加速度计和陀螺仪是101一大特色,当然得玩玩啦,就是冲这个来的嘛。本来我还在纠结怎么获取传感器的数据?怎么对数据进行滤波?怎么对数据进行融合?但是,这些现在都变的简单了,有现成的库文件CurieIMU和MadgwickAHRS可以用来获取和处理传感器得到的数据。
【产品链接】: Arduino 101
咳咳,玩起来:
1.下载程序:
在库文件中能找到六轴姿态传感器驱动库libraries\CurieIMU,里面有测试程序Accelerometer,这个程序一开始没有对数据进行校正,可以手动天加一下校正代码就好了,下面是添加好校正代码的程序:
/*
Copyright (c) 2015 Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.
This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
Lesser General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
*/
/*
This sketch example demonstrates how the BMI160 on the
Intel(R) Curie(TM) module can be used to read accelerometer data
*/
\#include <CurieIMU.h>
int calibrateOffsets = 1; // int to determine whether calibration takes place or not
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // initialize Serial communication
while (!Serial); // wait for the serial port to open
// initialize device
Serial.println("Initializing IMU device...");
CurieIMU.begin();
if (calibrateOffsets == 1) {
// use the code below to calibrate accel/gyro offset values
Serial.println("Internal sensor offsets BEFORE calibration...");
Serial.print(CurieIMU.getAccelerometerOffset(X_AXIS)); Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(CurieIMU.getAccelerometerOffset(Y_AXIS)); Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(CurieIMU.getAccelerometerOffset(Z_AXIS)); Serial.print("\t");
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Starting Acceleration calibration...");
CurieIMU.autoCalibrateAccelerometerOffset(X_AXIS, 0);
CurieIMU.autoCalibrateAccelerometerOffset(Y_AXIS, 0);
CurieIMU.autoCalibrateAccelerometerOffset(Z_AXIS, 1);
Serial.println(" Done");
Serial.println("Internal sensor offsets AFTER calibration...");
Serial.print(CurieIMU.getAccelerometerOffset(X_AXIS)); Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(CurieIMU.getAccelerometerOffset(Y_AXIS)); Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(CurieIMU.getAccelerometerOffset(Z_AXIS)); Serial.print("\t");
Serial.println("");
}
// Set the accelerometer range to 2G
CurieIMU.setAccelerometerRange(2);
}
void loop() {
int axRaw, ayRaw, azRaw; // raw accelerometer values
float ax, ay, az;
// read raw accelerometer measurements from device
CurieIMU.readAccelerometer(axRaw, ayRaw, azRaw);
// convert the raw accelerometer data to G's
ax = convertRawAcceleration(axRaw);
ay = convertRawAcceleration(ayRaw);
az = convertRawAcceleration(azRaw);
// display tab-separated accelerometer x/y/z values
Serial.print("a:\t");
Serial.print(ax);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(ay);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(az);
Serial.println();
// wait 5 seconds
delay(500);
}
float convertRawAcceleration(int aRaw) {
// since we are using 2G range
// -2g maps to a raw value of -32768
// +2g maps to a raw value of 32767
float a = (aRaw * 2.0) / 32768.0;
return a;
}
串口读出来的数据,很准确,可以转动板子看看每个轴的数据变化:
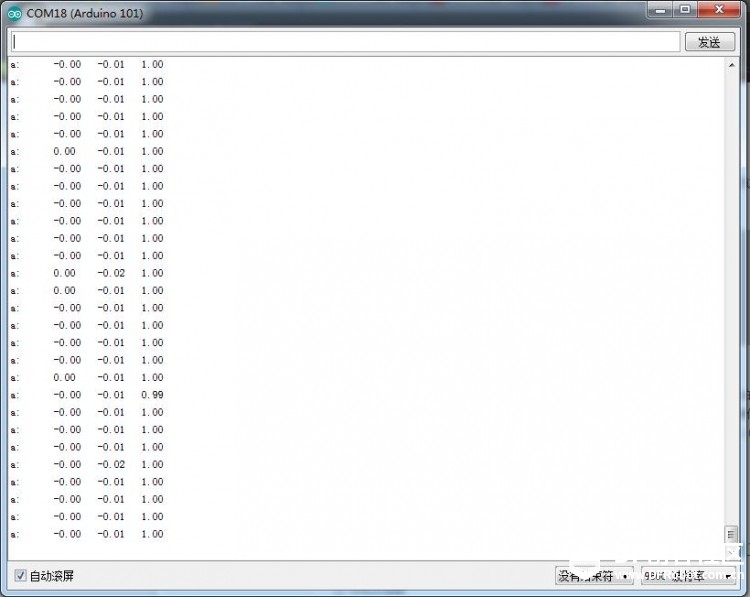
2.读取陀螺仪的数据:
下载程序,在库文件中能找到六轴姿态传感器驱动库libraries\CurieIMU,里面有测试程序Gyro,同样加几句代码事先校正一下数据,下面是添加好校正代码的程序:
/*
Copyright (c) 2015 Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.
This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
Lesser General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
*/
/*
This sketch example demonstrates how the BMI160 on the
Intel(R) Curie(TM) module can be used to read gyroscope data
*/
\#include "CurieIMU.h"
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // initialize Serial communication
while (!Serial); // wait for the serial port to open
// initialize device
Serial.println("Initializing IMU device...");
CurieIMU.begin();
Serial.print("Starting Gyroscope calibration...");
CurieIMU.autoCalibrateGyroOffset();
Serial.println(" Done");
// Set the accelerometer range to 250 degrees/second
CurieIMU.setGyroRange(250);
}
void loop() {
int gxRaw, gyRaw, gzRaw; // raw gyro values
float gx, gy, gz;
// read raw gyro measurements from device
CurieIMU.readGyro(gxRaw, gyRaw, gzRaw);
// convert the raw gyro data to degrees/second
gx = convertRawGyro(gxRaw);
gy = convertRawGyro(gyRaw);
gz = convertRawGyro(gzRaw);
// display tab-separated gyro x/y/z values
Serial.print("g:\t");
Serial.print(gx);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(gy);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(gz);
Serial.println();
// wait 5 seconds
delay(1000);
}
float convertRawGyro(int gRaw) {
// since we are using 250 degrees/seconds range
// -250 maps to a raw value of -32768
// +250 maps to a raw value of 32767
float g = (gRaw * 250.0) / 32768.0;
return g;
}
串口数据输出,这里我让开发板绕X轴旋转得到的数据,考虑手动操作的误差,y轴和z轴基本保持不变,数据看起来不错哦:
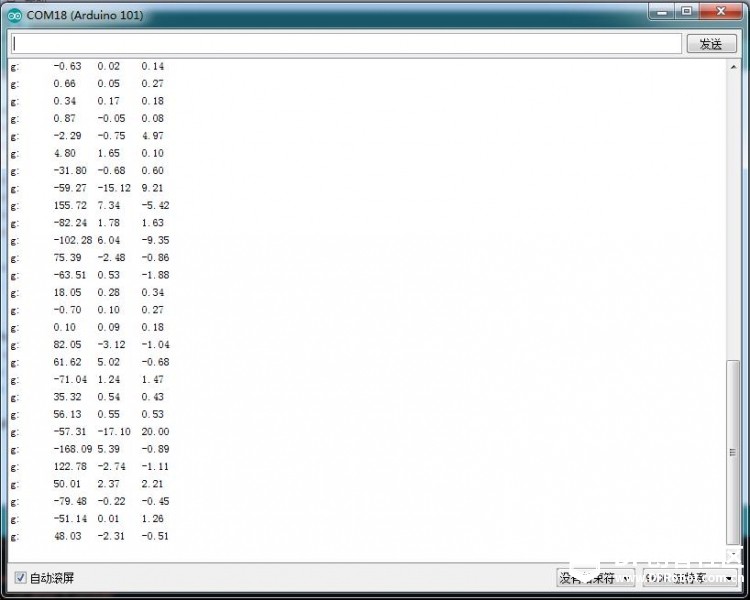
拓展:
既然加速度计和陀螺仪的数据读出来了,那么是不是该用这个数据来干点什么,嘿嘿嘿,是不是可以干坏事了啊:lol!下个教程教你怎么干坏事,不要太激动哦{:5_161:}。
看累了没,开心一刻:
刚才和朋友聊天,其中有谈到你,知道吗?我和他们吵了起来,还差点动手打起来,因为他们有的说你像猴子,有的说你像猩猩,实在太过分了!根本没有把你当猪看!{:5_199:}
【Arduino/Genuino 101 入门教程】
 沪公网安备31011502402448
沪公网安备31011502402448