / (2 * d2 * mag_b1_proj)); // theta b1
theta[2] = (theta[2] - acos((pow(mag_b1_proj, 2) + pow(p1, 2) - pow(mag_p2b1, 2)) / (2 * mag_b1_proj * p1))) * toDeg; // theta b1 continued calculation
// theta_b2
float b2s[3] = { nbc[x] * dot(b2, nbc), nbc[y] * dot(b2, nbc), nbc[z] * dot(b2, nbc) }; // vector 'b2s'
float mag_b2s = mag(b2s); // magnitude of vector 'b2s'
float b2_proj[3] = { b2[x] - b2s[x], b2[y] - b2s[y], b2[z] - b2s[z] }; // projection of vector 'b2' onto the bc plane
float mag_b2_proj = mag(b2_proj); // magnitude of vector 'b2' projected on the bc plane
float mag_p2b2 = sqrt(pow(p2, 2) - pow(mag_b2s, 2)); // magnitude of link p2 projected on the bc plane
theta[3] = acos(-dot(b2_proj, bc) / (2 * d2 * mag_b2_proj)); // theta b2
theta[3] = (theta[3] - acos((pow(mag_b2_proj, 2) + pow(p1, 2) - pow(mag_p2b2, 2)) / (2 * mag_b2_proj * p1))) * toDeg; // theta b2 continued calculation
// theta_c1
float c1s[3] = { nbc[x] * dot(c1, nbc), nbc[y] * dot(c1, nbc), nbc[z] * dot(c1, nbc) }; // vector 'c1s'
float mag_c1s = mag(c1s); // magnitude of vector 'c1s'
float c1_proj[3] = { c1[x] - c1s[x], c1[y] - c1s[y], c1[z] - c1s[z] }; // projection of vector 'c1' onto the bc plane
float mag_c1_proj = mag(c1_proj); // magnitude of vector 'c1' projected on the bc plane
float mag_p2c1 = sqrt(pow(p2, 2) - pow(mag_c1s, 2)); // magnitude of link p2 projected on the bc plane
theta[4] = acos(dot(c1_proj, bc) / (2 * d2 * mag_c1_proj)); // theta c1
theta[4] = (theta[4] - acos((pow(mag_c1_proj, 2) + pow(p1, 2) - pow(mag_p2c1, 2)) / (2 * mag_c1_proj * p1))) * toDeg; // theta c1 continued calculation
//theta_c2
float c2s[3] = { nac[x] * dot(c2, nac), nac[y] * dot(c2, nac), nac[z] * dot(c2, nac) }; // vector 'c2s'
float mag_c2s = mag(c2s); // magnitude of vector 'c2s'
float c2_proj[3] = { c2[x] - c2s[x], c2[y] - c2s[y], c2[z] - c2s[z] }; // projection of vector 'c2' onto the ac plane
float mag_c2_proj = mag(c2_proj); // magnitude of vector 'c2' projected on the ac plane
float mag_p2c2 = sqrt(pow(p2, 2) - pow(mag_c2s, 2)); // magnitude of link p2 projected on the ac plane
theta[5] = acos(dot(c2_proj, ac) / (2 * d2 * mag_c2_proj)); // theta c2
theta[5] = (theta[5] - acos((pow(mag_c2_proj, 2) + pow(p1, 2) - pow(mag_p2c2, 2)) / (2 * mag_c2_proj * p1))) * toDeg; // theta c2 continued calculation
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) { //checks for errors to see if theta values are between -40 and 40 degrees and if they are real numbers
//Serial.print(String("theta "+ID[i]+": ")); // prints servo ID
//Serial.println(theta[i], 6); // prints theta value
if (abs(theta[i]) > 40) {
Serial.println("ERROR: CURRENT VALUES EXCEED ANGLE RANGE");
stop();
}
if (isnan(theta[i])) {
Serial.println("ERROR: CURRENT VALUES CANNOT PHYSICALLY BE EXECUTED");
stop();
}
}
}
float mag(float array[]) { //finds the magnitude of an array of size 3
float mag = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
mag = mag + pow(array[i], 2); //adds component i of array squared
}
mag = sqrt(mag);
return mag;
}
float dot(float array1[], float array2[]) { //calculates the dot product of two arrays
return array1[0] * array2[0] + array1[1] * array2[1] + array1[2] * array2[2];
} 复制代码 
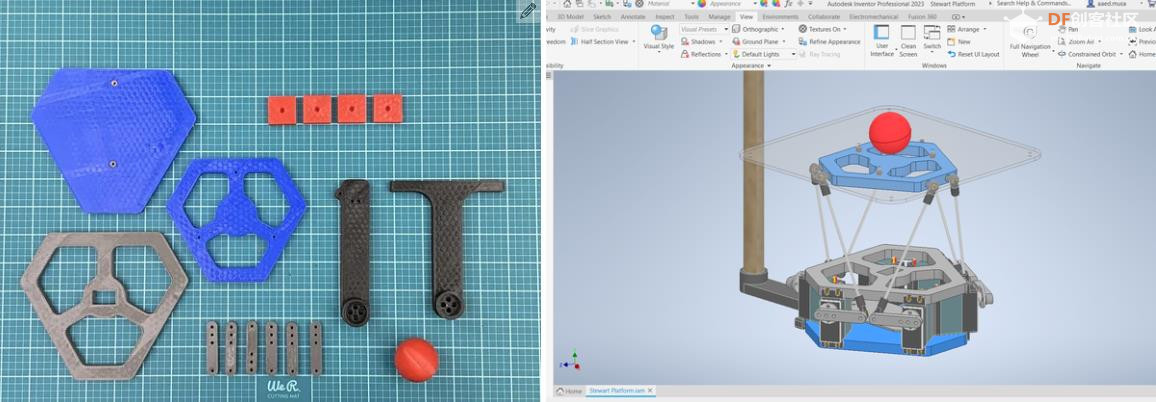
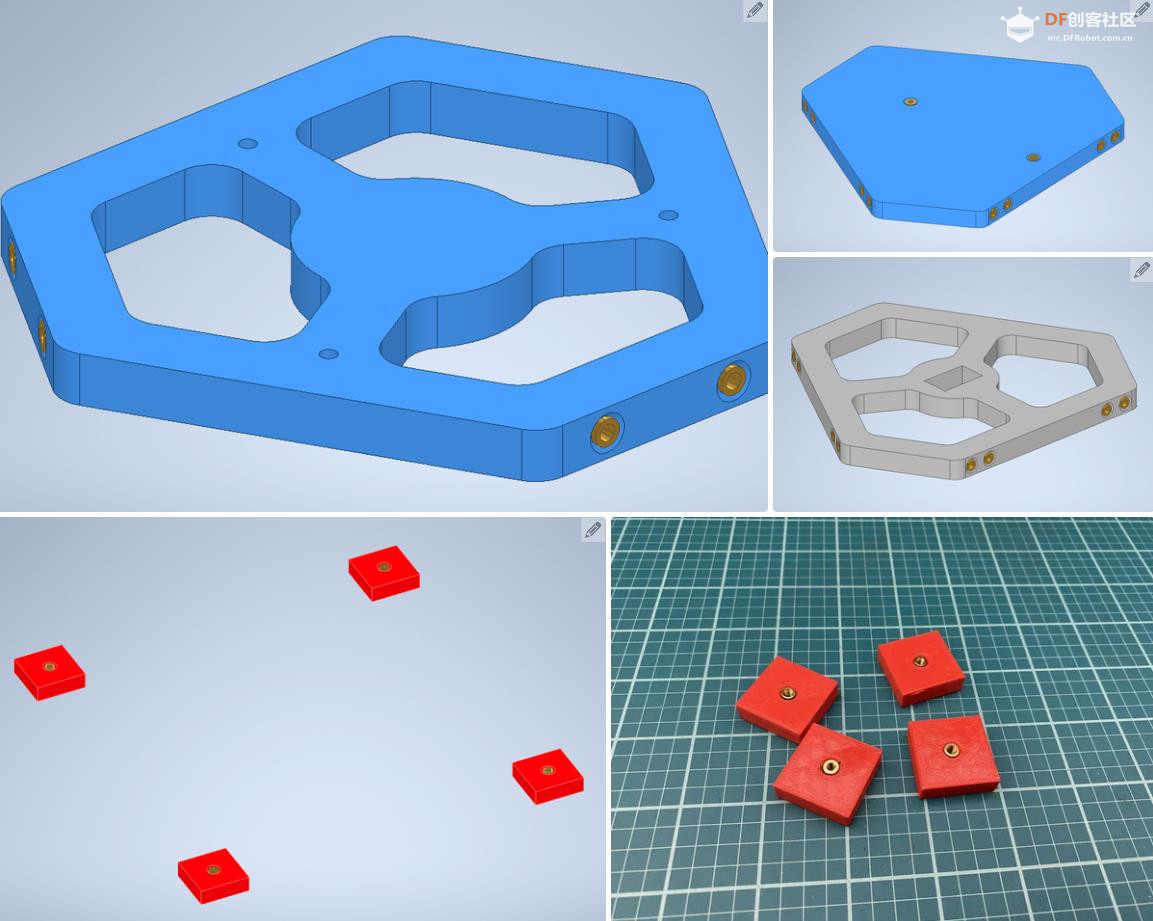
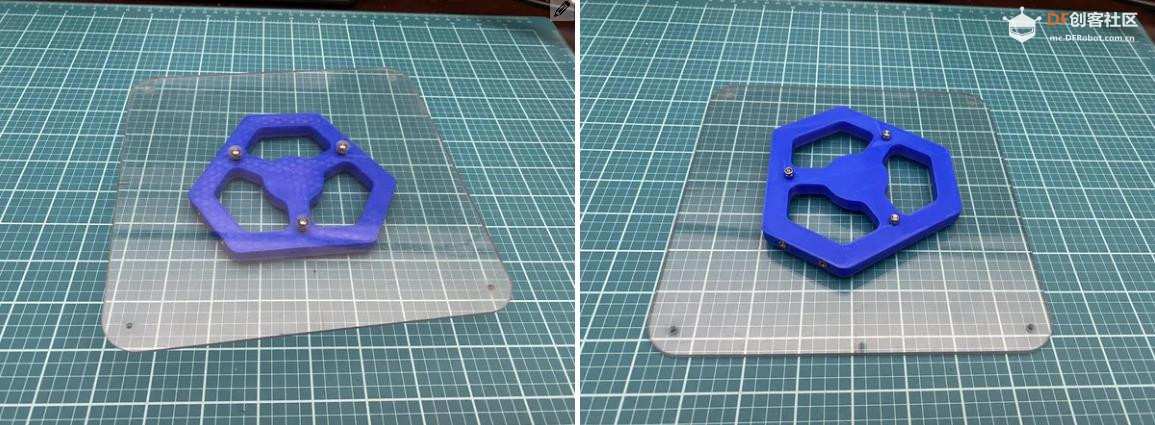


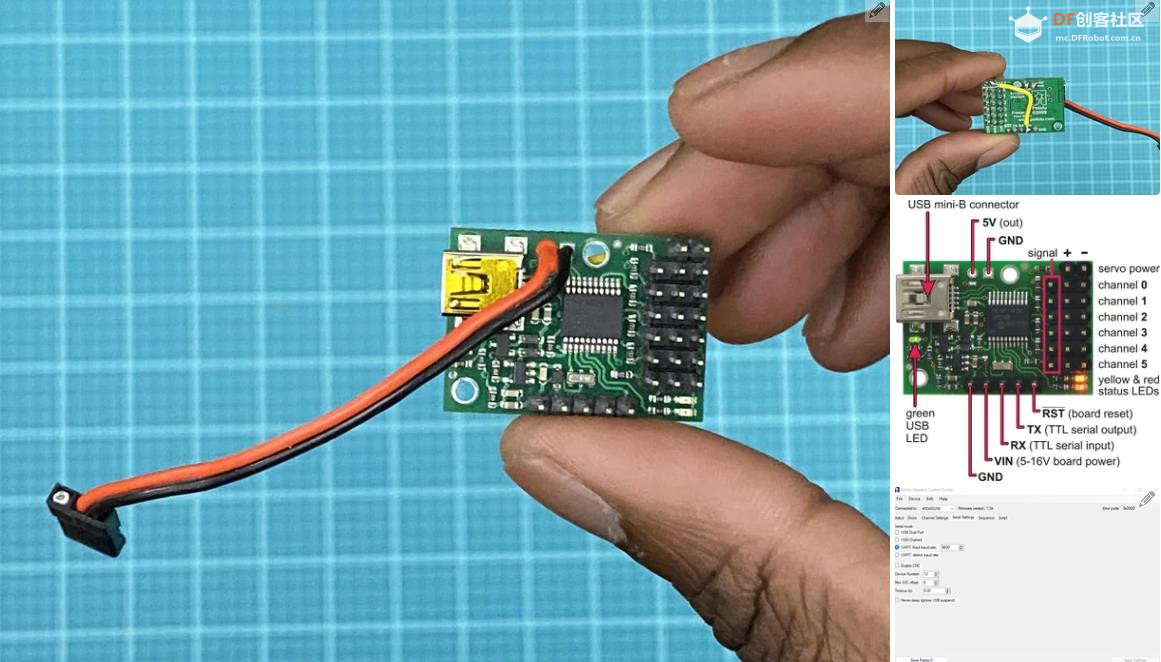
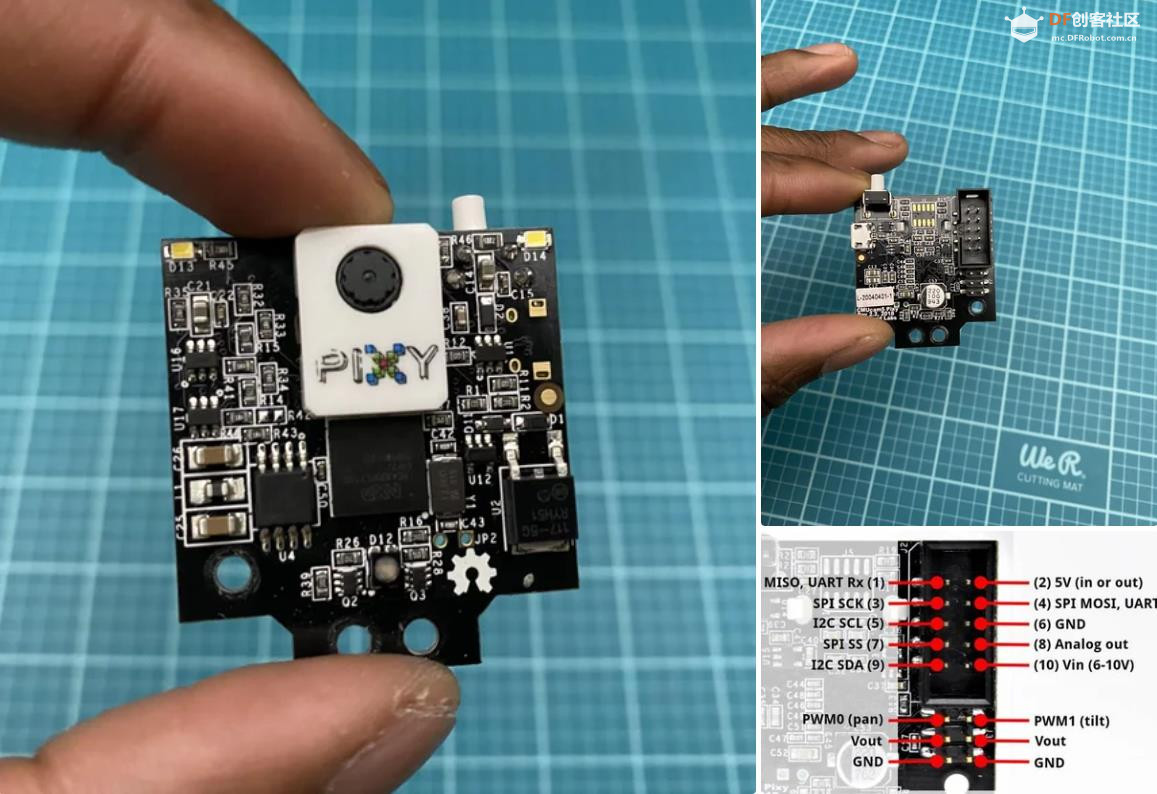
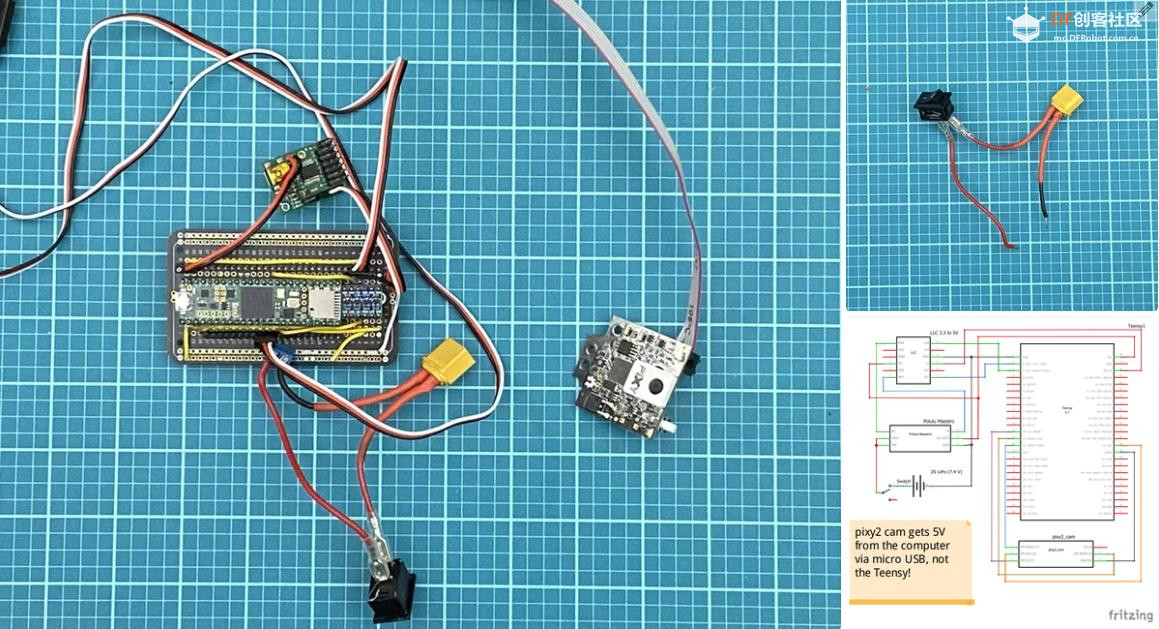
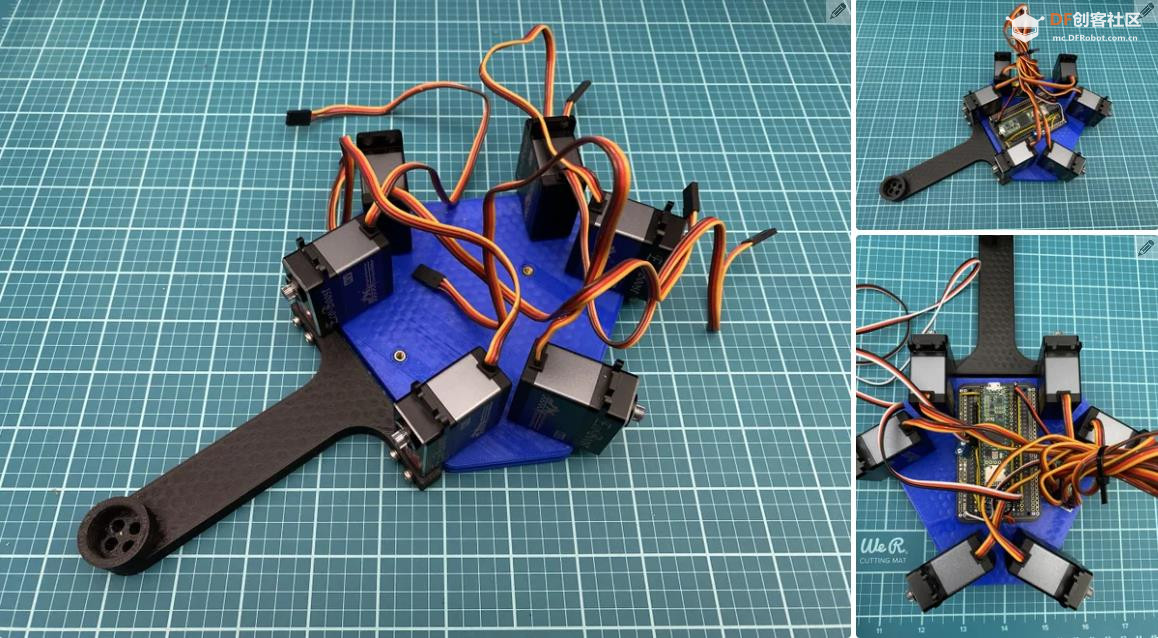
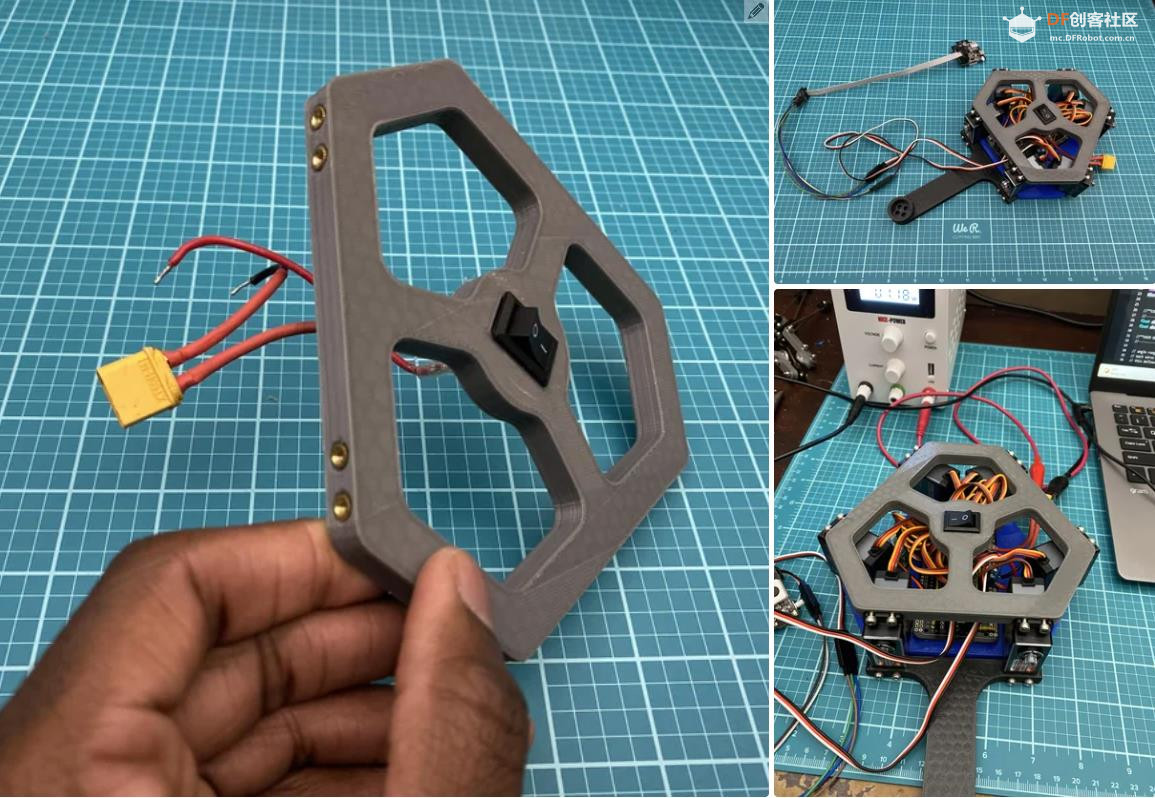




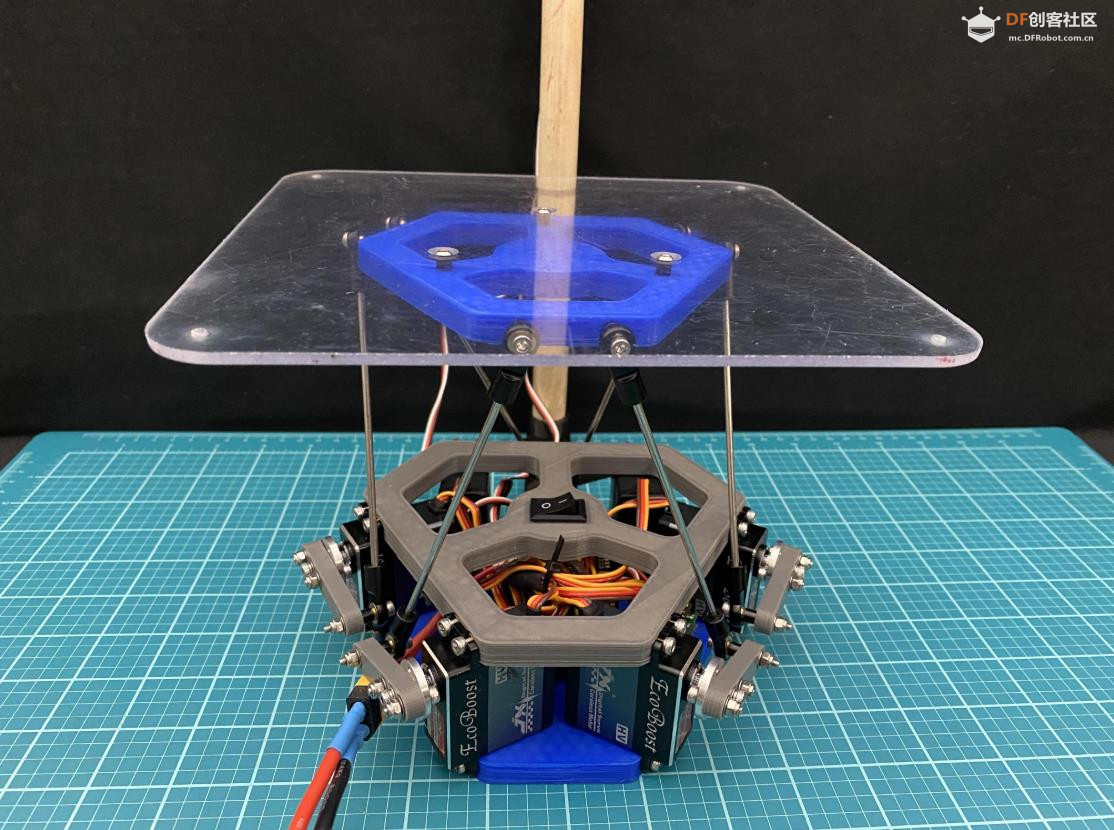
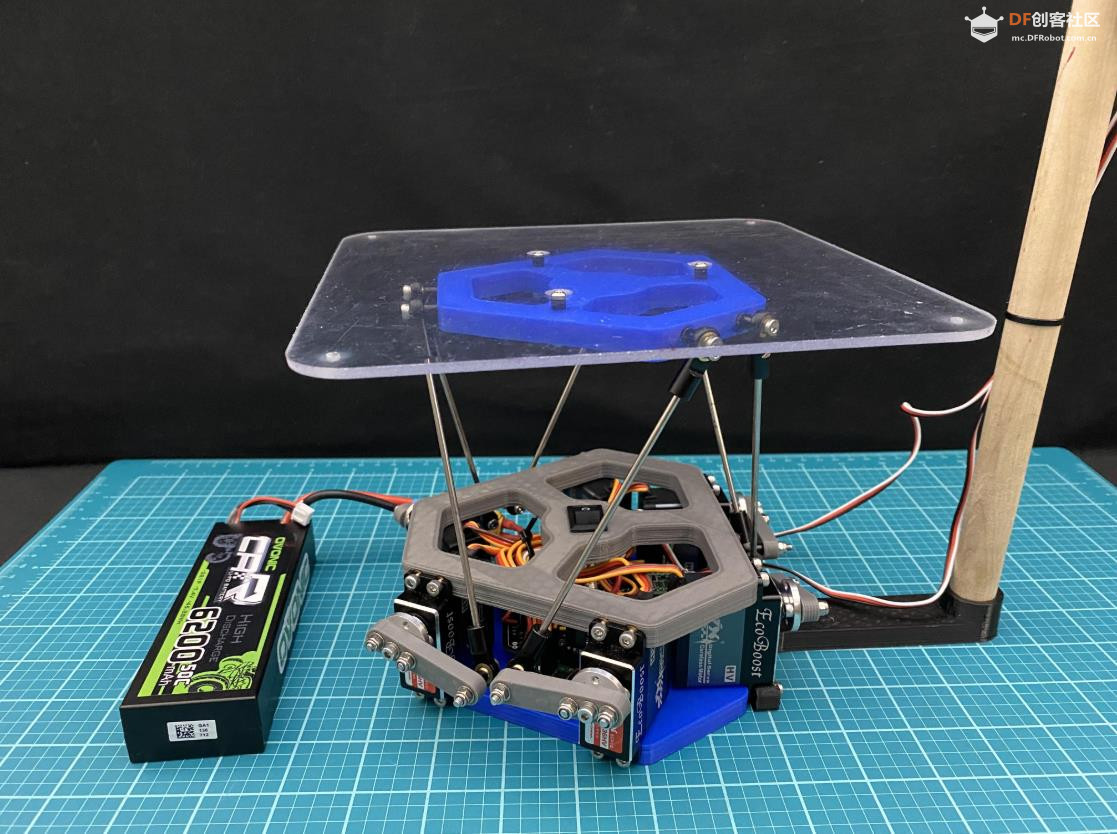
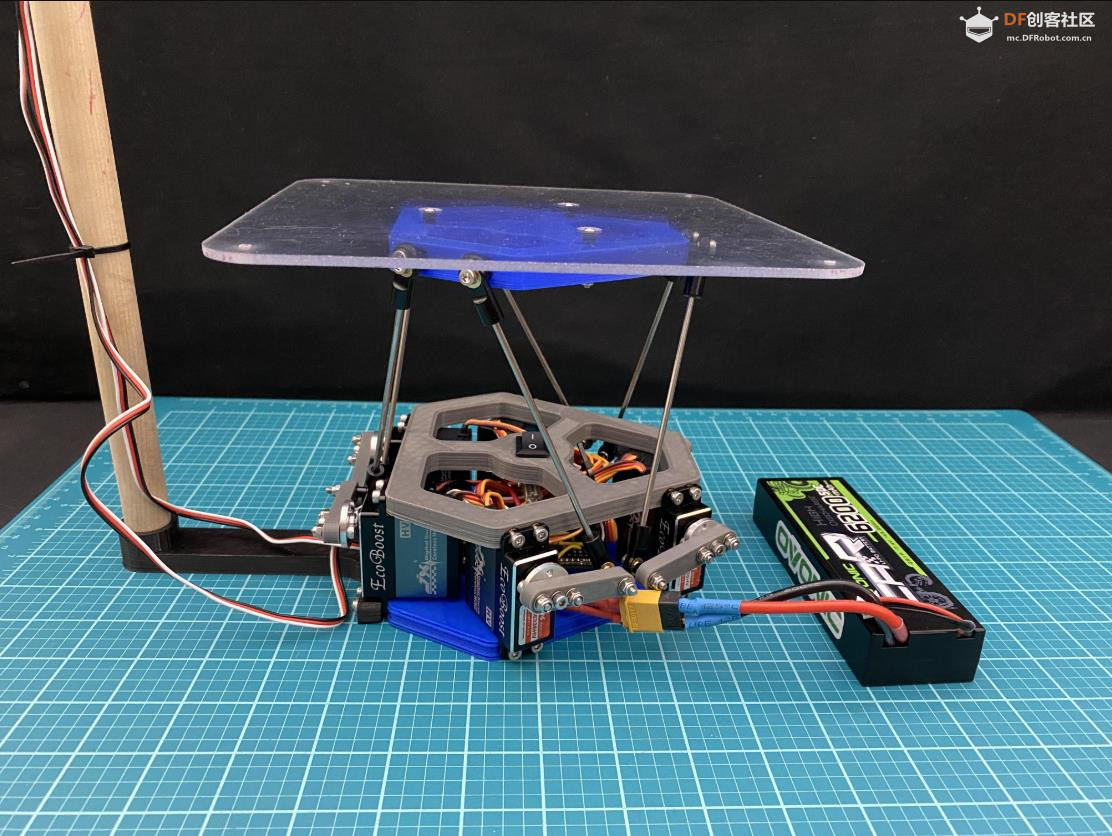
 沪公网安备31011502402448
沪公网安备31011502402448