【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+仿真编程+图形编程)
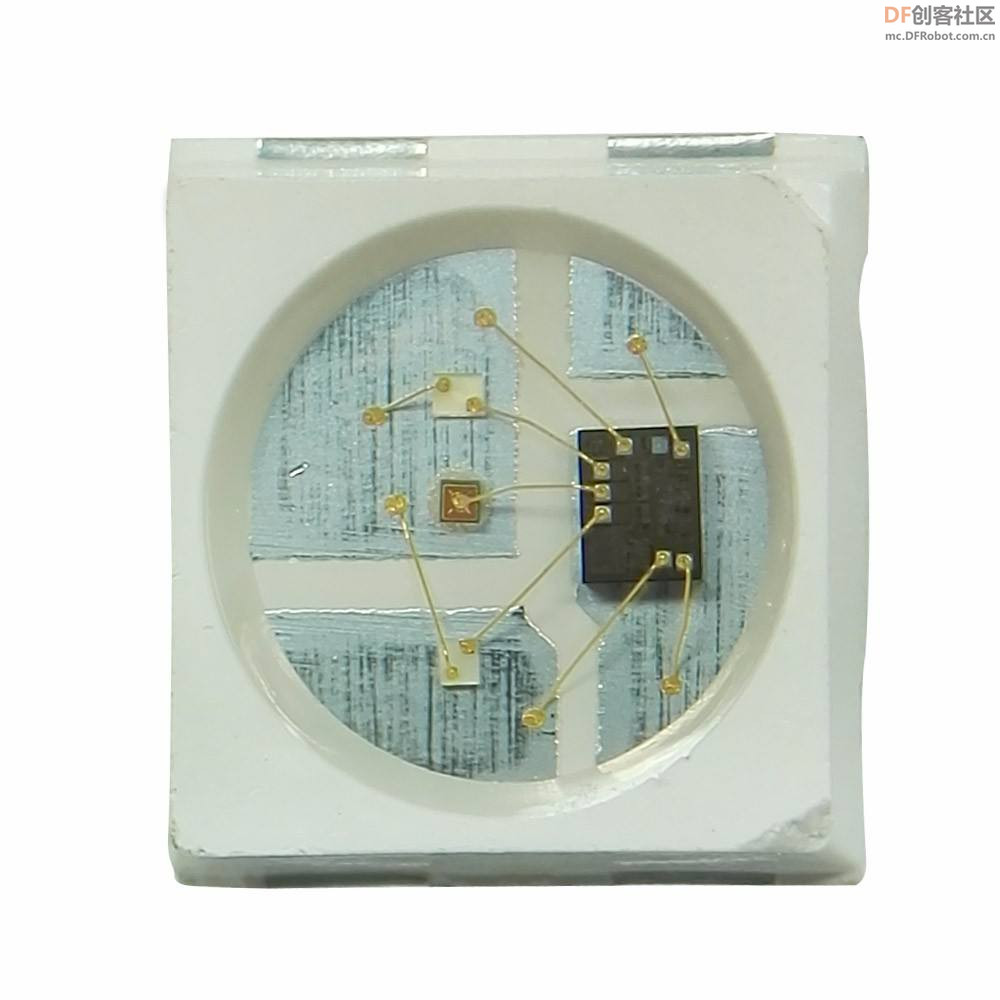
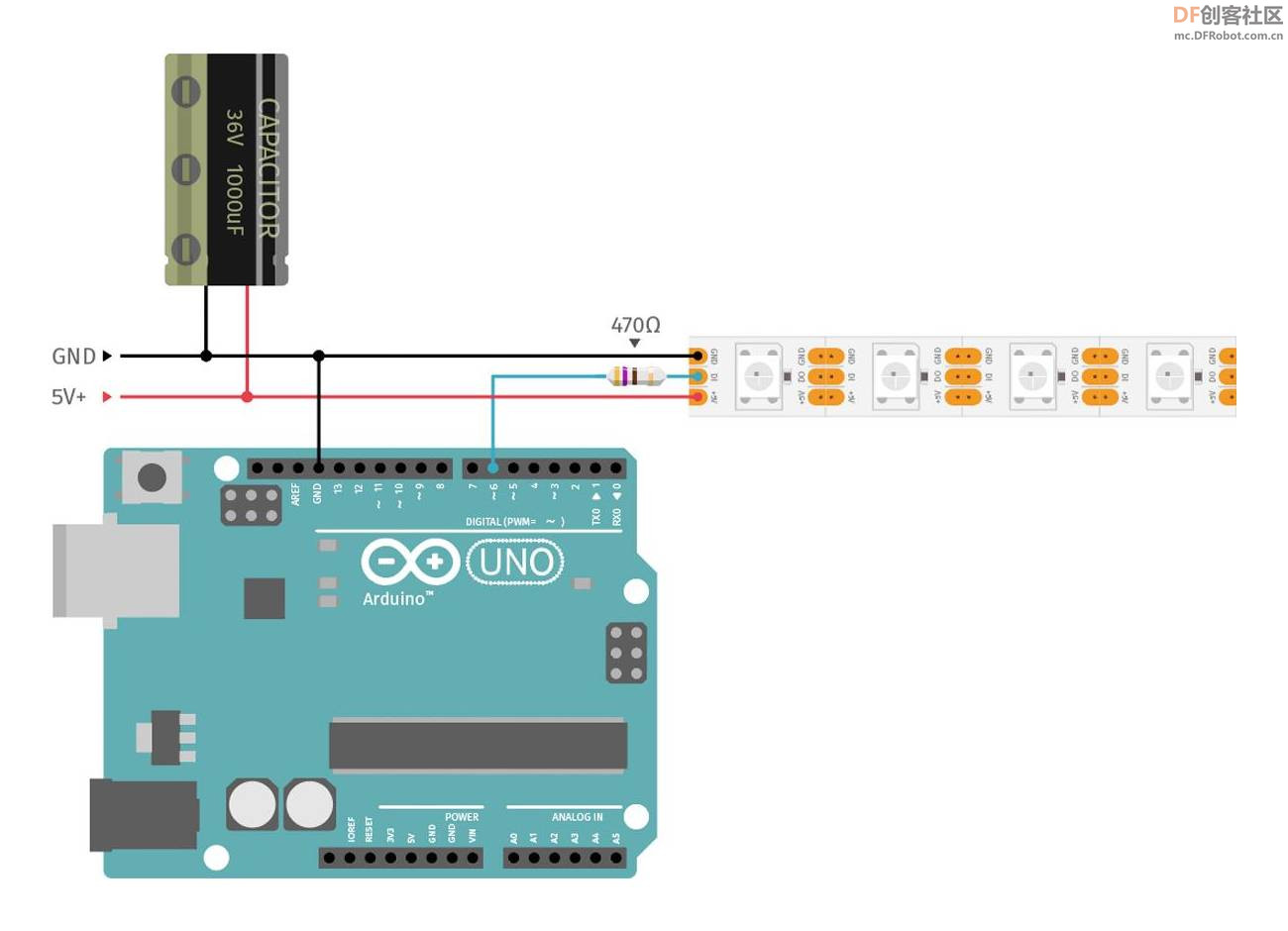
实验二百一十六:WS2812B幻彩LED灯带 5V全彩灯条5050灯珠内置IC炫彩单点单控软灯条模块
实验程序十九:八种模式的LED闪烁效果
*/
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#include <FastLED.h>
#include <EEPROM.h>
#define PIN 6
#define N_PIXELS 24
#define BG 0
#define COLOR_ORDER GRB // Try mixing up the letters (RGB, GBR, BRG, etc) for a whole new world of color combinations
#define BRIGHTNESS 50 // 0-255, higher number is brighter.
#define LED_TYPE WS2812B
#define MIC_PIN A4 // Microphone is attached to this analog pin
#define DC_OFFSET 10 // DC offset in mic signal - if unusure, leave 0
#define NOISE 10 // Noise/hum/interference in mic signal
#define SAMPLES 60 // Length of buffer for dynamic level adjustment
#define TOP (N_PIXELS + 2) // Allow dot to go slightly off scale
#define PEAK_FALL 20 // Rate of peak falling dot
#define N_PIXELS_HALF (N_PIXELS/2)
#define GRAVITY -9.81 // Downward (negative) acceleration of gravity in m/s^2
#define h0 1 // Starting height, in meters, of the ball (strip length)
#define NUM_BALLS 3 // Number of bouncing balls you want (recommend < 7, but 20 is fun in its own way)
#define SPEED .20 // Amount to increment RGB color by each cycle
int brightnessPin = A0, potPin = A1;
//config for balls
float h[NUM_BALLS] ; // An array of heights
float vImpact0 = sqrt( -2 * GRAVITY * h0 ); // Impact velocity of the ball when it hits the ground if "dropped" from the top of the strip
float vImpact[NUM_BALLS] ; // As time goes on the impact velocity will change, so make an array to store those values
float tCycle[NUM_BALLS] ; // The time since the last time the ball struck the ground
int pos[NUM_BALLS] ; // The integer position of the dot on the strip (LED index)
long tLast[NUM_BALLS] ; // The clock time of the last ground strike
float COR[NUM_BALLS] ; // Coefficient of Restitution (bounce damping)
float
greenOffset = 30,
blueOffset = 150;
byte
peak = 0, // Used for falling dot
dotCount = 0, // Frame counter for delaying dot-falling speed
volCount = 0; // Frame counter for storing past volume data
int
vol[SAMPLES], // Collection of prior volume samples
lvl = 10, // Current "dampened" audio level
minLvlAvg = 0, // For dynamic adjustment of graph low & high
maxLvlAvg = 512;
int brightnessValue, prevBrightnessValue;
int sensorDeviationBrightness = 1;
int sensitivityValue = 128; // 0 - 255, initial value (value read from the potentiometer if useSensorValues = true)
int maxSensitivity = 2 * 255; // let the 'volume' go up to 200%!
int ledBrightness = 255; // 0 - 255, initial value (value read from the potentiometer if useSensorValues = true)
int val;
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip = Adafruit_NeoPixel(N_PIXELS, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
// FOR SYLON ETC
uint8_t thisbeat = 23;
uint8_t thatbeat = 28;
uint8_t thisfade = 2; // How quickly does it fade? Lower = slower fade rate.
uint8_t thissat = 255; // The saturation, where 255 = brilliant colours.
uint8_t thisbri = 255;
//FOR JUGGLE
uint8_t numdots = 4; // Number of dots in use.
uint8_t faderate = 2; // How long should the trails be. Very low value = longer trails.
uint8_t hueinc = 16; // Incremental change in hue between each dot.
uint8_t thishue = 0; // Starting hue.
uint8_t curhue = 0;
uint8_t thisbright = 255; // How bright should the LED/display be.
uint8_t basebeat = 5;
uint8_t max_bright = 255;
// Twinkle
float redStates[N_PIXELS];
float blueStates[N_PIXELS];
float greenStates[N_PIXELS];
float Fade = 0.96;
// Vu meter 4
const uint32_t Red = strip.Color(255, 0, 0);
const uint32_t Yellow = strip.Color(255, 255, 0);
const uint32_t Green = strip.Color(0, 255, 0);
const uint32_t Blue = strip.Color(0, 0, 255);
const uint32_t White = strip.Color(255, 255, 255);
const uint32_t Dark = strip.Color(0, 0, 0);
unsigned int sample;
CRGB leds[N_PIXELS];
int myhue = 0;
// constants used here to set pin numbers:
const int buttonPin = 3; // the number of the pushbutton pin
// Variables will change:
int buttonPushCounter = 0; // counter for the number of button presses
int buttonState = 0; // current state of the button
int lastButtonState = 0;
//Ripple variables
int color;
int center = 0;
int step = -1;
int maxSteps = 8;
float fadeRate = 0.80;
int diff;
//background color
uint32_t currentBg = random(256);
uint32_t nextBg = currentBg;
void setup() {
delay( 2000 ); // power-up safety delay
FastLED.addLeds<WS2812B, PIN, COLOR_ORDER>(leds, N_PIXELS).setCorrection( TypicalLEDStrip );
FastLED.setBrightness( BRIGHTNESS );
analogReference(EXTERNAL);
memset(vol, 0, sizeof(vol));
LEDS.addLeds<LED_TYPE, PIN, COLOR_ORDER>(leds, N_PIXELS);
strip.begin();
strip.show(); // Initialize all pixels to 'off'
//initialize the serial port
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);
pinMode(2, OUTPUT);
//initialize the buttonPin as output
digitalWrite(buttonPin, HIGH);
digitalWrite(2, HIGH);
for (int i = 0 ; i < NUM_BALLS ; i++) { // Initialize variables
tLast[i] = millis();
h[i] = h0;
pos[i] = 0; // Balls start on the ground
vImpact[i] = vImpact0; // And "pop" up at vImpact0
tCycle[i] = 0;
COR[i] = 0.90 - float(i)/pow(NUM_BALLS,2);
}
}
void loop() {
brightnessValue = analogRead(brightnessPin);
brightnessValue = map(brightnessValue, 0, 1023, 0, 255);
if (abs(brightnessValue - prevBrightnessValue) > sensorDeviationBrightness) {
ledBrightness = brightnessValue;
strip.setBrightness(ledBrightness);
prevBrightnessValue = brightnessValue;
}
//for mic
uint8_t i;
uint16_t minLvl, maxLvl;
int n, height;
// end mic
buttonPushCounter=EEPROM.read(0);
// read the pushbutton input pin:
buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin);
// compare the buttonState to its previous state
if (buttonState != lastButtonState) {
// if the state has changed, increment the counter
if (buttonState == HIGH) {
// if the current state is HIGH then the button
// wend from off to on:
buttonPushCounter++;
Serial.println("on");
Serial.print("number of button pushes: ");
Serial.println(buttonPushCounter);
if(buttonPushCounter>=14) {
buttonPushCounter=1;}
EEPROM.write(0,buttonPushCounter);
}
else {
// if the current state is LOW then the button
// wend from on to off:
Serial.println("off");
}
}
// save the current state as the last state,
//for next time through the loop
lastButtonState = buttonState;
switch (buttonPushCounter){
case 1:
buttonPushCounter==1; {
vu(); // Red
break;}
case 2:
buttonPushCounter==2; {
vu2(); // Red
break;}
case 3:
buttonPushCounter==3; {
Vu3(); //
break;}
case 4:
buttonPushCounter==4; {
Vu4(); //
break;}
case 5:
buttonPushCounter==5; {
rainbow(150);
break;}
case 6:
buttonPushCounter==6; {
rainbow(20);
break;}
case 7:
buttonPushCounter==7; {
ripple();
break;}
case 8:
buttonPushCounter==8; {
ripple2();
break;}
case 9:
buttonPushCounter==9; {
Twinkle();
break;}
case 10:
buttonPushCounter==10; {
pattern2();
break;}
case 11:
buttonPushCounter==11; {
pattern3();
break;}
case 12:
buttonPushCounter==12; {
Balls(); //
break;}
case 13:
buttonPushCounter==13; {
colorWipe(strip.Color(0, 0, 0), 10); // A Black
break;}
}
}
void colorWipe(uint32_t c, uint8_t wait) {
for(uint16_t i=0; i<strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, c);
strip.show();
if (digitalRead(buttonPin) != lastButtonState) // <------------- add this
return; // <------------ and this
delay(wait);
}
}
void Vu4() {
uint8_t i;
uint16_t minLvl, maxLvl;
int n, height;
val = (analogRead(potPin));
val= map(val, 0, 1023, -10, 6);
n = analogRead(MIC_PIN); // Raw reading from mic
n = abs(n - 0 - DC_OFFSET); // Center on zero
n = (n <= NOISE) ? 0 : (n - NOISE); // Remove noise/hum
if(val<0){
n=n/(val*(-1));
}
if(val>0){
n=n*val;
}
lvl = ((lvl * 7) + n) >> 3; // "Dampened" reading (else looks twitchy)
// Calculate bar height based on dynamic min/max levels (fixed point):
height = TOP * (lvl - minLvlAvg) / (long)(maxLvlAvg - minLvlAvg);
if(height < 0L) height = 0; // Clip output
else if(height > TOP) height = TOP;
if(height > peak) peak = height; // Keep 'peak' dot at top
greenOffset += SPEED;
blueOffset += SPEED;
if (greenOffset >= 255) greenOffset = 0;
if (blueOffset >= 255) blueOffset = 0;
// Color pixels based on rainbow gradient
for(i=0; i<N_PIXELS_HALF; i++) {
if(i >= height) {
strip.setPixelColor(N_PIXELS_HALF-i-1, 0, 0, 0);
strip.setPixelColor(N_PIXELS_HALF+i, 0, 0, 0);
}
else {
uint32_t color = Wheel(map(i,0,N_PIXELS_HALF-1,(int)greenOffset, (int)blueOffset));
strip.setPixelColor(N_PIXELS_HALF-i-1,color);
strip.setPixelColor(N_PIXELS_HALF+i,color);
}
}
// Draw peak dot
if(peak > 0 && peak <= N_PIXELS_HALF-1) {
uint32_t color = Wheel(map(peak,0,N_PIXELS_HALF-1,30,150));
strip.setPixelColor(N_PIXELS_HALF-peak-1,color);
strip.setPixelColor(N_PIXELS_HALF+peak,color);
}
strip.show(); // Update strip
// Every few frames, make the peak pixel drop by 1:
if(++dotCount >= PEAK_FALL) { //fall rate
if(peak > 0) peak--;
dotCount = 0;
}
vol[volCount] = n; // Save sample for dynamic leveling
if(++volCount >= SAMPLES) volCount = 0; // Advance/rollover sample counter
// Get volume range of prior frames
minLvl = maxLvl = vol[0];
for(i=1; i<SAMPLES; i++) {
if(vol[i] < minLvl) minLvl = vol[i];
else if(vol[i] > maxLvl) maxLvl = vol[i];
}
// minLvl and maxLvl indicate the volume range over prior frames, used
// for vertically scaling the output graph (so it looks interesting
// regardless of volume level). If they're too close together though
// (e.g. at very low volume levels) the graph becomes super coarse
// and 'jumpy'...so keep some minimum distance between them (this
// also lets the graph go to zero when no sound is playing):
if((maxLvl - minLvl) < TOP) maxLvl = minLvl + TOP;
minLvlAvg = (minLvlAvg * 63 + minLvl) >> 6; // Dampen min/max levels
maxLvlAvg = (maxLvlAvg * 63 + maxLvl) >> 6; // (fake rolling average)
}
void Vu3() {
uint8_t i;
uint16_t minLvl, maxLvl;
int n, height;
val = (analogRead(potPin));
val= map(val, 0, 1023, -10, 6);
n = analogRead(MIC_PIN); // Raw reading from mic
n = abs(n - 0 - DC_OFFSET); // Center on zero
n = (n <= NOISE) ? 0 : (n - NOISE); // Remove noise/hum
if(val<0){
n=n/(val*(-1));
}
if(val>0){
n=n*val;
}
lvl = ((lvl * 7) + n) >> 3; // "Dampened" reading (else looks twitchy)
// Calculate bar height based on dynamic min/max levels (fixed point):
height = TOP * (lvl - minLvlAvg) / (long)(maxLvlAvg - minLvlAvg);
if (height < 0L) height = 0; // Clip output
else if (height > TOP) height = TOP;
if (height > peak) peak = height; // Keep 'peak' dot at top
greenOffset += SPEED;
blueOffset += SPEED;
if (greenOffset >= 255) greenOffset = 0;
if (blueOffset >= 255) blueOffset = 0;
// Color pixels based on rainbow gradient
for (i = 0; i < N_PIXELS; i++) {
if (i >= height) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, 0, 0, 0);
} else {
strip.setPixelColor(i, Wheel(
map(i, 0, strip.numPixels() - 1, (int)greenOffset, (int)blueOffset)
));
}
}
// Draw peak dot
if(peak > 0 && peak <= N_PIXELS-1) strip.setPixelColor(peak,Wheel(map(peak,0,strip.numPixels()-1,30,150)));
strip.show(); // Update strip
// Every few frames, make the peak pixel drop by 1:
if(++dotCount >= PEAK_FALL) { //fall rate
if(peak > 0) peak--;
dotCount = 0;
}
strip.show(); // Update strip
vol[volCount] = n;
if (++volCount >= SAMPLES) {
volCount = 0;
}
// Get volume range of prior frames
minLvl = maxLvl = vol[0];
for (i = 1; i < SAMPLES; i++) {
if (vol[i] < minLvl) {
minLvl = vol[i];
} else if (vol[i] > maxLvl) {
maxLvl = vol[i];
}
}
// minLvl and maxLvl indicate the volume range over prior frames, used
// for vertically scaling the output graph (so it looks interesting
// regardless of volume level). If they're too close together though
// (e.g. at very low volume levels) the graph becomes super coarse
// and 'jumpy'...so keep some minimum distance between them (this
// also lets the graph go to zero when no sound is playing):
if ((maxLvl - minLvl) < TOP) {
maxLvl = minLvl + TOP;
}
minLvlAvg = (minLvlAvg * 63 + minLvl) >> 6; // Dampen min/max levels
maxLvlAvg = (maxLvlAvg * 63 + maxLvl) >> 6; // (fake rolling average)
}
void Balls() {
for (int i = 0 ; i < NUM_BALLS ; i++) {
tCycle[i] = millis() - tLast[i] ; // Calculate the time since the last time the ball was on the ground
// A little kinematics equation calculates positon as a function of time, acceleration (gravity) and intial velocity
h[i] = 0.5 * GRAVITY * pow( tCycle[i]/1000 , 2.0 ) + vImpact[i] * tCycle[i]/1000;
if ( h[i] < 0 ) {
h[i] = 0; // If the ball crossed the threshold of the "ground," put it back on the ground
vImpact[i] = COR[i] * vImpact[i] ; // and recalculate its new upward velocity as it's old velocity * COR
tLast[i] = millis();
if ( vImpact[i] < 0.01 ) vImpact[i] = vImpact0; // If the ball is barely moving, "pop" it back up at vImpact0
}
pos[i] = round( h[i] * (N_PIXELS - 1) / h0); // Map "h" to a "pos" integer index position on the LED strip
}
//Choose color of LEDs, then the "pos" LED on
for (int i = 0 ; i < NUM_BALLS ; i++) leds[pos[i]] = CHSV( uint8_t (i * 40) , 255, 255);
FastLED.show();
//Then off for the next loop around
for (int i = 0 ; i < NUM_BALLS ; i++) {
leds[pos[i]] = CRGB::Black;
}
}
// Slightly different, this makes the rainbow equally distributed throughout
void rainbowCycle(uint8_t wait) {
uint16_t i, j;
for(j=0; j<256*5; j++) { // 5 cycles of all colors on wheel
for(i=0; i< strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, Wheel(((i * 256 / strip.numPixels()) + j) & 255));
}
strip.show();
if (digitalRead(buttonPin) != lastButtonState) // <------------- add this
return; // <------------ and this
delay(wait);
}
}
// HERE
void vu() {
uint8_t i;
uint16_t minLvl, maxLvl;
int n, height;
val = (analogRead(potPin));
val= map(val, 0, 1023, -10, 6);
n = analogRead(MIC_PIN); // Raw reading from mic
n = abs(n - 0 - DC_OFFSET); // Center on zero
n = (n <= NOISE) ? 0 : (n - NOISE); // Remove noise/hum
if(val<0){
n=n/(val*(-1));
}
if(val>0){
n=n*val;
}
lvl = ((lvl * 7) + n) >> 3; // "Dampened" reading (else looks twitchy)
// Calculate bar height based on dynamic min/max levels (fixed point):
height = TOP * (lvl - minLvlAvg) / (long)(maxLvlAvg - minLvlAvg);
if(height < 0L) height = 0; // Clip output
else if(height > TOP) height = TOP;
if(height > peak) peak = height; // Keep 'peak' dot at top
// Color pixels based on rainbow gradient
for(i=0; i<N_PIXELS; i++) {
if(i >= height) strip.setPixelColor(i, 0, 0, 0);
else strip.setPixelColor(i,Wheel(map(i,0,strip.numPixels()-1,30,150)));
}
// Draw peak dot
if(peak > 0 && peak <= N_PIXELS-1) strip.setPixelColor(peak,Wheel(map(peak,0,strip.numPixels()-1,30,150)));
strip.show(); // Update strip
// Every few frames, make the peak pixel drop by 1:
if(++dotCount >= PEAK_FALL) { //fall rate
if(peak > 0) peak--;
dotCount = 0;
}
vol[volCount] = n; // Save sample for dynamic leveling
if(++volCount >= SAMPLES) volCount = 0; // Advance/rollover sample counter
// Get volume range of prior frames
minLvl = maxLvl = vol[0];
for(i=1; i<SAMPLES; i++) {
if(vol[i] < minLvl) minLvl = vol[i];
else if(vol[i] > maxLvl) maxLvl = vol[i];
}
// minLvl and maxLvl indicate the volume range over prior frames, used
// for vertically scaling the output graph (so it looks interesting
// regardless of volume level). If they're too close together though
// (e.g. at very low volume levels) the graph becomes super coarse
// and 'jumpy'...so keep some minimum distance between them (this
// also lets the graph go to zero when no sound is playing):
if((maxLvl - minLvl) < TOP) maxLvl = minLvl + TOP;
minLvlAvg = (minLvlAvg * 63 + minLvl) >> 6; // Dampen min/max levels
maxLvlAvg = (maxLvlAvg * 63 + maxLvl) >> 6; // (fake rolling average)
}
// Input a value 0 to 255 to get a color value.
// The colors are a transition r - g - b - back to r.
uint32_t Wheel(byte WheelPos) {
if(WheelPos < 85) {
return strip.Color(WheelPos * 3, 255 - WheelPos * 3, 0);
} else if(WheelPos < 170) {
WheelPos -= 85;
return strip.Color(255 - WheelPos * 3, 0, WheelPos * 3);
} else {
WheelPos -= 170;
return strip.Color(0, WheelPos * 3, 255 - WheelPos * 3);
}
}
void vu2() {
uint8_t i;
uint16_t minLvl, maxLvl;
int n, height;
val = (analogRead(potPin));
val= map(val, 0, 1023, -10, 6);
n = analogRead(MIC_PIN); // Raw reading from mic
n = abs(n - 0 - DC_OFFSET); // Center on zero
n = (n <= NOISE) ? 0 : (n - NOISE); // Remove noise/hum
if(val<0){
n=n/(val*(-1));
}
if(val>0){
n=n*val;
}
lvl = ((lvl * 7) + n) >> 3; // "Dampened" reading (else looks twitchy)
// Calculate bar height based on dynamic min/max levels (fixed point):
height = TOP * (lvl - minLvlAvg) / (long)(maxLvlAvg - minLvlAvg);
if(height < 0L) height = 0; // Clip output
else if(height > TOP) height = TOP;
if(height > peak) peak = height; // Keep 'peak' dot at top
// Color pixels based on rainbow gradient
for(i=0; i<N_PIXELS_HALF; i++) {
if(i >= height) {
strip.setPixelColor(N_PIXELS_HALF-i-1, 0, 0, 0);
strip.setPixelColor(N_PIXELS_HALF+i, 0, 0, 0);
}
else {
uint32_t color = Wheel(map(i,0,N_PIXELS_HALF-1,30,150));
strip.setPixelColor(N_PIXELS_HALF-i-1,color);
strip.setPixelColor(N_PIXELS_HALF+i,color);
}
}
// Draw peak dot
if(peak > 0 && peak <= N_PIXELS_HALF-1) {
uint32_t color = Wheel(map(peak,0,N_PIXELS_HALF-1,30,150));
strip.setPixelColor(N_PIXELS_HALF-peak-1,color);
strip.setPixelColor(N_PIXELS_HALF+peak,color);
}
strip.show(); // Update strip
// Every few frames, make the peak pixel drop by 1:
if(++dotCount >= PEAK_FALL) { //fall rate
if(peak > 0) peak--;
dotCount = 0;
}
vol[volCount] = n; // Save sample for dynamic leveling
if(++volCount >= SAMPLES) volCount = 0; // Advance/rollover sample counter
// Get volume range of prior frames
minLvl = maxLvl = vol[0];
for(i=1; i<SAMPLES; i++) {
if(vol[i] < minLvl) minLvl = vol[i];
else if(vol[i] > maxLvl) maxLvl = vol[i];
}
// minLvl and maxLvl indicate the volume range over prior frames, used
// for vertically scaling the output graph (so it looks interesting
// regardless of volume level). If they're too close together though
// (e.g. at very low volume levels) the graph becomes super coarse
// and 'jumpy'...so keep some minimum distance between them (this
// also lets the graph go to zero when no sound is playing):
if((maxLvl - minLvl) < TOP) maxLvl = minLvl + TOP;
minLvlAvg = (minLvlAvg * 63 + minLvl) >> 6; // Dampen min/max levels
maxLvlAvg = (maxLvlAvg * 63 + maxLvl) >> 6; // (fake rolling average)
}
//here................
void ripple() {
if (currentBg == nextBg) {
nextBg = random(256);
}
else if (nextBg > currentBg) {
currentBg++;
} else {
currentBg--;
}
for(uint16_t l = 0; l < N_PIXELS; l++) {
leds[l] = CHSV(currentBg, 255, 50); // strip.setPixelColor(l, Wheel(currentBg, 0.1));
}
if (step == -1) {
center = random(N_PIXELS);
color = random(256);
step = 0;
}
if (step == 0) {
leds[center] = CHSV(color, 255, 255); // strip.setPixelColor(center, Wheel(color, 1));
step ++;
}
else {
if (step < maxSteps) {
Serial.println(pow(fadeRate,step));
leds[wrap(center + step)] = CHSV(color, 255, pow(fadeRate, step)*255); // strip.setPixelColor(wrap(center + step), Wheel(color, pow(fadeRate, step)));
leds[wrap(center - step)] = CHSV(color, 255, pow(fadeRate, step)*255); // strip.setPixelColor(wrap(center - step), Wheel(color, pow(fadeRate, step)));
if (step > 3) {
leds[wrap(center + step - 3)] = CHSV(color, 255, pow(fadeRate, step - 2)*255); // strip.setPixelColor(wrap(center + step - 3), Wheel(color, pow(fadeRate, step - 2)));
leds[wrap(center - step + 3)] = CHSV(color, 255, pow(fadeRate, step - 2)*255); // strip.setPixelColor(wrap(center - step + 3), Wheel(color, pow(fadeRate, step - 2)));
}
step ++;
}
else {
step = -1;
}
}
LEDS.show();
delay(50);
}
int wrap(int step) {
if(step < 0) return N_PIXELS + step;
if(step > N_PIXELS - 1) return step - N_PIXELS;
return step;
}
void one_color_allHSV(int ahue, int abright) { // SET ALL LEDS TO ONE COLOR (HSV)
for (int i = 0 ; i < N_PIXELS; i++ ) {
leds[i] = CHSV(ahue, 255, abright);
}
}
void ripple2() {
if (BG){
if (currentBg == nextBg) {
nextBg = random(256);
}
else if (nextBg > currentBg) {
currentBg++;
} else {
currentBg--;
}
for(uint16_t l = 0; l < N_PIXELS; l++) {
strip.setPixelColor(l, Wheel(currentBg, 0.1));
}
} else {
for(uint16_t l = 0; l < N_PIXELS; l++) {
strip.setPixelColor(l, 0, 0, 0);
}
}
if (step == -1) {
center = random(N_PIXELS);
color = random(256);
step = 0;
}
if (step == 0) {
strip.setPixelColor(center, Wheel(color, 1));
step ++;
}
else {
if (step < maxSteps) {
strip.setPixelColor(wrap(center + step), Wheel(color, pow(fadeRate, step)));
strip.setPixelColor(wrap(center - step), Wheel(color, pow(fadeRate, step)));
if (step > 3) {
strip.setPixelColor(wrap(center + step - 3), Wheel(color, pow(fadeRate, step - 2)));
strip.setPixelColor(wrap(center - step + 3), Wheel(color, pow(fadeRate, step - 2)));
}
step ++;
}
else {
step = -1;
}
}
strip.show();
delay(50);
}
//int wrap(int step) {
// if(step < 0) return Pixels + step;
// if(step > Pixels - 1) return step - Pixels;
// return step;
//}
// Input a value 0 to 255 to get a color value.
// The colours are a transition r - g - b - back to r.
uint32_t Wheel(byte WheelPos, float opacity) {
if(WheelPos < 85) {
return strip.Color((WheelPos * 3) * opacity, (255 - WheelPos * 3) * opacity, 0);
}
else if(WheelPos < 170) {
WheelPos -= 85;
return strip.Color((255 - WheelPos * 3) * opacity, 0, (WheelPos * 3) * opacity);
}
else {
WheelPos -= 170;
return strip.Color(0, (WheelPos * 3) * opacity, (255 - WheelPos * 3) * opacity);
}
}
void pattern2() {
sinelon(); // Call our sequence.
show_at_max_brightness_for_power(); // Power managed display of LED's.
} // loop()
void sinelon() {
// a colored dot sweeping back and forth, with fading trails
fadeToBlackBy( leds, N_PIXELS, thisfade);
int pos1 = beatsin16(thisbeat,0,N_PIXELS);
int pos2 = beatsin16(thatbeat,0,N_PIXELS);
leds[(pos1+pos2)/2] += CHSV( myhue++/64, thissat, thisbri);
}
// Pattern 3 - JUGGLE
void pattern3() {
ChangeMe();
juggle();
show_at_max_brightness_for_power(); // Power managed display of LED's.
} // loop()
void juggle() { // Several colored dots, weaving in and out of sync with each other
curhue = thishue; // Reset the hue values.
fadeToBlackBy(leds, N_PIXELS, faderate);
for( int i = 0; i < numdots; i++) {
leds[beatsin16(basebeat+i+numdots,0,N_PIXELS)] += CHSV(curhue, thissat, thisbright); //beat16 is a FastLED 3.1 function
curhue += hueinc;
}
} // juggle()
void ChangeMe() { // A time (rather than loop) based demo sequencer. This gives us full control over the length of each sequence.
uint8_t secondHand = (millis() / 1000) % 30; // IMPORTANT!!! Change '30' to a different value to change duration of the loop.
static uint8_t lastSecond = 99; // Static variable, means it's only defined once. This is our 'debounce' variable.
if (lastSecond != secondHand) { // Debounce to make sure we're not repeating an assignment.
lastSecond = secondHand;
if (secondHand == 0) {numdots=1; faderate=2;} // You can change values here, one at a time , or altogether.
if (secondHand == 10) {numdots=4; thishue=128; faderate=8;}
if (secondHand == 20) {hueinc=48; thishue=random8();} // Only gets called once, and not continuously for the next several seconds. Therefore, no rainbows.
}
} // ChangeMe()
void Twinkle () {
if (random(25) == 1) {
uint16_t i = random(N_PIXELS);
if (redStates[i] < 1 && greenStates[i] < 1 && blueStates[i] < 1) {
redStates[i] = random(256);
greenStates[i] = random(256);
blueStates[i] = random(256);
}
}
for(uint16_t l = 0; l < N_PIXELS; l++) {
if (redStates[l] > 1 || greenStates[l] > 1 || blueStates[l] > 1) {
strip.setPixelColor(l, redStates[l], greenStates[l], blueStates[l]);
if (redStates[l] > 1) {
redStates[l] = redStates[l] * Fade;
} else {
redStates[l] = 0;
}
if (greenStates[l] > 1) {
greenStates[l] = greenStates[l] * Fade;
} else {
greenStates[l] = 0;
}
if (blueStates[l] > 1) {
blueStates[l] = blueStates[l] * Fade;
} else {
blueStates[l] = 0;
}
} else {
strip.setPixelColor(l, 0, 0, 0);
}
}
strip.show();
delay(10);
}
// TOO HERE
void rainbow(uint8_t wait) {
uint16_t i, j;
for(j=0; j<256; j++) {
for(i=0; i<strip.numPixels(); i++) {
strip.setPixelColor(i, Wheel((i+j) & 255));
}
strip.show();
// check if a button pressed
if (digitalRead(buttonPin) != lastButtonState) // <------------- add this
return; // <------------ and this
delay(wait);
}
} 复制代码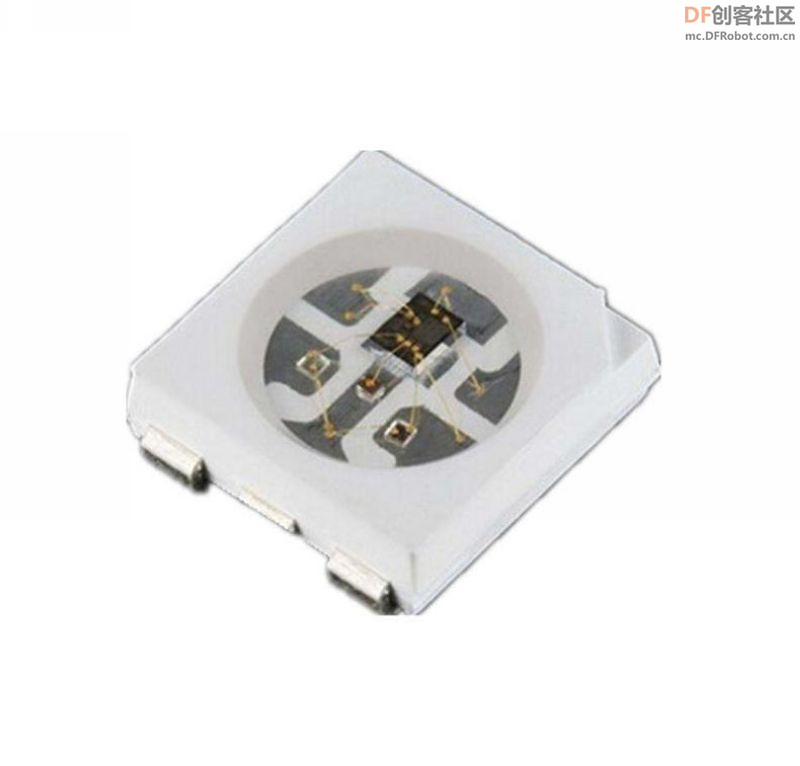 

 沪公网安备31011502402448
沪公网安备31011502402448