本帖最后由 云天 于 2021-8-8 21:14 编辑 一、OpenCV人脸识别之一:数据收集和预处理 程序的功能就是打开电脑摄像头,采集自己100张人脸图片
import cv2
def getTrainingData(window_name, camera_id, path_name, max_num): # path_name是图片存储目录,max_num是需要捕捉的图片数量
cv2.namedWindow(window_name) # 创建窗口
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(camera_id) # 打开摄像头
classifier = cv2.CascadeClassifier('haarshare/haarcascade_frontalface_alt2.xml') # 加载分类器
color = (0,255,0) # 人脸矩形框的颜色
num = 0 # 记录存储的图片数量
while cap.isOpened():
ok, frame = cap.read()
if not ok:
break
gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 灰度化
faceRects=classifier.detectMultiScale(gray,scaleFactor=1.2,minNeighbors=3,minSize=(32,32))
if len(faceRects) > 0:
for faceRect in faceRects:
x,y,w,h = faceRect
# 捕捉到的图片的名字,这里用到了格式化字符串的输出
image_name = '%s%d.jpg' % (path_name, num) # 注意这里图片名一定要加上扩展名,否则后面imwrite的时候会报错:could not find a writer for the specified extension in function cv::imwrite_ 参考:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/9868963/cvimwrite-could-not-find-a-writer-for-the-specified-extension
image = frame[y:y+h, x:x+w] # 将当前帧含人脸部分保存为图片,注意这里存的还是彩色图片,前面检测时灰度化是为了降低计算量;这里访问的是从y位开始到y+h-1位
cv2.imwrite(image_name, image)
num += 1
# 超过指定最大保存数量则退出循环
if num > max_num:
break
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x,y), (x+w,y+h), color, 2) # 画出矩形框
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX # 获取内置字体
cv2.putText(frame, ('%d'%num), (x+30, y+30), font, 1, (255,0,255), 4) # 调用函数,对人脸坐标位置,添加一个(x+30,y+30)的矩形框用于显示当前捕捉到了多少人脸图片
if num > max_num:
break
cv2.imshow(window_name, frame)
c = cv2.waitKey(10)
if c & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()#释放摄像头并销毁所有窗口
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
print('Finished.')
#主函数
if __name__ =='__main__':
print ('catching your face and writting into disk...')
getTrainingData('getTrainData',0,'training_data/',100) # 注意这里的training_data_xx 文件夹就在程序工作目录下
复制代码 二、模型训练
#import OpenCV module
import cv2
#import os module for reading training data directories and paths
import os
#import numpy to convert python lists to numpy arrays as
#it is needed by OpenCV face recognizers
import numpy as np
#使用OpenCV用来检测脸部的函数
def detect_face(img):
#将测试图像转换为灰度图像,因为opencv人脸检测器需要灰度图像
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#加载OpenCV人脸检测器,我正在使用的是快速的LBP
#还有一个更准确但缓慢的Haar分类器
face_cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier('haarshare/lbpcascade_frontalface.xml')
#让我们检测多尺度(一些图像可能比其他图像更接近相机)图像
#结果是一张脸的列表
faces = face_cascade.detectMultiScale(gray, scaleFactor=1.2, minNeighbors=5);
#如果未检测到面部,则返回原始图像
if (len(faces) == 0):
return None, None
#假设只有一张脸,
#提取面部区域
(x, y, w, h) = faces[0]
#只返回图像的正面部分
return gray[y:y+w, x:x+h], faces[0]
#该功能将读取所有人的训练图像,从每个图像检测人脸
#并将返回两个完全相同大小的列表,一个列表
# 每张脸的脸部和另一列标签
def prepare_training_data(data_folder_path):
#------STEP-1--------
#获取数据文件夹中的目录(每个主题的一个目录)
dirs = os.listdir(data_folder_path)
#列表来保存所有主题的面孔
faces = []
#列表以保存所有主题的标签
labels = []
#让我们浏览每个目录并阅读其中的图像
for dir_name in dirs:
#我们的主题目录以字母's'开头
#如果有的话,忽略任何不相关的目录
if not dir_name.startswith("s"):
continue;
#------STEP-2--------
#从dir_name中提取主题的标签号
#目录名称格式= slabel
#,所以从dir_name中删除字母''会给我们标签
label = int(dir_name.replace("s", ""))
#建立包含当前主题主题图像的目录路径
#sample subject_dir_path = "training-data/s1"
subject_dir_path = data_folder_path + "/" + dir_name
#获取给定主题目录内的图像名称
subject_images_names = os.listdir(subject_dir_path)
#------STEP-3--------
#浏览每个图片的名称,阅读图片,
#检测脸部并将脸部添加到脸部列表
for image_name in subject_images_names:
#忽略.DS_Store之类的系统文件
if image_name.startswith("."):
continue;
#建立图像路径
#sample image path = training-data/s1/1.pgm
image_path = subject_dir_path + "/" + image_name
#阅读图像
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
#显示图像窗口以显示图像
cv2.imshow("Training on image...", image)
cv2.waitKey(100)
#侦测脸部
face, rect = detect_face(image)
#------STEP-4--------
#为了本教程的目的
#我们将忽略未检测到的脸部
if face is not None:
#将脸添加到脸部列表
faces.append(face)
#为这张脸添加标签
labels.append(label)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
cv2.waitKey(1)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
return faces, labels
#让我们先准备好我们的训练数据
#数据将在两个相同大小的列表中
#一个列表将包含所有的面孔
#数据将在两个相同大小的列表中
print("Preparing data...")
faces, labels = prepare_training_data("training_data")
print("Data prepared")
#打印总面和标签
print("Total faces: ", len(faces))
print("Total labels: ", len(labels))
print("Preparing train....")
face_recognizer = cv2.face.LBPHFaceRecognizer_create()
face_recognizer.train(faces, np.array(labels))
face_recognizer.write('trainer.yml')
print("faces trained. Exiting Program")
复制代码 人脸模型。 【识别人脸】 简单说下流程:
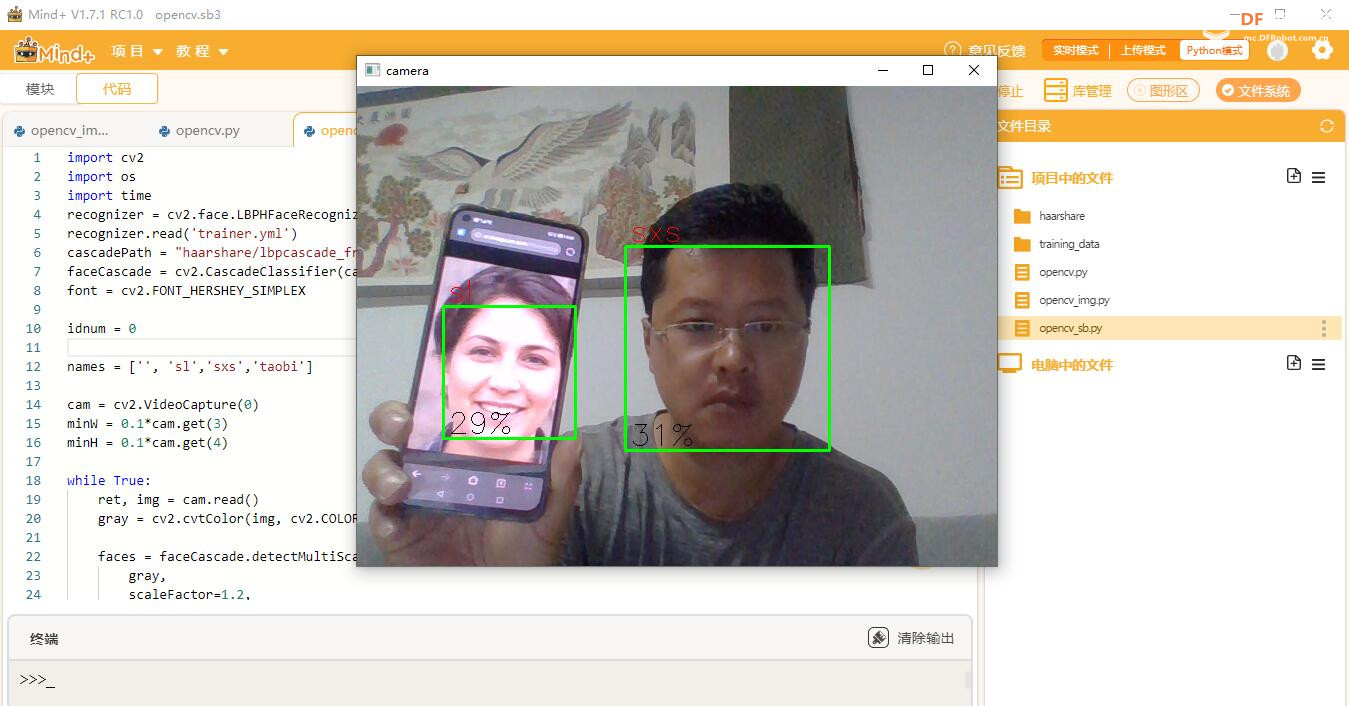
打开摄像头。 加载人脸检测器,加载人脸模型。 人脸检测 把检测到的人脸与人脸模型里面的对比,找出这是谁的脸。 如果人脸是自己的,显示自己的名字。
import cv2
import os
import time
recognizer = cv2.face.LBPHFaceRecognizer_create()
recognizer.read('trainer.yml')
cascadePath = "haarshare/lbpcascade_frontalface.xml"
faceCascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier(cascadePath)
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
idnum = 0
names = ['', 'sl','sxs','taobi']
cam = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
minW = 0.1*cam.get(3)
minH = 0.1*cam.get(4)
while True:
ret, img = cam.read()
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
faces = faceCascade.detectMultiScale(
gray,
scaleFactor=1.2,
minNeighbors=5,
minSize=(int(minW), int(minH))
)
for (x, y, w, h) in faces:
cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
idnum, confidence = recognizer.predict(gray[y:y+h, x:x+w])
if confidence < 100:
idnum = names[idnum]
confidence = "{0}%".format(round(100 - confidence))
else:
idnum = "unknown"
confidence = "{0}%".format(round(100 - confidence))
cv2.putText(img, str(idnum), (x+5, y-5), font, 1, (0, 0, 255), 1)
cv2.putText(img, str(confidence), (x+5, y+h-5), font, 1, (0, 0, 0), 1)
cv2.imshow('camera', img)
k = cv2.waitKey(10)
if k == 27:
break
cam.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# def draw_rectangle(img, rect):
# (x, y, w, h) = rect
# cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
# #function to draw text on give image starting from
# #passed (x, y) coordinates.
# def draw_text(img, text, x, y):
# cv2.putText(img, text, (x, y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 1.5, (0, 255, 0), 2)
# def detect_face(img):
# #convert the test image to gray image as opencv face detector expects gray images
# gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# cascadePath = 'opencv-files/lbpcascade_frontalface.xml'
# face_cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier(cascadePath)
# #load OpenCV face detector, I am using LBP which is fast
# #there is also a more accurate but slow Haar classifier
# #face_cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier('opencv-files/haarcascade_frontalface_alt.xml')
# #let's detect multiscale (some images may be closer to camera than others) images
# #result is a list of faces
# faces = face_cascade.detectMultiScale(gray, scaleFactor=1.2, minNeighbors=5);
# #if no faces are detected then return original img
# print(len(faces))
# if (len(faces) == 0):
# return None, None
# #under the assumption that there will be only one face,
# #extract the face area
# (x, y, w, h) = faces[0]
# #return only the face part of the image
# return gray[y:y+w, x:x+h], faces[0]
# face_recognizer = cv2.face.LBPHFaceRecognizer_create()
# face_recognizer.read('trainer.yml')
# names = ['', 'Bob','xxx','Taotaotao']
# print("Predicting images...")
# #load test images
# test_img = cv2.imread("1.jpg")
# #perform a prediction
# img = test_img.copy()
# start=time.clock()
# face, rect = detect_face(img)
# label, confidence = face_recognizer.predict(face)
# label_text = names[label]
# end=time.clock()
# draw_rectangle(img, rect)
# draw_text(img, label_text, rect[0], rect[1]-5)
# print("Prediction complete time %s"%(end-start))
# #display both images
# cv2.imshow("0000", cv2.resize(img, (400, 500)))
# cv2.waitKey(3600)
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()
复制代码 
 沪公网安备31011502402448
沪公网安备31011502402448