|
8095| 2
|
[项目分享] 【天天向上】Maixduino AI 开发板试用(二)MaixPy之人脸识别 |
|
本帖最后由 云天 于 2020-7-12 09:38 编辑 人脸识别 从古至今,人脸是进行身份辨识的重要方式。在古代,政府为了达到对特定人员的身份识别、防控围捕的目的,会发布“海捕文书”。海捕文书中包括了人员的画像、涉案信息等,通过悬赏及威慑测试调动人民群众积极性,实现对人员的发现、举报、抓捕;在现代,在身份证、驾驶证、护照等重要的个人证件上,均会印刷或粘贴人脸照片,但是这种身份识别本质上是“见物如见人,认物不认人”,它忽视了人们最本质的需要,而人脸识别技术的出现和日益成熟,在实际应用中显现出巨大的优势。 人脸识别是基于人的脸部特征信息进行身份识别的一种生物识别技术。针对输入的人脸图像或者视频流,首先判断其是否存在人脸,如果存在人脸,则进一步的给出每个脸的位置、大小和各个主要面部器官的位置信息。然后依据这些信息,进一步提取每个人脸中所蕴涵的身份特征数据,并将其与已知的人脸进行对比,从而识别每个人脸的身份。人脸识别主要用于身份识别。由于视频监控正在快速普及,众多的视频监控应用迫切需要一种远距离、用户非配合状态下的快速身份识别技术,以求远距离快速确认人员身份,实现智能预警,而人脸识别技术无疑是最佳的选择。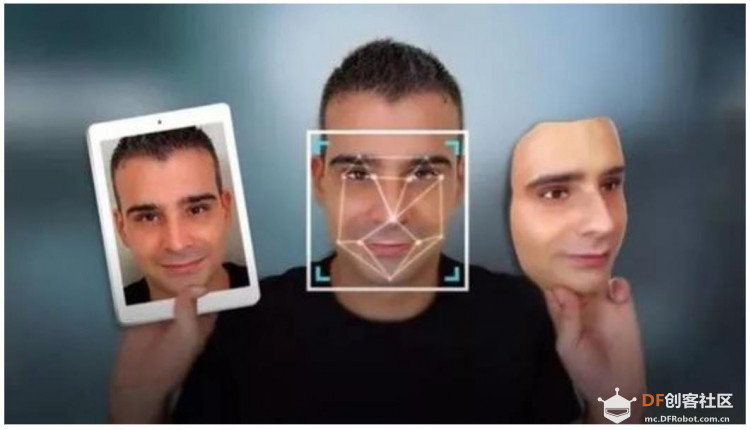  人脸识别技术优势 • 非强制性:系统在用户在无意识的状态下就可获取人脸图像,不需要专门配合; • 非接触性:用户不需要和设备直接接触,就能获取人脸图像,提取人脸特征进行检测; • 并发性:在实际应用场景下可以进行同时多个人脸的分拣、判断及识别; 除此之外,还有操作简单、结果直观、隐蔽性好等特点。  Maixpy人脸识别模型(Maixpy Face-Recognition Model)
第一步:获取key gen机器码(Get key Gen machine code)并下载 下载地址:https://en.bbs.sipeed.com/uploads/default/original/1X/bca0832bed92a1ada63bd05327688784e2ef14d1.zip 解压到 key_gen_v1.2.bin 第二步:使用kflash_gui 烧录key_gen_v1.2.bin 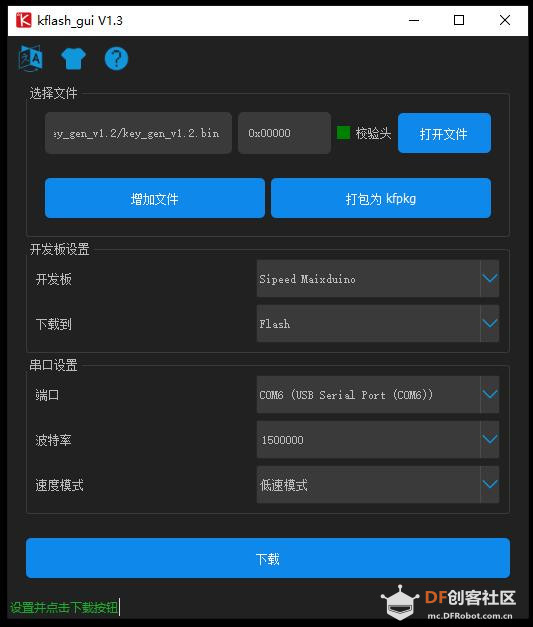 第三步:打开串口,Generate key end 生成密钥结束  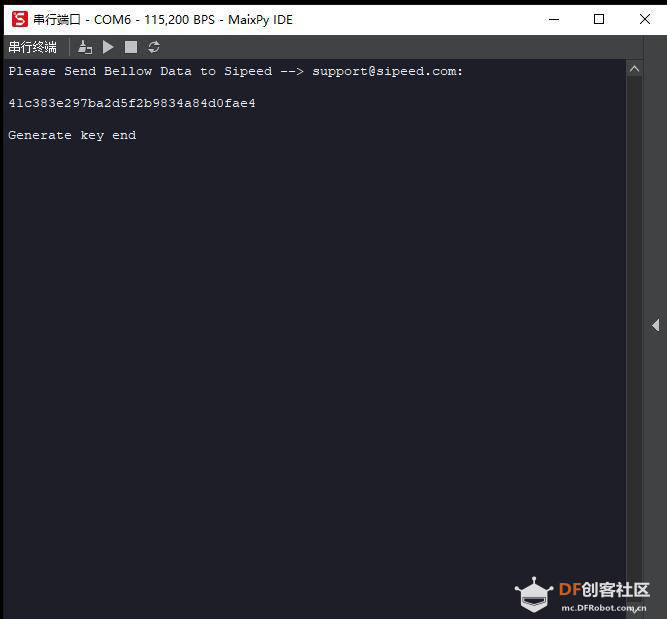 第四步:获取mpy脚本 (Get MPY script) [mw_shl_code=python,false]import sensor import image import lcd import KPU as kpu import time from Maix import FPIOA, GPIO import gc from fpioa_manager import fm from board import board_info task_fd = kpu.load(0x200000) task_ld = kpu.load(0x300000) task_fe = kpu.load(0x400000) clock = time.clock() fm.register(board_info.BOOT_KEY, fm.fpioa.GPIOHS0) key_gpio = GPIO(GPIO.GPIOHS0, GPIO.IN) start_processing = False def set_key_state(*_): global start_processing start_processing = True key_gpio.irq(set_key_state, GPIO.IRQ_RISING, GPIO.WAKEUP_NOT_SUPPORT) lcd.init() sensor.reset() sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.RGB565) sensor.set_framesize(sensor.QVGA) sensor.set_hmirror(1) sensor.set_vflip(1) sensor.run(1) anchor = (1.889, 2.5245, 2.9465, 3.94056, 3.99987, 5.3658, 5.155437, 6.92275, 6.718375, 9.01025) # anchor for face detect dst_point = [(44, 59), (84, 59), (64, 82), (47, 105), (81, 105)] # standard face key point position a = kpu.init_yolo2(task_fd, 0.5, 0.3, 5, anchor) img_lcd = image.Image() img_face = image.Image(size=(128, 128)) a = img_face.pix_to_ai() record_ftr = [] record_ftrs = [] names = ['Mr.1', 'Mr.2', 'Mr.3', 'Mr.4', 'Mr.5', 'Mr.6', 'Mr.7', 'Mr.8', 'Mr.9', 'Mr.10'] while(1): img = sensor.snapshot() clock.tick() code = kpu.run_yolo2(task_fd, img) if code: for i in code: # Cut face and resize to 128x128 a = img.draw_rectangle(i.rect()) face_cut = img.cut(i.x(), i.y(), i.w(), i.h()) face_cut_128 = face_cut.resize(128, 128) a = face_cut_128.pix_to_ai() #a = img.draw_image(face_cut_128, (0,0)) # Landmark for face 5 points fmap = kpu.forward(task_ld, face_cut_128) plist = fmap[:] le = (i.x()+int(plist[0]*i.w() - 10), i.y()+int(plist[1]*i.h())) re = (i.x()+int(plist[2]*i.w()), i.y()+int(plist[3]*i.h())) nose = (i.x()+int(plist[4]*i.w()), i.y()+int(plist[5]*i.h())) lm = (i.x()+int(plist[6]*i.w()), i.y()+int(plist[7]*i.h())) rm = (i.x()+int(plist[8]*i.w()), i.y()+int(plist[9]*i.h())) a = img.draw_circle(le[0], le[1], 4) a = img.draw_circle(re[0], re[1], 4) a = img.draw_circle(nose[0], nose[1], 4) a = img.draw_circle(lm[0], lm[1], 4) a = img.draw_circle(rm[0], rm[1], 4) # align face to standard position src_point = [le, re, nose, lm, rm] T = image.get_affine_transform(src_point, dst_point) a = image.warp_affine_ai(img, img_face, T) a = img_face.ai_to_pix() #a = img.draw_image(img_face, (128,0)) del(face_cut_128) # calculate face feature vector fmap = kpu.forward(task_fe, img_face) feature = kpu.face_encode(fmap[:]) reg_flag = False scores = [] for j in range(len(record_ftrs)): score = kpu.face_compare(record_ftrs[j], feature) scores.append(score) max_score = 0 index = 0 for k in range(len(scores)): if max_score < scores[k]: max_score = scores[k] index = k if max_score > 85: a = img.draw_string(i.x(), i.y(), ("%s :%2.1f" % ( names[index], max_score)), color=(0, 255, 0), scale=2) else: a = img.draw_string(i.x(), i.y(), ("X :%2.1f" % ( max_score)), color=(255, 0, 0), scale=2) if start_processing: record_ftr = feature record_ftrs.append(record_ftr) start_processing = False break fps = clock.fps() print("%2.1f fps" % fps) a = lcd.display(img) gc.collect() # kpu.memtest() #a = kpu.deinit(task_fe) #a = kpu.deinit(task_ld) #a = kpu.deinit(task_fd) [/mw_shl_code] 第五步:访问Maixhub 模型平台首页, 注册并登录 第六步:选择[MaixPy 人脸识别模型],点击下载按钮 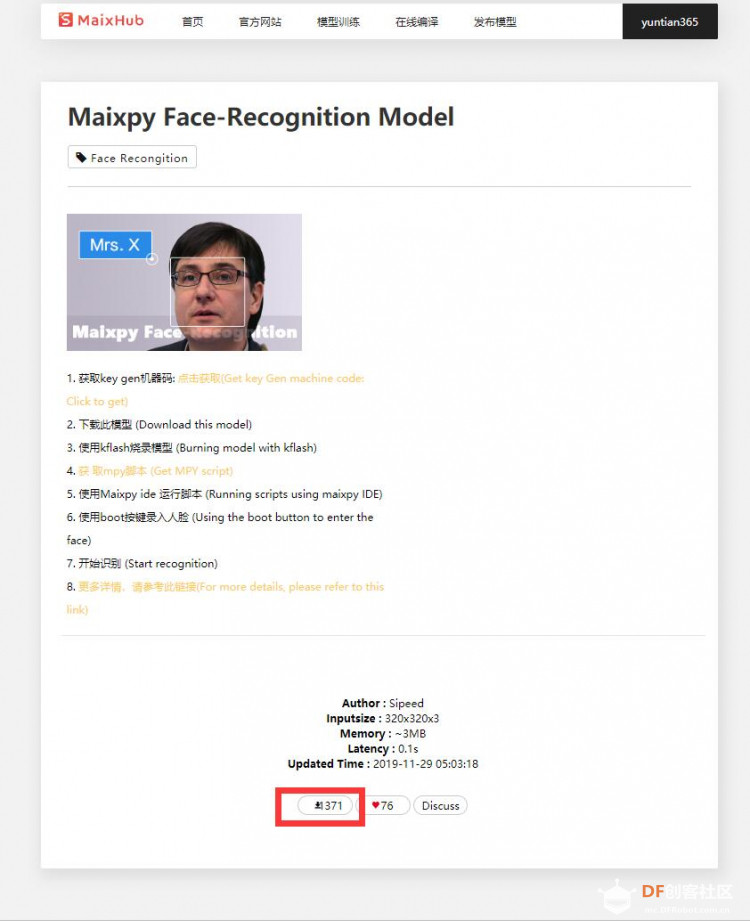 第七步:填写32位机器码,点击提交即可获得人脸识别模型 注意:此步点击提交后需耐心等待约30秒,未开始下载前请不要关闭页面。 Note: Please wait patiently for about 30 seconds after clicking Submit in this step Please do not close the page before downloading.. 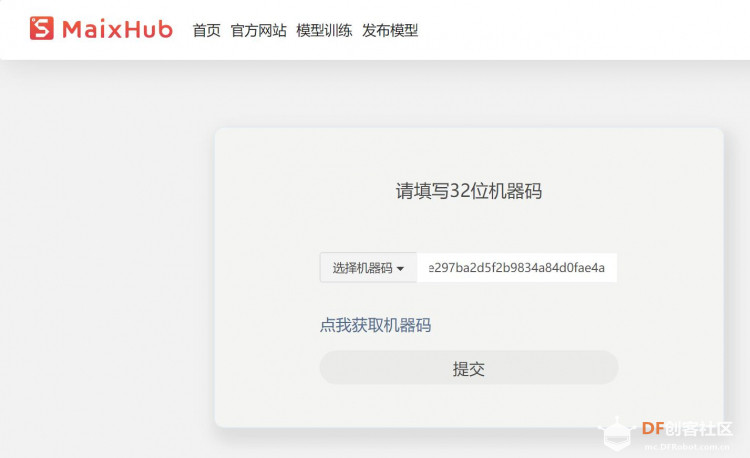 第八步:使用 kflash_gui 烧录上一步获取的kfpkg模型 Use kflash_gui to flash the kfpkg model obtained in the previous step. 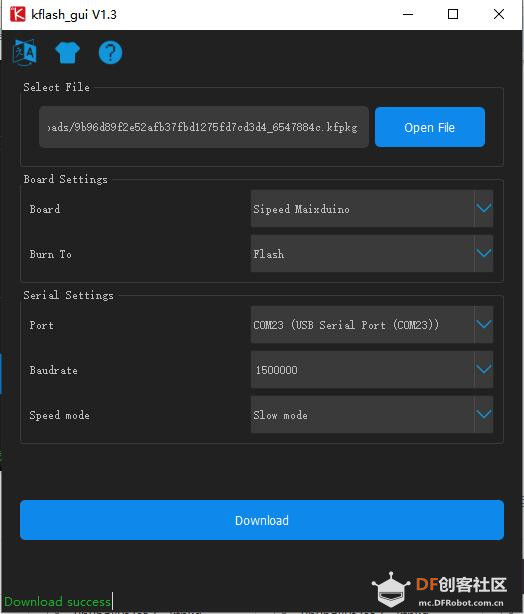 第九步:使用 MaixPy IDE 运行 MaixPy 人脸识别脚本 Run MaixPy Face Recognition Script with MaixPy IDE 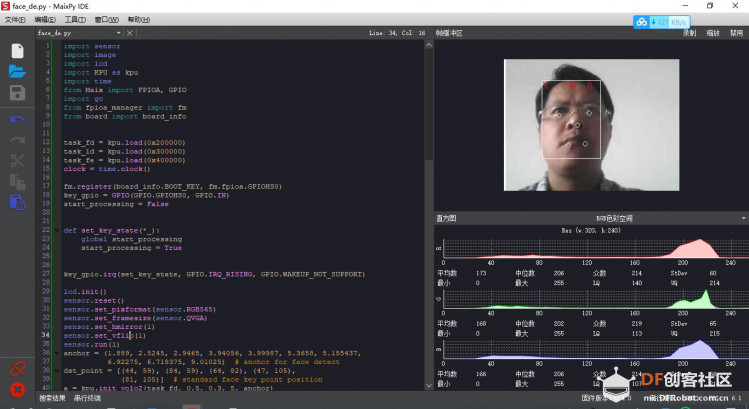 视频演示: 人脸识别脚本解读 Interpretation of face recognition script `import sensor,image,lcd # import 相关库 import KPU as kpu import time from Maix import FPIOA,GPIO task_fd = kpu.load(0×200000) # 从flash 0×200000 加载人脸检测模型 task_ld = kpu.load(0×300000) # 从flash 0×300000 加载人脸五点关键点检测模型 task_fe = kpu.load(0×400000) # 从flash 0×400000 加载人脸196维特征值模型 clock = time.clock() # 初始化系统时钟,计算帧率 key_pin=16 # 设置按键引脚 FPIO16 fpioa = FPIOA() fpioa.set_function(key_pin,FPIOA.GPIO7) key_gpio=GPIO(GPIO.GPIO7,GPIO.IN) last_key_state=1 key_pressed=0 # 初始化按键引脚 分配GPIO7 到 FPIO16 def check_key(): # 按键检测函数,用于在循环中检测按键是否按下,下降沿有效 global last_key_state global key_pressed val=key_gpio.value() if last_key_state == 1 and val == 0: key_pressed=1 else: key_pressed=0 last_key_state = val lcd.init() # 初始化lcd Cut face and resize to 128×128sensor.reset() #初始化sensor 摄像头 sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.RGB565) sensor.set_framesize(sensor.QVGA) sensor.set_hmirror(1) #设置摄像头镜像 sensor.set_vflip(1) #设置摄像头翻转 sensor.run(1) #使能摄像头 anchor = (1.889, 2.5245, 2.9465, 3.94056, 3.99987, 5.3658, 5.155437, 6.92275, 6.718375, 9.01025) #anchor for face detect 用于人脸检测的Anchor dst_point = [(44,59),(84,59),(64,82),(47,105),(81,105)] #standard face key point position 标准正脸的5关键点坐标 分别为 左眼 右眼 鼻子 左嘴角 右嘴角 a = kpu.init_yolo2(task_fd, 0.5, 0.3, 5, anchor) #初始化人脸检测模型 img_lcd=image.Image() # 设置显示buf img_face=image.Image(size=(128,128)) #设置 128 * 128 人脸图片buf a=img_face.pix_to_ai() # 将图片转为kpu接受的格式 record_ftr=[] #空列表 用于存储当前196维特征 record_ftrs=[] #空列表 用于存储按键记录下人脸特征, 可以将特征以txt等文件形式保存到sd卡后,读取到此列表,即可实现人脸断电存储。 names = [‘Mr.1’, ‘Mr.2’, ‘Mr.3’, ‘Mr.4’, ‘Mr.5’, ‘Mr.6’, ‘Mr.7’, ‘Mr.8’, ‘Mr.9’ , ‘Mr.10’] # 人名标签,与上面列表特征值一一对应。 while(1): # 主循环 check_key() #按键检测 img = sensor.snapshot() #从摄像头获取一张图片 clock.tick() #记录时刻,用于计算帧率 code = kpu.run_yolo2(task_fd, img) # 运行人脸检测模型,获取人脸坐标位置 if code: # 如果检测到人脸 for i in code: # 迭代坐标框 a = img.draw_rectangle(i.rect()) # 在屏幕显示人脸方框 Landmark for face 5 pointsface_cut=img.cut(i.x(),i.y(),i.w(),i.h()) # 裁剪人脸部分图片到 face_cut face_cut_128=face_cut.resize(128,128) # 将裁出的人脸图片 缩放到128 * 128像素 a=face_cut_128.pix_to_ai() # 将猜出图片转换为kpu接受的格式 #a = img.draw_image(face_cut_128, (0,0)) fmap = kpu.forward(task_ld, face_cut_128) # 运行人脸5点关键点检测模型 align face to standard positionplist=fmap[:] # 获取关键点预测结果 le=(i.x()+int(plist[0]i.w() - 10), i.y()+int(plist[1]i.h())) # 计算左眼位置, 这里在w方向-10 用来补偿模型转换带来的精度损失 re=(i.x()+int(plist[2]i.w()), i.y()+int(plist[3]i.h())) # 计算右眼位置 nose=(i.x()+int(plist[4]i.w()), i.y()+int(plist[5]i.h())) #计算鼻子位置 lm=(i.x()+int(plist[6]i.w()), i.y()+int(plist[7]i.h())) #计算左嘴角位置 rm=(i.x()+int(plist[8]i.w()), i.y()+int(plist[9]i.h())) #右嘴角位置 a = img.draw_circle(le[0], le[1], 4) a = img.draw_circle(re[0], re[1], 4) a = img.draw_circle(nose[0], nose[1], 4) a = img.draw_circle(lm[0], lm[1], 4) a = img.draw_circle(rm[0], rm[1], 4) # 在相应位置处画小圆圈 src_point = [le, re, nose, lm, rm] # 图片中 5 坐标的位置 calculate face feature vectorT=image.get_affine_transform(src_point, dst_point) # 根据获得的5点坐标与标准正脸坐标获取仿射变换矩阵 a=image.warp_affine_ai(img, img_face, T) #对原始图片人脸图片进行仿射变换,变换为正脸图像 a=img_face.ai_to_pix() # 将正脸图像转为kpu格式 #a = img.draw_image(img_face, (128,0)) del(face_cut_128) # 释放裁剪人脸部分图片 fmap = kpu.forward(task_fe, img_face) # 计算正脸图片的196维特征值 feature=kpu.face_encode(fmap[:]) #获取计算结果 reg_flag = False scores = [] # 存储特征比对分数 for j in range(len(record_ftrs)): #迭代已存特征值 score = kpu.face_compare(record_ftrs[j], feature) #计算当前人脸特征值与已存特征值的分数 scores.append(score) #添加分数总表 max_score = 0 index = 0 for k in range(len(scores)): #迭代所有比对分数,找到最大分数和索引值 if max_score < scores[k]: max_score = scores[k] index = k if max_score > 85: # 如果最大分数大于85, 可以被认定为同一个人 a = img.draw_string(i.x(),i.y(), (“%s :%2.1f” % (names[index], max_score)), color=(0,255,0),scale=2) # 显示人名 与 分数 else: a = img.draw_string(i.x(),i.y(), (“X :%2.1f” % (max_score)), color=(255,0,0),scale=2) #显示未知 与 分数 if key_pressed == 1: #如果检测到按键 key_pressed = 0 #重置按键状态 record_ftr = feature record_ftrs.append(record_ftr) #将当前特征添加到已知特征列表 break fps =clock.fps() #计算帧率 print(“%2.1f fps”%fps) #打印帧率 a = lcd.display(img) #刷屏显示 #kpu.memtest() #a = kpu.deinit(task_fe) #a = kpu.deinit(task_ld) #a = kpu.deinit(task_fd) |
 沪公网安备31011502402448
沪公网安备31011502402448© 2013-2026 Comsenz Inc. Powered by Discuz! X3.4 Licensed