|
65786| 70
|
[项目] 【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(158)---QMC5883L三轴罗盘 |
|
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+图形编程+仿真编程) 实验一百五十八:QMC5883L电子指南针罗盘模块 三轴磁场传感器GY-271 项目十一:使用Adafruit库的HMC5883 磁力计测试 实验开源代码 |
|
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+图形编程+仿真编程) 实验一百五十八:QMC5883L电子指南针罗盘模块 三轴磁场传感器GY-271 项目之十:根据当前位置来校正磁偏角 实验开源代码 |
|
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+图形编程+仿真编程) 实验一百五十八:QMC5883L电子指南针罗盘模块 三轴磁场传感器GY-271 项目十三:尝试不使用驱动库来读取XYZ 实验开源代码 |
|
本帖最后由 驴友花雕 于 2021-9-29 11:00 编辑 Arduino 系列传感器和执行器模块实验目录清单: 一块扩展板完成Arduino的10类37项实验(代码+图形+仿真) https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-280845-1-1.html 连杆形式的腿机构十一种:盘点机器人行走背后的机械原理 https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-308097-1-1.html 【花雕动手做】超低成本,尝试五十元的麦克纳姆轮小车! https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-307863-1-1.html 【花雕动手做】超迷你哦,用徽商香烟盒做个智能小车! https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-307907-1-1.html 【花雕动手做】太搞笑啦,一支胶管制成二只蠕动机器人 https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-308046-1-1.html 【花雕动手做】快餐盒盖,极低成本搭建机器人实验平台 https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-308063-1-1.html 【花雕动手做】特别苗条,使用微波传感器控制的纤细小车 https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-308866-1-1.html 【花雕动手做】脑洞大开、五花八门的简易机器人66种 https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-307900-1-1.html 实验一百五十八:QMC5883L电子指南针罗盘模块 三轴磁场传感器GY-271 https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-308195-1-1.html 实验一百六十三:BMI160 6轴惯性运动传感器 16位3轴加速度+超低功耗3轴陀螺仪 I2C/SPI 14LGA https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-310371-1-1.html 实验一百六十五:2.4 英寸 TFT LCD 触摸屏模块 XPT2046 PCB ILI9341 240x320 像素 8 位 SPI 串口显示器 300mA https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-309803-1-1.html 实验一百七十六:6mm大尺寸8x8LED方块方格点阵模块 可级联 红绿蓝白色 可选8级亮度 https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-309845-1-1.html 实验一百八十一:1.3寸OLED液晶屏 I2C IIC通信 4针模块 1106/1306驱动 128*64像素 https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-311123-1-1.html 实验一百八十三:GY-530 VL53L0X 激光测距 ToF测距 飞行时间测距传感器模块 IIC通信协议 https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-310273-1-1.html 实验一百八十五:MAX4466声音传感器 驻极体话筒放大器 麦克风可调功放模块 microphone https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-310193-1-1.html 实验一百八十九:TDA1308 硅麦克风 数字咪头放大模块 拾音器放大板 楼氏SUNLEPHANT https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-310246-1-1.html 实验一百九十三:TCS34725颜色识别传感器 RGB IIC明光感应模块 ColorSensor https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-310209-1-1.html 实验二百:RCWL-0515微波雷达感应开关 人体感应 智能感应探测传感器 12-15米远距离2.7G微波检测模块 https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-310313-1-1.html 实验二百零三:Air724UG合宙 Cat14G模块 DTU物联网UART串口通信数据TCP透传 核心板组合套餐 https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-310342-1-1.html 实验二百零七:I2C红色8*8LED点阵模块ht16k33驱动1088BS树莓派物联网可扩展编程 https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-310951-1-1.html 实验二百零九:Gravity: I2C & UART BC20 NB-IoT & GNSS通信模块 NB-IoT广域低功耗无线通信 GPS/北斗精准定位 https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-310433-1-1.html |
|
QMC5883L特征 (1)霍尼韦尔(中国)QMC5883L是一款表面贴装多芯片模块,设计用于具有数字接口的低场磁感应,适用于低成本指南针和磁力计等应用 (2)结合低噪声AMR传感器的12位ADC在±8高斯场中实现5毫高斯场分辨率 (3)低电压运行,低功耗; 支持内置的自检 (4)内置式皮带驱动电路,I2C数字接口,宽磁场范围(+/- 8 oe) (5)工作电压:3.3v-5v; PCB尺寸:1.3 x 2.3厘米(QMC5883L尺寸:3.0 x 3.0 x 0.9毫米),带有16引脚无铅芯片载体(LCC)  |
|
QMC5883L是一款多芯片三轴磁传感器。 这个表面贴装的小尺寸芯片集成了磁传感器信号条件ASIC,面向高精度应用,例如无人机,机器人,移动设备中的指南针,导航和游戏个人手持设备。 QMC5883L基于最新的高分辨率,霍尼韦尔AMR技术授权的磁阻技术。结合定制设计的16位ADC ASIC,它具有以下优势:低噪声,高精度,低功耗,偏移消除和温度补偿。 QMC5883L启用1°至2°指南针航向精度。 I2C串行总线可简化接口。QMC5883L位于3x3x0.9mm3中表面贴装16针焊盘栅格阵列(LGA)封装。 功能 1、3x3x0.9 mm3中的3轴磁阻传感器陆地栅格阵列封装(LGA),保证在扩展的温度范围内工作-40°C至+85°C。 2、具有低噪声AMR传感器的16位ADC实现2毫高斯场分辨率。 3、宽磁场范围(±8高斯)。 4、温度补偿数据输出和温度输出。 5、具有标准模式和快速模式的I2C接口。 6、宽范围工作电压(2.16V至3.6V)和低功耗(75uA)。 7、无铅封装构造。 8、提供软件和算法支持。 优点 1、体积小,适用于高度集成的产品。 信号有已数字化和校准。 2、启用1°至2°度的罗盘航向精度,允许导航和LBS应用。 3、最大化传感器的完整动态范围和分辨率。 4、在宽广的范围内自动保持传感器的灵敏度工作温度范围。 5、用于快速数据通信的高速接口,最大200Hz数据输出速率。 6、兼容电池供电的应用。 7、符合RoHS标准。 8、可获得罗盘航向、硬磁、软磁以及自动校准库。  |
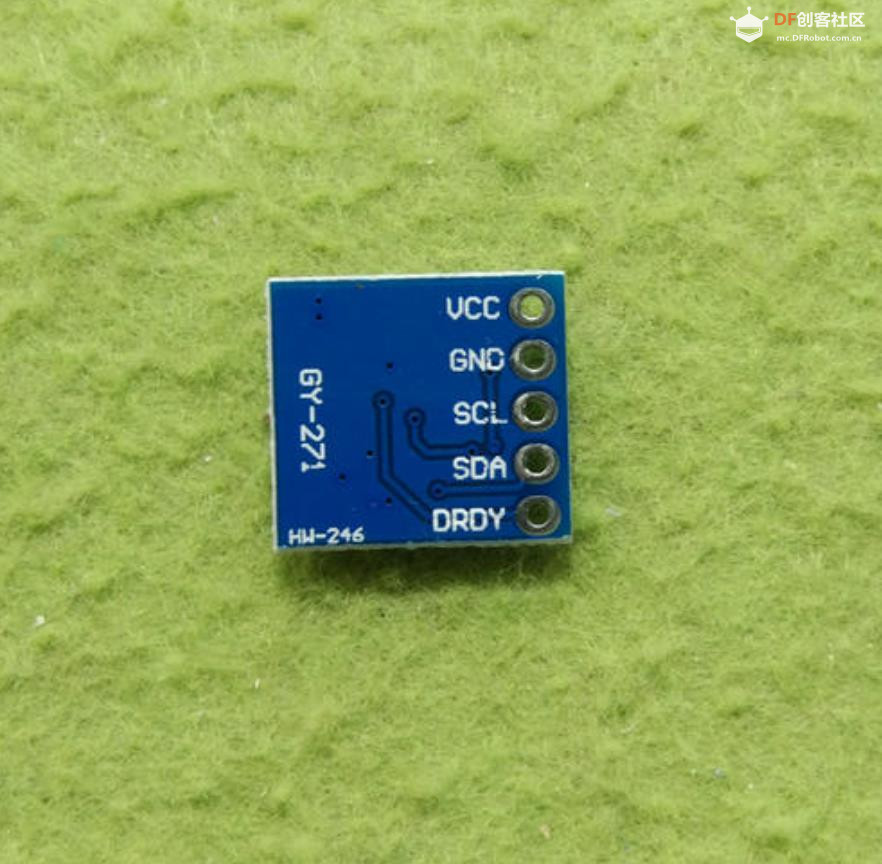 引脚功能 VCC + 5V-电源引脚,给它3.3v-5VDC。 对于Arduino,建议5v GND-接地引脚 SDA和SCL-这些是I2C数据和时钟引脚,用于从模块向微控制器发送和接收数据。 这些引脚上有1万上拉至3.3v引脚。 您可以将这些引脚连接到5V I2C线路,板上有电平转换器,可将引脚安全降低到3V DRDY-这是“数据就绪”引脚输出。 如果要高速流传输数据(每秒超过100次),则可以在准备好读取数据时收听此引脚。 有关使用DRDY引脚的更多详细信息,请参见数据表,我们不使用它,因为我们读得不快! Build the circuit QMC5883L--------------- Uno/Mega2560 VCC------------------- 5V GND------------------- GND SCL------------------- A5/ pin21 mega2560 SDA------------------- A4/pin20 mega2560 DRDY------------------ N/C |
|
QMC5883L模块的几个定义: AMR Bridge:三轴磁性传感器 MUX:多路复用通道 PGA:可编程控制的传感器信号增益放大器 Signal Conditioning:进行磁场信号校正及补偿的数字模块 ADC:16位的模数转换器 I2C:总线形式 NVM:用于校正的非易失性存储器 SET/RST Driver:用于初始化磁性传感器的内部驱动 Reference:用于内部偏移的电压/电流基准 Clock Gen.:内部振荡器,用于内部操作 POR:上电复位 Temperature Sensor:用于内部精度/偏移的温度传感器,也可以用于测量温度并输出 QMC5883L有两种工作模式:连续测量模式和待命模式。 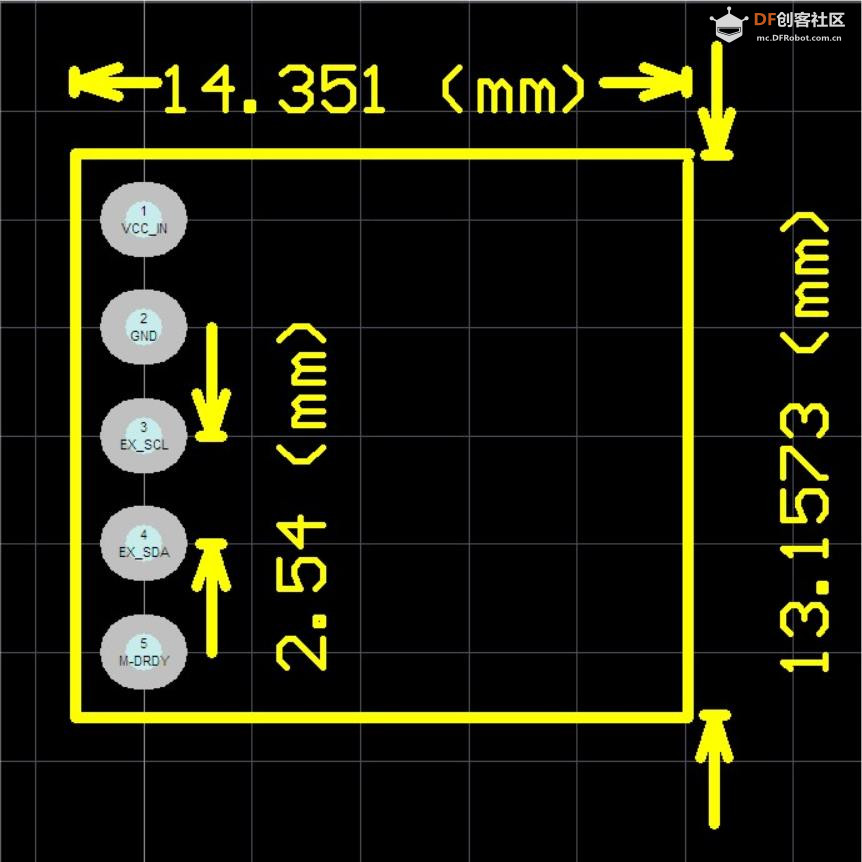 |
 沪公网安备31011502402448
沪公网安备31011502402448© 2013-2026 Comsenz Inc. Powered by Discuz! X3.4 Licensed