
很多开发人员在转换完 TensorRT 加速引擎之后,最后准备调用起来执行推理任务的时候,就遇到一些障碍。这个环节是需要开发人员自行撰写相关代码,去执行读入数据(前处理)、执行推理、显示结果(后处理)等工作,如下图最右边的部分。
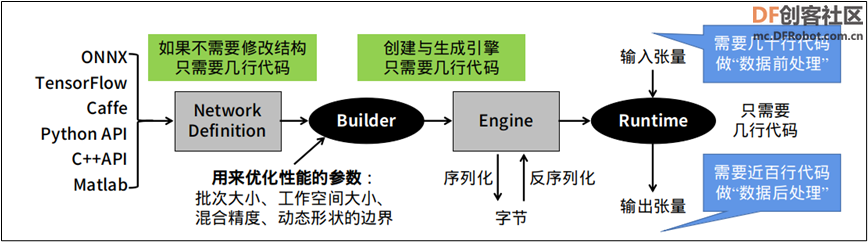
这部分的麻烦之处,在于每个神经网络的结构不相同,并没有“通用”的代码可以适用于大部分的网络结构,需要针对指定神经网络去撰写对应的代码,最重要是需要清除这个模型的输入 (input bold) 与输出 (outpold) 的名称与张量结构。
本文以前面在 TAO 工具套件中使用的 ssd 神经网络为范例,提供基础的“前后处理”范例代码给读者参考,这是从 NVIDIA 中国区开发者社区所举办过多届 “Sky 黑客松”比赛中,所提供的开源内容中提取的重点,主要如下:
1、数据前处理:
-
- def _preprocess_trt(img, shape=(300, 300)):
- """TRT SSD推理前的数据前处理"""
- img = cv2.resize(img, shape)
- img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1)).astype(np.float32)
- return img
这里 “shape=(300,300)” 为张量的尺度,根据模型训练时的长宽两个变量,至于 transpose 里的 (2,0,1) 是固定的,不需调整。
2、数据后处理:
- def _postprocess_trt(img, output, conf_th, output_layout):
- """TRT SSD推理后的结果的数据处理步骤."""
- img_h, img_w, _ = img.shape
- boxes, confs, clss = [], [], []
- for prefix in range(0, len(output), output_layout):
- index = int(output[prefix+0])
- conf = float(output[prefix+2])
- if conf < conf_th:
- continue
- x1 = int(output[prefix+3] * img_w)
- y1 = int(output[prefix+4] * img_h)
- x2 = int(output[prefix+5] * img_w)
- y2 = int(output[prefix+6] * img_h)
- cls = int(output[prefix+1])
- boxes.append((x1, y1, x2, y2))
- confs.append(conf)
- clss.append(cls)
- return boxes, confs, clss # 返回标框坐标、置信度、类别
这里最重要的 x1, y1,x2, y2 坐标值,必须根据 SSD 神经网络所定义的规范去进行修改,其他部分可以通用于大部分神经网络。
3、定义 TrtSSD 类封装运行 TRT SSD 所需的东西:
- class TrtSSD(object):
- # 加载自定义组建,如果TRT版本小于7.0需要额外生成flattenconcat自定义组件库
- def _load_plugins(self):
- if trt.__version__[0] < '7':
- ctypes.CDLL("ssd/libflattenconcat.so")
- trt.init_libnvinfer_plugins(self.trt_logger, '')
- #加载通过Transfer Learning Toolkit生成的推理引擎
- def _load_engine(self):
- TRTbin = 'ssd/TRT_%s.bin' % self.model #请根据实际状况自行修改
- with open(TRTbin, 'rb') as f, trt.Runtime(self.trt_logger) as runtime:
- return runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read())
- #通过加载的引擎,生成可执行的上下文
- def _create_context(self):
- for binding in self.engine:
- size = trt.volume(self.engine.get_binding_shape(binding)) * \
- self.engine.max_batch_size
- ##注意:这里的host_mem需要使用pagelocked memory,以免内存被释放
- host_mem = cuda.pagelocked_empty(size, np.float32)
- cuda_mem = cuda.mem_alloc(host_mem.nbytes)
- self.bindings.append(int(cuda_mem))
- if self.engine.binding_is_input(binding):
- self.host_inputs.append(host_mem)
- self.cuda_inputs.append(cuda_mem)
- else:
- self.host_outputs.append(host_mem)
- self.cuda_outputs.append(cuda_mem)
- return self.engine.create_execution_context()
- # 初始化引擎
- def __init__(self, model, input_shape, output_layout=7):
- self.model = model
- self.input_shape = input_shape
- self.output_layout = output_layout
- self.trt_logger = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.INFO)
- self._load_plugins()
- self.engine = self._load_engine()
-
- self.host_inputs = []
- self.cuda_inputs = []
- self.host_outputs = []
- self.cuda_outputs = []
- self.bindings = []
- self.stream = cuda.Stream()
- self.context = self._create_context()
- # 释放引擎,释放GPU显存,释放CUDA流
- def __del__(self):
- del self.stream
- del self.cuda_outputs
- del self.cuda_inputs
- # 利用生成的可执行上下文执行推理
- def detect(self, img, conf_th=0.3):
- img_resized = _preprocess_trt(img, self.input_shape)
- np.copyto(self.host_inputs[0], img_resized.ravel())
- # 将处理好的图片从CPU内存中复制到GPU显存
- cuda.memcpy_htod_async(
- self.cuda_inputs[0], self.host_inputs[0], self.stream)
- # 开始执行推理任务
- self.context.execute_async(
- batch_size=1,
- bindings=self.bindings,
- stream_handle=self.stream.handle)
- # 将推理结果输出从GPU显存复制到CPU内存
- cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(
- self.host_outputs[1], self.cuda_outputs[1], self.stream)
- cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(
- self.host_outputs[0], self.cuda_outputs[0], self.stream)
- self.stream.synchronize()
-
- output = self.host_outputs[0]
- return _postprocess_trt(img, output, conf_th, self.output_layout)
上面三个部分对不同神经网络都是不同的内容,如果要参考 YOLO 神经网络的对应内容,推荐参考 https://github.com/jkjung-avt/tensorrt_demos开源项目,里面有完整的 YOLOv3 与 YOLOv4 的详细内容。
本文的开源代码可以在此链接下载完整的内容与配套的工具。
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1fGLBnzqtnRNpfD3PbileOA 密码: 99et
| 

 沪公网安备31011502402448
沪公网安备31011502402448